Final ID: MP440
High Burden of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors Among Adolescents with Overweight or Obesity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
The cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome is a driver of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Stage 2 CKM (metabolic risk factors or chronic kidney disease) is an important threshold for intervention to prevent progression to stage 3 (subclinical CVD). The 2023 AHA CKM presidential advisory calls for early life assessment for CKM, but CKM risk factor data in contemporary pediatric populations are limited.
Research Question:
Among adolescents with overweight or obesity, what is the prevalence of additional CKM risk factors?
Methods:
This study used the most recent well child visit (2021-2023) from children aged 13-17y to identify those with BMI ≥85th percentile (overweight threshold) in a Northern California healthcare system who had measures of blood pressure (BP), hemoglobin A1c, and non-fasting triglyceride (TG) within 1-year of the visit. Adapted CKM metabolic risk factors included hypertensive BP ≥130/80, elevated TG≥150 mg/dL, and prediabetes A1c ≥5.7%. Demographic predictors of having at least 1 metabolic risk factor (in addition to overweight/obesity) were examined using logistic regression, adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity and neighborhood deprivation index.
Results:
Among 34,262 adolescents with overweight/obesity (mean age 15.6±1.4y, 49.2% female); 20.7% were non-Hispanic white (NHW), 40.1% Hispanic, 17.4% Asian/Pacific Islander (PI), 9.4% Black and 12.3% other/unknown. While all adolescents had at least overweight, 40.8% had moderate and 29.9% had severe obesity (BMI 100-119% and ≥120% of 95th percentile, respectively).
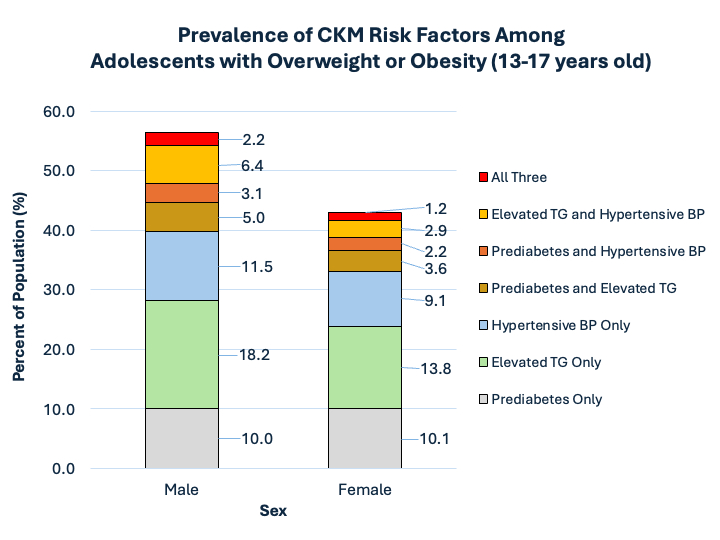
Overall, 49.7% of adolescents with overweight/obesity had at least one CKM metabolic risk factor (56.5% of males, 42.8% of females) and 15.3% had multiple (16.8% of males, 9.8% females, Figure). Males were more likely than females to have a CKM metabolic risk factor (OR 1.72 [95%CI 1.65-1.80]), as were Asian/PI (OR 1.32 [1.23-1.42]) and Hispanic (OR 1.15 [1.08-1.22]) but not Black adolescents (OR 1.03 [0.95-1.12]) vs NHW. For the subset with obesity, 55.2% had a CKM metabolic risk factor; 16.4% had multiple.
Conclusions:
Half of all adolescents with overweight or obesity had a CKM metabolic risk factor, including many with multiple risk factors. The growing burden of stage 2 CKM risk factors in this high-risk population supports the need for targeted lifestyle interventions and more intensive management. Adolescents with overweight or obesity should be aggressively screened for CKM risk conditions before adulthood.
The cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome is a driver of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Stage 2 CKM (metabolic risk factors or chronic kidney disease) is an important threshold for intervention to prevent progression to stage 3 (subclinical CVD). The 2023 AHA CKM presidential advisory calls for early life assessment for CKM, but CKM risk factor data in contemporary pediatric populations are limited.
Research Question:
Among adolescents with overweight or obesity, what is the prevalence of additional CKM risk factors?
Methods:
This study used the most recent well child visit (2021-2023) from children aged 13-17y to identify those with BMI ≥85th percentile (overweight threshold) in a Northern California healthcare system who had measures of blood pressure (BP), hemoglobin A1c, and non-fasting triglyceride (TG) within 1-year of the visit. Adapted CKM metabolic risk factors included hypertensive BP ≥130/80, elevated TG≥150 mg/dL, and prediabetes A1c ≥5.7%. Demographic predictors of having at least 1 metabolic risk factor (in addition to overweight/obesity) were examined using logistic regression, adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity and neighborhood deprivation index.
Results:
Among 34,262 adolescents with overweight/obesity (mean age 15.6±1.4y, 49.2% female); 20.7% were non-Hispanic white (NHW), 40.1% Hispanic, 17.4% Asian/Pacific Islander (PI), 9.4% Black and 12.3% other/unknown. While all adolescents had at least overweight, 40.8% had moderate and 29.9% had severe obesity (BMI 100-119% and ≥120% of 95th percentile, respectively).
Overall, 49.7% of adolescents with overweight/obesity had at least one CKM metabolic risk factor (56.5% of males, 42.8% of females) and 15.3% had multiple (16.8% of males, 9.8% females, Figure). Males were more likely than females to have a CKM metabolic risk factor (OR 1.72 [95%CI 1.65-1.80]), as were Asian/PI (OR 1.32 [1.23-1.42]) and Hispanic (OR 1.15 [1.08-1.22]) but not Black adolescents (OR 1.03 [0.95-1.12]) vs NHW. For the subset with obesity, 55.2% had a CKM metabolic risk factor; 16.4% had multiple.
Conclusions:
Half of all adolescents with overweight or obesity had a CKM metabolic risk factor, including many with multiple risk factors. The growing burden of stage 2 CKM risk factors in this high-risk population supports the need for targeted lifestyle interventions and more intensive management. Adolescents with overweight or obesity should be aggressively screened for CKM risk conditions before adulthood.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-Varying Implications of Recalibration of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction in a New England-Based Healthcare System
Cho So Mi, Natarajan Pradeep, Rivera Rachel, Koyama Satoshi, Kim Min Seo, Honigberg Michael, Bhattacharya Romit, Paruchuri Kaavya, Allen Norrina, Hornsby Whitney
A Novel Machine Learning-based Adverse Cardiovascular Events Risk Algorithm For Cancer Patients Treated With Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsWahi Shawn, Cross James, Mora Ruben, Im Yunju, Kwan Jennifer