Final ID: Mo1010
Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous Tenecteplase Prior to Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND:
Intravenous thrombolysis before mechanical thrombectomy may enhance reperfusion before, during, and after the procedure but also increase the risk of intracranial hemorrhage. Tenecteplase (TNK), a genetically modified variant of alteplase with greater fibrin specificity and a longer half-life, allows single-bolus administration, offering practical and pharmacological advantages. These features have sparked interest in its use for acute stroke. However, its impact on outcomes when used prior to mechanical thrombectomy in large vessel occlusion (LVO) remains to be fully defined.
METHODS:
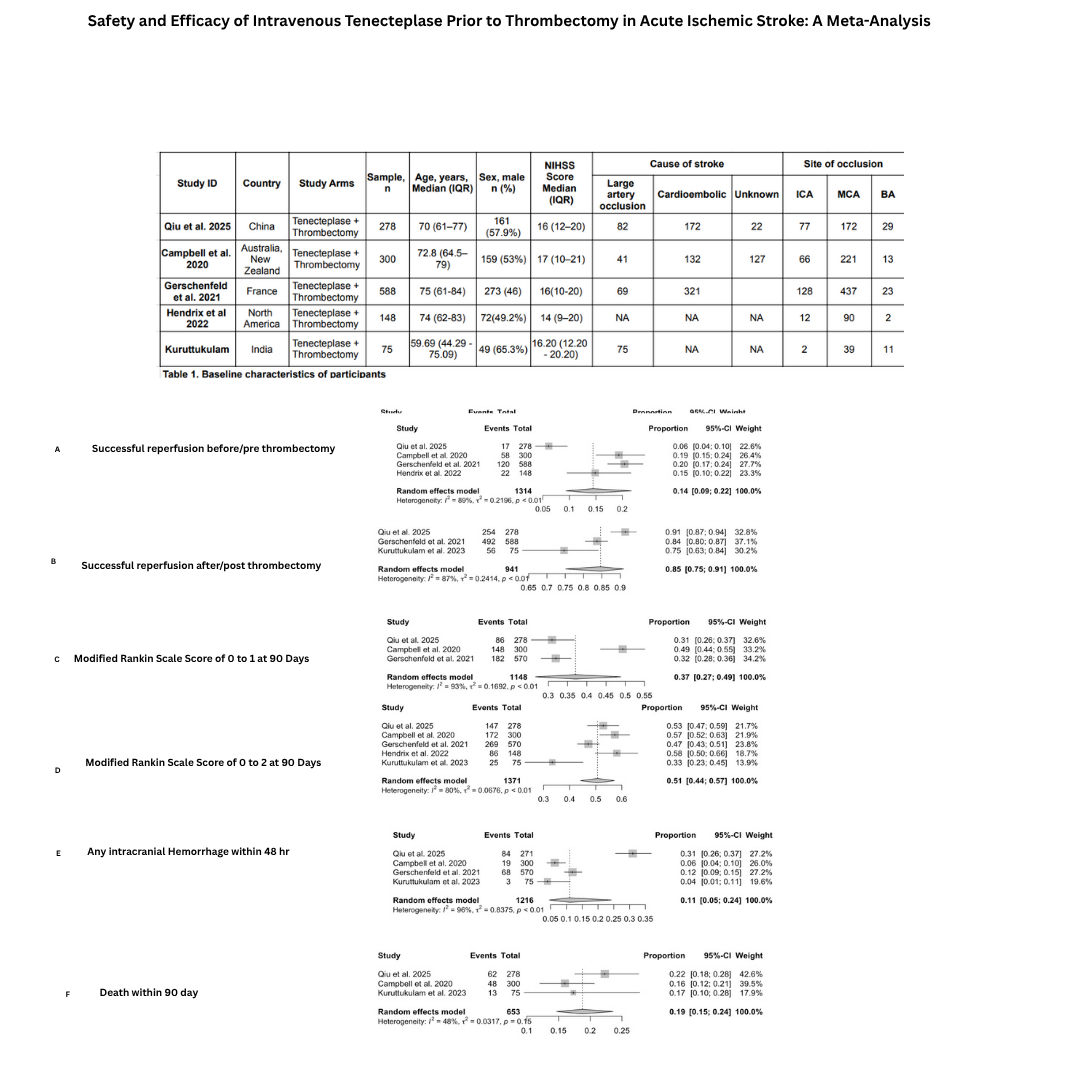
We conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis of five clinical trials, including a total of 1,389 patients with acute ischemic stroke who received intravenous TNK prior to mechanical thrombectomy. A meta-analysis of proportions was performed using a random-effects model to calculate pooled estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Primary efficacy outcomes included successful reperfusion both before and after thrombectomy, and excellent functional recovery—defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0–1 at 90 days. Functional independence, defined as mRS 0–2 at 90 days, was also assessed. Safety outcomes included any intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) within 48 hours and all-cause mortality at 90 days.
RESULTS:
Successful reperfusion before thrombectomy was observed in 14% of patients (95% CI, 9%–22%), while post-thrombectomy reperfusion was achieved in 85% (95% CI, 75%–91%), indicating a potential benefit of TNK in enhancing recanalization. At 90 days, 37% of patients (95% CI, 27%–49%) achieved excellent functional outcomes (mRS 0–1). Functional independence (mRS 0–2) was achieved in 50.7% of patients (95% CI, 44.2%–57.2%). Mortality at 90 days was 11% (95% CI, 5%–24%). However, intracranial hemorrhage within 48 hours occurred in 37% (95% CI, 27%–49%), raising safety considerations.
CONCLUSIONS:
This meta-analysis of five clinical trials suggests that intravenous tenecteplase prior to mechanical thrombectomy is associated with favorable reperfusion and functional outcomes in patients with LVO stroke. However, the elevated risk of intracranial hemorrhage findings supports the importance of careful patient selection. These findings support the continued investigation of TNK in randomized controlled trials to further define its safety and efficacy profile in acute stroke care.
Intravenous thrombolysis before mechanical thrombectomy may enhance reperfusion before, during, and after the procedure but also increase the risk of intracranial hemorrhage. Tenecteplase (TNK), a genetically modified variant of alteplase with greater fibrin specificity and a longer half-life, allows single-bolus administration, offering practical and pharmacological advantages. These features have sparked interest in its use for acute stroke. However, its impact on outcomes when used prior to mechanical thrombectomy in large vessel occlusion (LVO) remains to be fully defined.
METHODS:
We conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis of five clinical trials, including a total of 1,389 patients with acute ischemic stroke who received intravenous TNK prior to mechanical thrombectomy. A meta-analysis of proportions was performed using a random-effects model to calculate pooled estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Primary efficacy outcomes included successful reperfusion both before and after thrombectomy, and excellent functional recovery—defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0–1 at 90 days. Functional independence, defined as mRS 0–2 at 90 days, was also assessed. Safety outcomes included any intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) within 48 hours and all-cause mortality at 90 days.
RESULTS:
Successful reperfusion before thrombectomy was observed in 14% of patients (95% CI, 9%–22%), while post-thrombectomy reperfusion was achieved in 85% (95% CI, 75%–91%), indicating a potential benefit of TNK in enhancing recanalization. At 90 days, 37% of patients (95% CI, 27%–49%) achieved excellent functional outcomes (mRS 0–1). Functional independence (mRS 0–2) was achieved in 50.7% of patients (95% CI, 44.2%–57.2%). Mortality at 90 days was 11% (95% CI, 5%–24%). However, intracranial hemorrhage within 48 hours occurred in 37% (95% CI, 27%–49%), raising safety considerations.
CONCLUSIONS:
This meta-analysis of five clinical trials suggests that intravenous tenecteplase prior to mechanical thrombectomy is associated with favorable reperfusion and functional outcomes in patients with LVO stroke. However, the elevated risk of intracranial hemorrhage findings supports the importance of careful patient selection. These findings support the continued investigation of TNK in randomized controlled trials to further define its safety and efficacy profile in acute stroke care.
More abstracts on this topic:
Alzheimer’s Disease and Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage
Zhang Cenai, Bruce Samuel, Navi Babak, Murthy Santosh, Kamel Hooman
A Case Series of Papillary Fibroelastomas on the Coumadin ridgeAboukhatwa Omar, Akiki Elias, Kurmann Reto, Larson Kathryn, Keeney Michael, Bois Melanie, Klarich Kyle