Final ID: MP283
Ex Vivo Machine Perfusion Versus Static Cold Storage in Adult Heart Transplantation: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Ex vivo machine perfusion (MP) is increasingly used to preserve donor hearts, particularly from extended criteria or distant donors. While it offers logistical and physiological advantages, its safety and efficacy compared to conventional static cold storage (SCS) remain uncertain.
Purpose
To assess whether MP is comparable to SCS in terms of safety and clinical outcomes in adult orthotopic heart transplantation (OHT).
Methods
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane CENTRAL for randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing MP (normothermic or hypothermic) to SCS in adult OHT. Our search strategy aimed to capture the most up-to-date evidence available, including studies published through May 2025. Outcomes included: 30-day and 1-year survival, primary graft dysfunction (PGD), severe adverse events (SAEs), acute cellular rejection, renal replacement therapy (RRT), ICU and hospital length of stay, time on ventilator, and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) time. Odds ratios (ORs) were pooled using a random-effects model, with their 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results
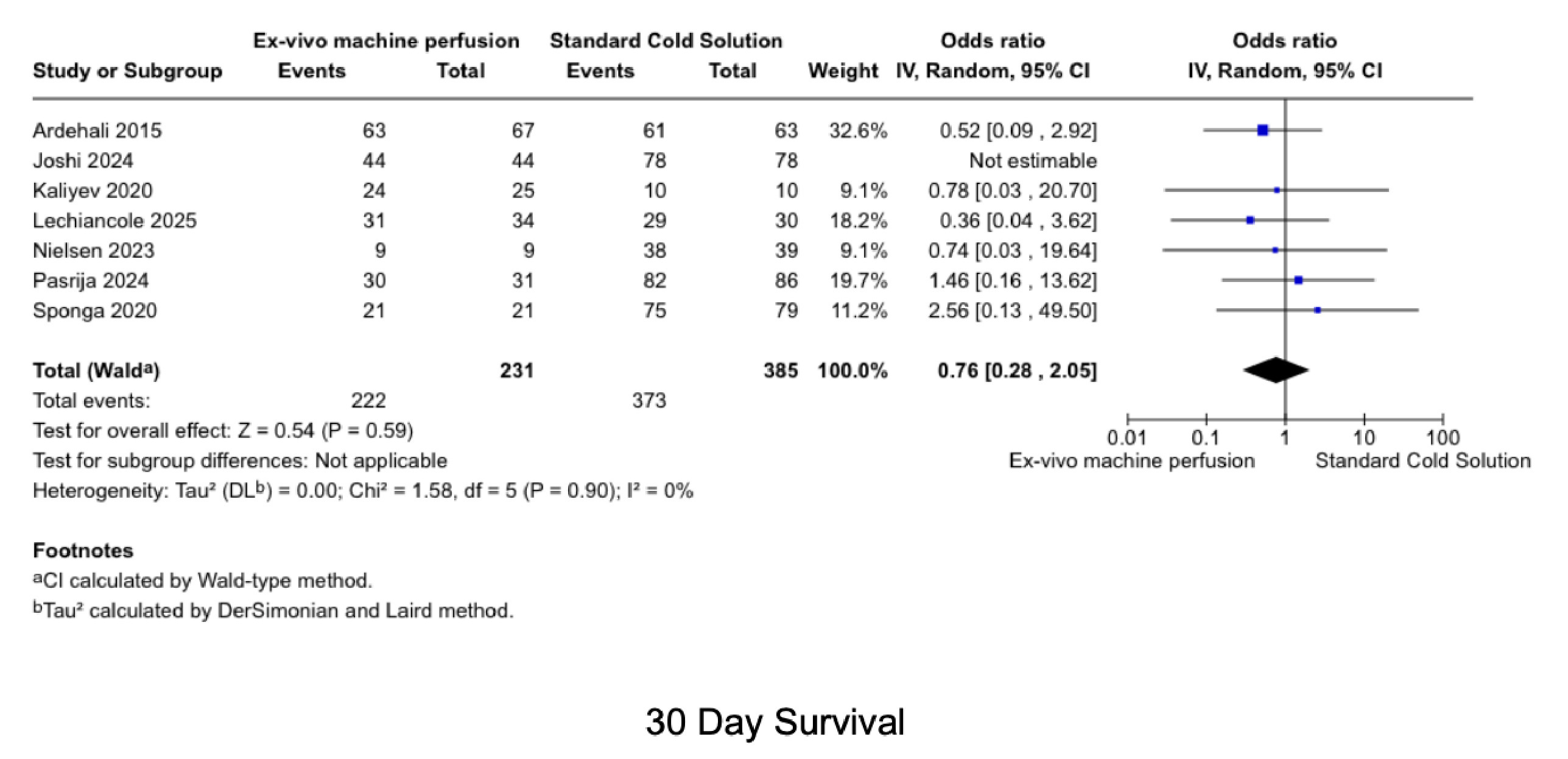
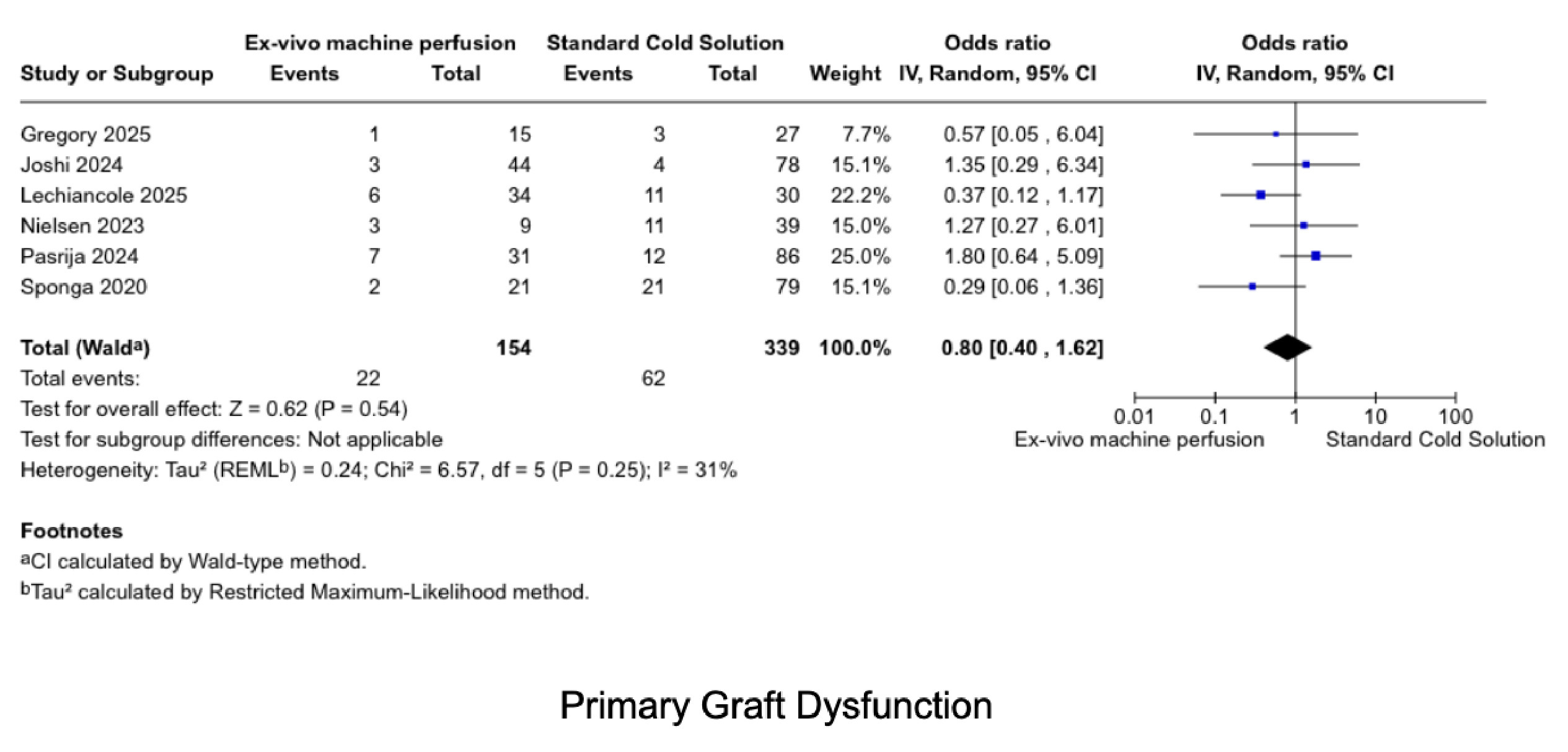
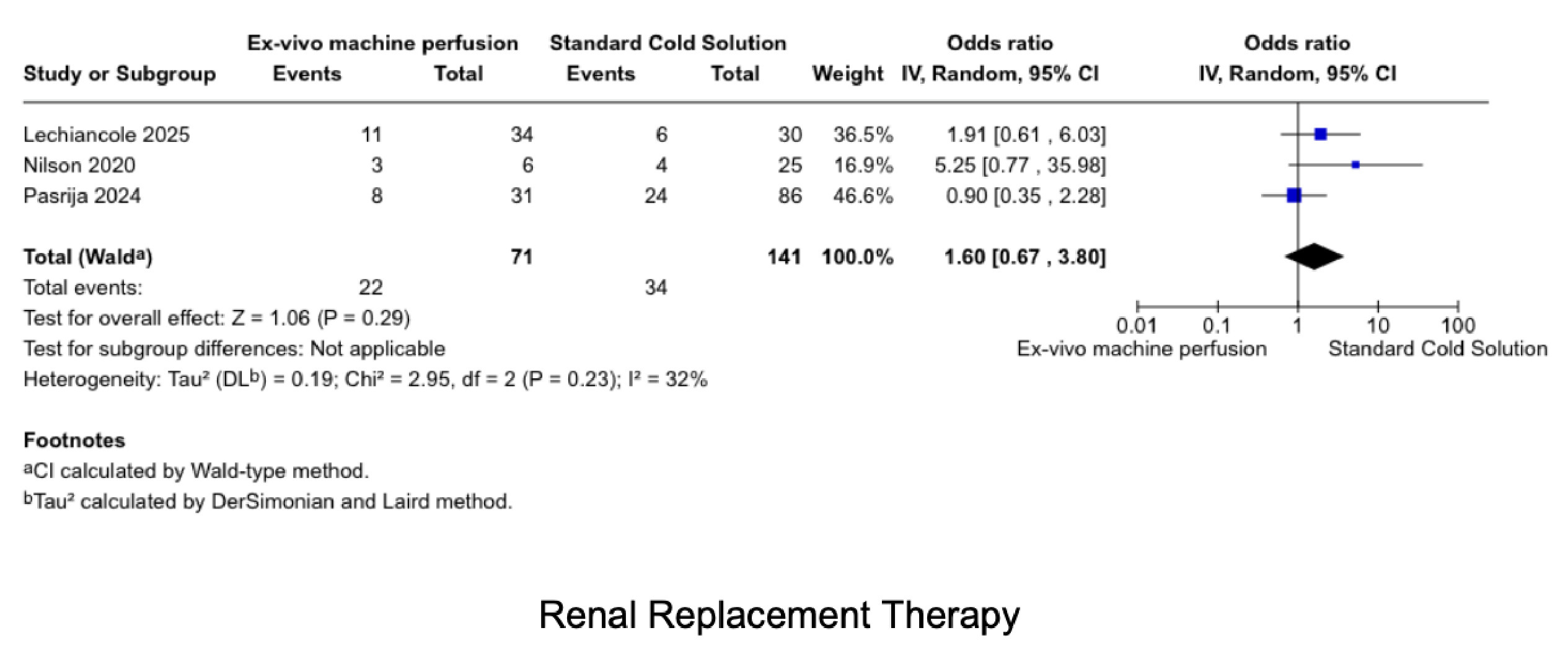
Ten studies involving 613 patients (MP: 254; SCS: 359) were included. MP was not associated with worse outcomes compared to SCS in 30-day survival (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.28–2.05), 1-year survival (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.28–1.35), PGD (OR 0.80, 95% CI 0.40–1.62), SAEs (OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.29–1.71), or acute cellular rejection (OR 1.10, 95% CI 0.68–1.78). No significant differences were observed in RRT (OR 1.60, 95% CI 0.67–3.80), ICU stay (MD 0.61 days, 95% CI -0.31 to 1.53), hospital stay (MD -3.86 days, 95% CI -24.22 to 16.49), time on ventilator (MD 0.17 hours, 95% CI -5.93 to 6.26), or CPB time (MD 4.06 minutes, 95% CI -10.84 to 18.96). Heterogeneity was low to moderate across all outcomes.
Conclusion
Ex vivo machine perfusion is comparable to static cold storage in terms of safety and clinical outcomes in adult heart transplantation. These findings support its use as a safe alternative preservation method, particularly when aiming to increase the donor pool or facilitate long-distance or marginal organ procurement.
Background
Ex vivo machine perfusion (MP) is increasingly used to preserve donor hearts, particularly from extended criteria or distant donors. While it offers logistical and physiological advantages, its safety and efficacy compared to conventional static cold storage (SCS) remain uncertain.
Purpose
To assess whether MP is comparable to SCS in terms of safety and clinical outcomes in adult orthotopic heart transplantation (OHT).
Methods
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane CENTRAL for randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing MP (normothermic or hypothermic) to SCS in adult OHT. Our search strategy aimed to capture the most up-to-date evidence available, including studies published through May 2025. Outcomes included: 30-day and 1-year survival, primary graft dysfunction (PGD), severe adverse events (SAEs), acute cellular rejection, renal replacement therapy (RRT), ICU and hospital length of stay, time on ventilator, and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) time. Odds ratios (ORs) were pooled using a random-effects model, with their 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results
Ten studies involving 613 patients (MP: 254; SCS: 359) were included. MP was not associated with worse outcomes compared to SCS in 30-day survival (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.28–2.05), 1-year survival (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.28–1.35), PGD (OR 0.80, 95% CI 0.40–1.62), SAEs (OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.29–1.71), or acute cellular rejection (OR 1.10, 95% CI 0.68–1.78). No significant differences were observed in RRT (OR 1.60, 95% CI 0.67–3.80), ICU stay (MD 0.61 days, 95% CI -0.31 to 1.53), hospital stay (MD -3.86 days, 95% CI -24.22 to 16.49), time on ventilator (MD 0.17 hours, 95% CI -5.93 to 6.26), or CPB time (MD 4.06 minutes, 95% CI -10.84 to 18.96). Heterogeneity was low to moderate across all outcomes.
Conclusion
Ex vivo machine perfusion is comparable to static cold storage in terms of safety and clinical outcomes in adult heart transplantation. These findings support its use as a safe alternative preservation method, particularly when aiming to increase the donor pool or facilitate long-distance or marginal organ procurement.
More abstracts on this topic:
Clinical management of select patients with surgically implanted Impella 5.5 left ventricular assist devices on a cardiovascular step-down unit
Ospina Meg, Bull Lindsey, Inampudi Chakradhari, Mcmurray Jeff, Tedford Ryan, Witer Lucas, Bhandari Krishna, Yourshaw Jeffrey, Houston Brian, Kilic Arman, Carnicelli Anthony, Griffin Jan, Van Bakel Adrian, Jackson Gregory, Rao Vishal N., Atkins Jessica, Hajj Jennifer, Dodson Kaylen, Summer Mary Kathryn
Cardiopulmonary Bypass and Aortic Cross-Clamp Times as Predictors of Outcomes in ECMO-Supported Cardiotomy PatientsBanker Himanshi, Sarangi Swapna, Jena Anek, Seelhammer Troy, Bohman John, Haney John, Chaudhary Sanjay, Guru Pramod