Final ID: MP1366
Utilizing Epicardial Adipose Tissue As A Risk Marker For Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) “fat-omics” is an inflammation-sensitive depot that may provide prognostic information in cardiometabolic disease. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is associated with high rates of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and heart failure (HF). We assess the utility of opportunistic EAT radiomic analysis in patients with CKD undergoing CT calcium-score (CTCS) scans and its association and mediation of adverse events.
Hypothesis: Stage-specific EAT features in CKD mediates MACE and HF risk.
Methods: Using data obtained from the CLARIFY registry (NCT04075162), a large prospective study of no-charge CAC testing, we performed descriptive analysis on patients with CKD via a 1:1 propensity matching approach after balancing for age, race, gender, hypertension, smoking, medications, and CAC score. Due to limited power, CKD was categorized into the combined stage (GFR <60), stage 3a (CKD-3a with GFR 45-59), and CKD stages 3b-4 (CKD-3b4 with GFR 15-30). A validated AI segmentation tool was used to segment EAT, followed by extraction of >200 “fat-omics” features from EAT in 4 inferior-to-superior cardiac spanning slab quartiles (PQ) Hounsfield unit (HU) histogram bins (20-HU increments), and more. We performed time to event Kaplan Meier analysis in propensity-matched and the unmatched cohorts for MACE and HF, and mediation analyses to quantify the proportion of effects mediated by significant fat-omics features.
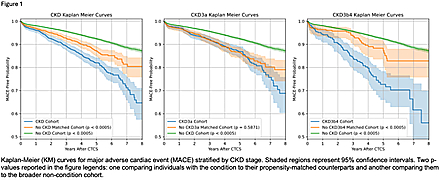
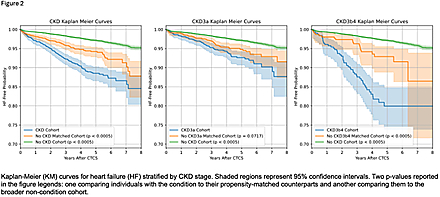
Results: A total of 1594 patients with CKD (1170 CKD-3a and 308 CKD-3b4) were included in the study. In the overall CKD group, there were 5 unique EAT features including total HU skewness and kurtosis HU in the superior slab of the heart, involving major coronary arteries. CKD-3a had 61 unique features and CKD3b-4 had 53 unique features. When compared to the propensity-matched non-CKD cohort, the overall CKD group and CKD 3b-4 had significantly worse MACE-free probability (p<0.005) (Figure 1) and worse HF-free probability (p<0.005) (Figure 2). Mediation analysis in the CKD 3b-4 cohort revealed 8 EAT features in the superior slab of the heart (PQ4) in the higher HU range (130-50) that mediated MACE. 11 features that significantly mediated HF also mainly involved the superior slab.
Conclusions: Propensity-matched CKD patients have higher MACE and HF events when compared to non-CKD patients. CKD patients have distinct EAT features and appear to be in the mediation pathway for MACE and HF risk.
Hypothesis: Stage-specific EAT features in CKD mediates MACE and HF risk.
Methods: Using data obtained from the CLARIFY registry (NCT04075162), a large prospective study of no-charge CAC testing, we performed descriptive analysis on patients with CKD via a 1:1 propensity matching approach after balancing for age, race, gender, hypertension, smoking, medications, and CAC score. Due to limited power, CKD was categorized into the combined stage (GFR <60), stage 3a (CKD-3a with GFR 45-59), and CKD stages 3b-4 (CKD-3b4 with GFR 15-30). A validated AI segmentation tool was used to segment EAT, followed by extraction of >200 “fat-omics” features from EAT in 4 inferior-to-superior cardiac spanning slab quartiles (PQ) Hounsfield unit (HU) histogram bins (20-HU increments), and more. We performed time to event Kaplan Meier analysis in propensity-matched and the unmatched cohorts for MACE and HF, and mediation analyses to quantify the proportion of effects mediated by significant fat-omics features.
Results: A total of 1594 patients with CKD (1170 CKD-3a and 308 CKD-3b4) were included in the study. In the overall CKD group, there were 5 unique EAT features including total HU skewness and kurtosis HU in the superior slab of the heart, involving major coronary arteries. CKD-3a had 61 unique features and CKD3b-4 had 53 unique features. When compared to the propensity-matched non-CKD cohort, the overall CKD group and CKD 3b-4 had significantly worse MACE-free probability (p<0.005) (Figure 1) and worse HF-free probability (p<0.005) (Figure 2). Mediation analysis in the CKD 3b-4 cohort revealed 8 EAT features in the superior slab of the heart (PQ4) in the higher HU range (130-50) that mediated MACE. 11 features that significantly mediated HF also mainly involved the superior slab.
Conclusions: Propensity-matched CKD patients have higher MACE and HF events when compared to non-CKD patients. CKD patients have distinct EAT features and appear to be in the mediation pathway for MACE and HF risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adiposomal microRNAs Mediate Vascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Associated Type 2 Diabetes
Mirza Imaduddin, Morsy Mohammed, Levitan Irena, Raj Usha, Mahmoud Abeer
Age-standardized trends in Incidence Rates of Noncommunicable diseases among Adults Aged 30 to 79 in Senegal from 2000 to 2019Gaye Ngone, Ka Mame, Kyem Damaris, Jobe Modou, Sattler Elisabeth, Gary-webb Tiffany, Gaye Bamba