Final ID: MP334
Predicting Peak Heart Rate from Resting 12-Lead ECGs in Patients Undergoing Stress Testing using Deep Learning
Introduction: Cardiovascular stress testing is crucial for the evaluation of ischemic cardiomyopathy and inducible arrhythmias. Inappropriate heart rate (HR) response during stress, or chronotropic incompetence, is associated with sinus node disease, conduction system abnormalities, and decreased functional capacity. However, inappropriate exercise tolerance often presents during stress testing, necessitating early termination. Early identification of those who are unable to complete testing due to exercise intolerance or chronotropic incompetence could streamline subsequent testing and management. This study investigates the feasibility of using deep learning models to predict peak HR using resting 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG).
Research Questions: Can a deep learning model effectively learn from resting 12-lead ECG waveforms to: (1) classify whether a patient's peak heart rate will exceed predicted peak HR defined as (230-age) × 0.8, and (2) predict the peak heart rate achieved during a stress test?
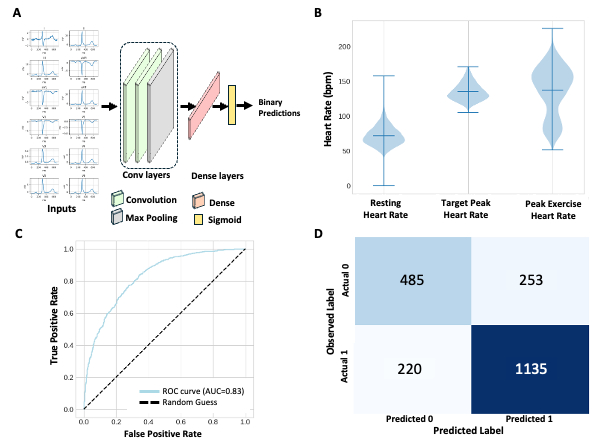
Methods: A total of 7,625 stress test records were obtained from a single institution, from which 6986 samples (4893 training/validation, 2093 test) were included. Preprocessing involved extracting 12-lead ECG signals, identifying the resting waveform and the peak HR during stress. All 12 standard leads were required for inclusion, and ECG waveforms were padded to a uniform sequence length. The processed data was used to train two separate convolutional neural networks for predicting appropriate stress response and the peak HR.
Results: The training/validation set had a mean peak HR of 137.5 beats per minute (SD = 34.9) and the testing set had a mean peak HR of 137.0 (SD = 35.3). The proportion of samples that met age-based peak HR threshold in the training/validation and testing set is 64.7% and 65.9% respectively. The model achieved an AUROC of 0.83 (95% CI 0.81-0.85) and an F1-score of 0.85 for the classification task. A separate model with similar architecture predicted peak HR with an R-value of 0.69 (95% CI 0.67-0.72) and root mean square error of 26.2 beats per minute (95% CI 25.3-27.2).
Conclusion: Our findings show that the resting ECG can be leveraged for the prediction of HR response prior to stress testing. Successful models could offer clinicians a valuable non-invasive tool for early risk stratification, guiding patient management in the evaluation of ischemic heart disease, and identifying those at risk for chronotropic incompetence.
- Liu, Xichong ( Stanford Health Care , Stanford , California , United States )
- Ashley, Euan ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Perez, Marco ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Narayan, Sanjiv ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Rogers, Albert ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Bandyopadhyay, Sabyasachi ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Ganesan, Prasanth ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Somani, Sulaiman ( Stanford Health Care , Stanford , California , United States )
- Brennan, Kelly ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Karius, Alexander ( Stanford Health Care , Stanford , California , United States )
- Baykaner, Tina ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Perino, Alexander ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Wang, Paul ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Stress Matters: Innovations in Physiologic Testing Across Multimodality Imaging
Saturday, 11/08/2025 , 03:15PM - 04:25PM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Erekat Asala, Stein Laura, Delman Bradley, Karp Adam, Kupersmith Mark, Kummer Benjamin
Age-related Differences in Peak Oxygen Uptake in Patients with Multimorbidity Undergoing Cardiac RehabilitationGomes Pauline, Miller Sophie, Chacin-suarez Audry, Olson Thomas
More abstracts from these authors:
Brennan Kelly, Narayan Sanjiv, Rogers Albert, Bandyopadhyay Sabyasachi, Ganesan Prasanth, Ansari Rayan, Somani Sulaiman, Liu Xichong, Baykaner Tina, Perino Alexander, Wang Paul
Automated End-to-End Framework for Extracting Raw ECG Waveforms and ST Segment Values from ECG Reports and Predicting ST Elevation by Machine LearningGanesan Prasanth, Wang Paul, Ashley Euan, Perez Marco, Narayan Sanjiv, Rogers Albert, Liu Xichong, Bandyopadhyay Sabyasachi, Ansari Rayan, Somani Sulaiman, Brennan Kelly, Karius Alexander, Baykaner Tina, Perino Alexander