Final ID: MP1065
Predicting Heart Failure with Improved Ejection Fraction Using Electronic Health Record-Based Models with Contemporary GDMT
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Given the dynamic and increasingly modifiable nature of LVEF, static, cross-sectional LVEF-based classification alone is incomplete. Recognizing this, the 2022 AHA/ACC HF Guidelines introduced a new classification of HF with improved EF (HFimpEF). Understanding factors associated with HFimpEF may have implications for drug and device intensification; however, limited contemporary data with modern GDMT use exist to inform this question.
Objective: To describe patient characteristics associated with incident HFimpEF across a large, diverse, multisite integrated healthcare delivery system.
Methods: We identified patients who were diagnosed with incident HFrEF between January 2013-December 2023 across Kaiser Permanente Northern California, a large integrated healthcare delivery system. We defined incident HFimpEF as a follow-up LVEF >40% within 12 months of HFrEF diagnosis. Patients who died, disenrolled from the health plan, or did not receive a follow-up LVEF were classified as having persistent HFrEF. Regularized logistic regression was used to identify predictors of incident HFimpEF. To examine the importance of post-diagnosis guideline directed medical therapy (GDMT) use in predicting HFimpEF, we re-indexed the cohort at 90 days post-HFrEF and added GDMT change from time of incident HFrEF and the new index date as new covariates. We then re-trained models to examine the relative importance of GDMT use compared to characteristics at the time of HFrEF diagnosis.
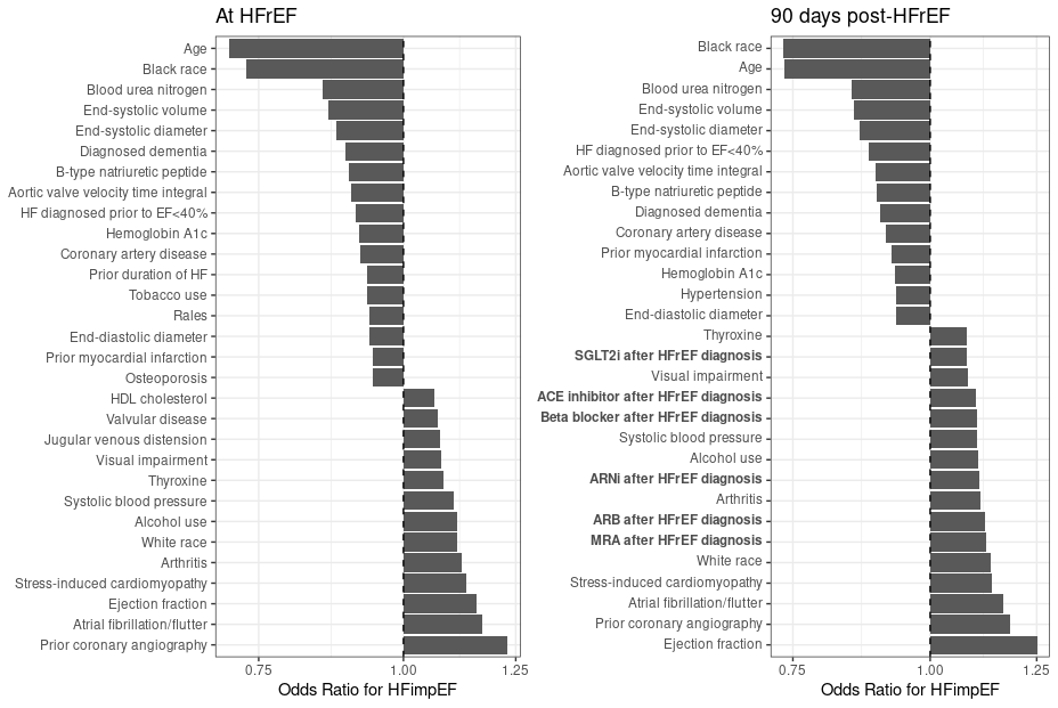
Results: Among 33,163 adults with newly diagnosed HFrEF [mean (SD) LVEF 31% (7.5%)], 13,117 (39.6%) experienced HFimpEF within 12 months. In multivariable models, potential reversible forms of cardiomyopathy (e.g. atrial fibrillation, alcohol use), higher baseline LVEF, lower BNP and smaller LV volumes, and lower burden of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) comorbidities (lower history of MI, lower HbA1c) were among the top predictors of incident HFimpEF (Figure, Panel A). After accounting for GDMT initiation between incident HFrEF and 90 days post- HFrEF, we found that all GDMT medications initiated were positively associated with developing incident HFimpEF and were included among the top predictors of incident HFimpEF (Figure, Panel B).
Conclusion: Early GDMT initiation is strongly associated with HFimpEF, particularly in patients with fewer CKM comorbidities. Future research should explore tailored treatment strategies for patients most likely to benefit from early intervention.
Objective: To describe patient characteristics associated with incident HFimpEF across a large, diverse, multisite integrated healthcare delivery system.
Methods: We identified patients who were diagnosed with incident HFrEF between January 2013-December 2023 across Kaiser Permanente Northern California, a large integrated healthcare delivery system. We defined incident HFimpEF as a follow-up LVEF >40% within 12 months of HFrEF diagnosis. Patients who died, disenrolled from the health plan, or did not receive a follow-up LVEF were classified as having persistent HFrEF. Regularized logistic regression was used to identify predictors of incident HFimpEF. To examine the importance of post-diagnosis guideline directed medical therapy (GDMT) use in predicting HFimpEF, we re-indexed the cohort at 90 days post-HFrEF and added GDMT change from time of incident HFrEF and the new index date as new covariates. We then re-trained models to examine the relative importance of GDMT use compared to characteristics at the time of HFrEF diagnosis.
Results: Among 33,163 adults with newly diagnosed HFrEF [mean (SD) LVEF 31% (7.5%)], 13,117 (39.6%) experienced HFimpEF within 12 months. In multivariable models, potential reversible forms of cardiomyopathy (e.g. atrial fibrillation, alcohol use), higher baseline LVEF, lower BNP and smaller LV volumes, and lower burden of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) comorbidities (lower history of MI, lower HbA1c) were among the top predictors of incident HFimpEF (Figure, Panel A). After accounting for GDMT initiation between incident HFrEF and 90 days post- HFrEF, we found that all GDMT medications initiated were positively associated with developing incident HFimpEF and were included among the top predictors of incident HFimpEF (Figure, Panel B).
Conclusion: Early GDMT initiation is strongly associated with HFimpEF, particularly in patients with fewer CKM comorbidities. Future research should explore tailored treatment strategies for patients most likely to benefit from early intervention.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1 Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies Promote Heart Failure Though Activation of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP1/Phosphodiesterase 4B Pathway
Cao Ning, Qiu Hui, Li Hongwei
A Case of Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Systemic Thromboembolism in a Young Patient on Testosterone Replacement TherapySabri Muhammad, Ijaz Naila, Nadeem Ramsha, Checchio Lucy, Riaz Faiza