Final ID: Sa3114
Transcatheter Mitral Edge-to-Edge Repair versus Surgical Mitral Valve Repair in Elderly Patients with Heart Failure: A Propensity Matched Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER; MitraClip) has emerged as a less invasive alternative to surgical mitral valve repair (SMVr) in older adults with mitral regurgitation and heart failure (HF). However, comparative real-world data on outcomes between these approaches in elderly patients remain limited.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of the TriNetX global health network to identify adults over 65 years with heart failure (HF) who underwent transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER; MitraClip) or surgical mitral valve repair (SMVr). Patients were ascertained using ICD-10 codes. Baseline demographics (age, race), comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease), and outpatient medication use (β-blockers, ACE inhibitors/ARBs, statins, anticoagulants) were collected. A 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) algorithm—matching on age, race, key comorbidities, and medication use—was applied to generate two balanced cohorts. We then compared short-term (30-day) and long-term (1-year) outcomes between matched M-TEER and SMVr groups, including all-cause mortality, heart failure exacerbation, neurological, respiratory, and vascular complications, acute kidney injury (AKI), mechanical ventilator use, and readmission. Risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated, and statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
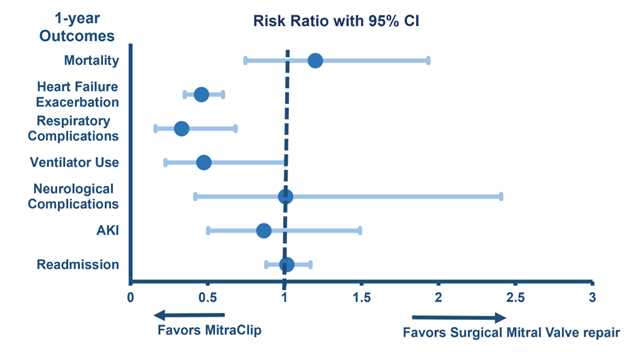
Among 5,096 older adults undergoing M-TEER and 2,812 undergoing SMVr, PSM yielded two well-balanced cohorts of 1,020 patients each (mean age 80.1 ± 7.7 years; 40% female; 10.1% Black). At both 30 days and 1 year, the M-TEER group experienced significantly fewer respiratory complications (p = 0.002), reduced mechanical ventilator use (p = 0.046), and lower rates of heart failure exacerbation (p < 0.001) compared to SMVr. However, SMVr was associated with a lower all-cause mortality rate at 1 year (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In older adults with HF, M-TEER was associated with fewer cardiopulmonary complications and HF exacerbations, while SMVr conferred improved long-term survival. These findings highlight the need to individualize procedural decisions based on patient comorbidity profiles and clinical goals.
Transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER; MitraClip) has emerged as a less invasive alternative to surgical mitral valve repair (SMVr) in older adults with mitral regurgitation and heart failure (HF). However, comparative real-world data on outcomes between these approaches in elderly patients remain limited.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of the TriNetX global health network to identify adults over 65 years with heart failure (HF) who underwent transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER; MitraClip) or surgical mitral valve repair (SMVr). Patients were ascertained using ICD-10 codes. Baseline demographics (age, race), comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease), and outpatient medication use (β-blockers, ACE inhibitors/ARBs, statins, anticoagulants) were collected. A 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) algorithm—matching on age, race, key comorbidities, and medication use—was applied to generate two balanced cohorts. We then compared short-term (30-day) and long-term (1-year) outcomes between matched M-TEER and SMVr groups, including all-cause mortality, heart failure exacerbation, neurological, respiratory, and vascular complications, acute kidney injury (AKI), mechanical ventilator use, and readmission. Risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated, and statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
Among 5,096 older adults undergoing M-TEER and 2,812 undergoing SMVr, PSM yielded two well-balanced cohorts of 1,020 patients each (mean age 80.1 ± 7.7 years; 40% female; 10.1% Black). At both 30 days and 1 year, the M-TEER group experienced significantly fewer respiratory complications (p = 0.002), reduced mechanical ventilator use (p = 0.046), and lower rates of heart failure exacerbation (p < 0.001) compared to SMVr. However, SMVr was associated with a lower all-cause mortality rate at 1 year (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In older adults with HF, M-TEER was associated with fewer cardiopulmonary complications and HF exacerbations, while SMVr conferred improved long-term survival. These findings highlight the need to individualize procedural decisions based on patient comorbidity profiles and clinical goals.
More abstracts on this topic:
From Gut to Lung: Lipoxygenase Dependent Oxylipin Amplification Drives 15-HETE Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in C57BL6/J Mice
Oconnor Ellen, Reddy Srinivasa, Emamimeybodi Maryam, Medzikovic Lejla, Hatamnejad Mohammad Reza, Dehghanitafti Ateyeh, Li Min, Ruffenach Gregoire, Mukherjee Pallavi, Eghbali Mansoureh
Association of Structural Remodeling and Mitral Annular Disjunction with Significant Premature Ventricular Contraction Burden in Patients with Mitral Valve Prolapse: A Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging StudyCalcagno Tess, Kwon Deborah, Wang Tom Kai Ming, Kalahasti Vidyasagar, Santangeli Pasquale, Wazni Oussama, Griffin Brian, Chen David, Nguyen Christopher, Sroubek Jakub