Final ID: MP912
Dual Pathway Inhibition prescription after percutaneous vascular intervention is low, and dependent on physician and treating facility practice patterns
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Industry-funded level one data supports dual pathway inhibition (DPI; aspirin and low-dose rivaroxaban) after percutaneous vascular interventions (PVI), but interventionalists debate its widespread adoption.
Research Questions: What are the rates of and factors associated with pre and post-PVI DPI prescription in the Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI)?
Methods: We queried the VQI for PVI (2022-2024), excluding acute limb ischemia, aneurysmal disease, COVID+ patients, and those on full dose anticoagulation. DPI was defined as any antiplatelet therapy plus 2.5mg twice daily of rivaroxaban. Mann-Kendal tests evaluated pre- and post-PVI antithrombotic prescription trends. Mixed-effects logistic regression modeled factors associated with pre- and post-PVI DPI prescription, clustered by physician and treating facility, to evaluate the influence of provider and practice-level variation beyond patient characteristics.
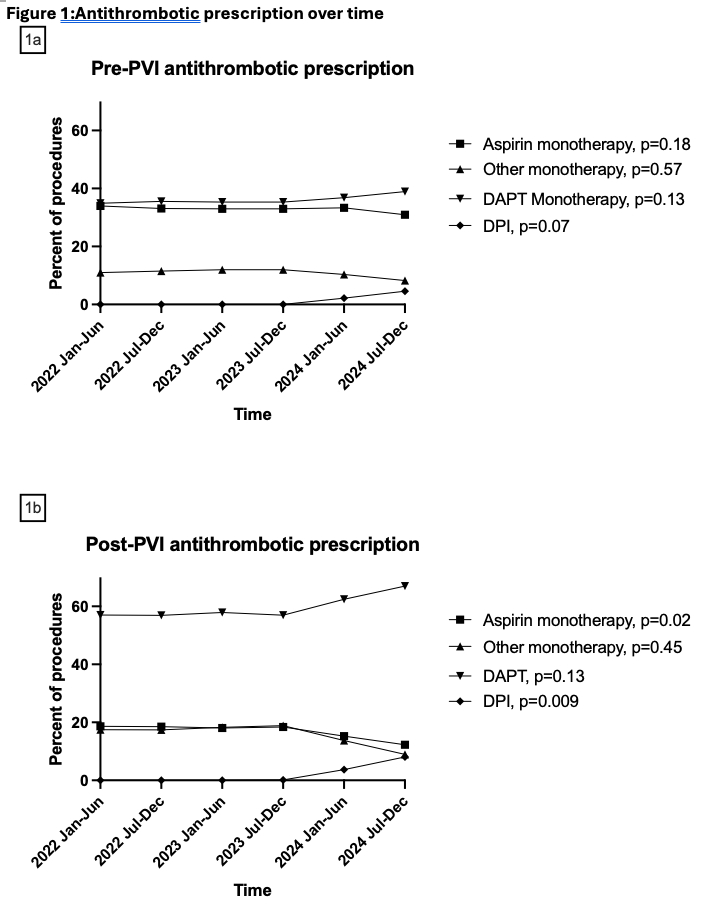
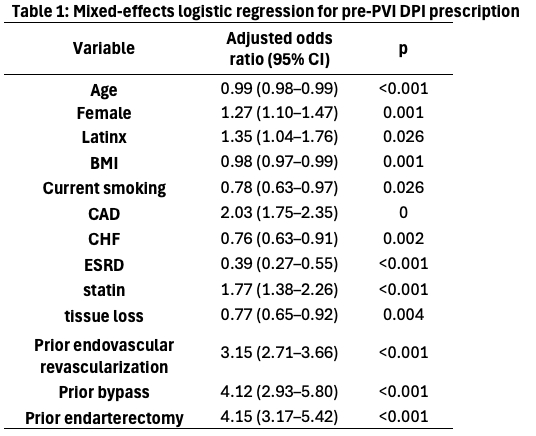
Results: There were no significant changes in pre-PVI prescription patterns over the study period. DPI prescription increased non-significantly from 0/20,058 (0%) in early 2022 to 434/9,488 (4.6%) in late 2024 (Figure 1a). Female sex, Latinx ethnicity, CAD, statin, and prior revascularization were associated with increased pre-PVI DPI prescription. Increasing age and BMI, CHF, ESRD, current smoking, and tissue loss were negatively associated with pre-PVI DPI prescription (Table 1). Physician accounted for 17.4% of variation in pre-PVI DPI prescribing, while treating facility accounted for 14.4% for a total of 31.8%.
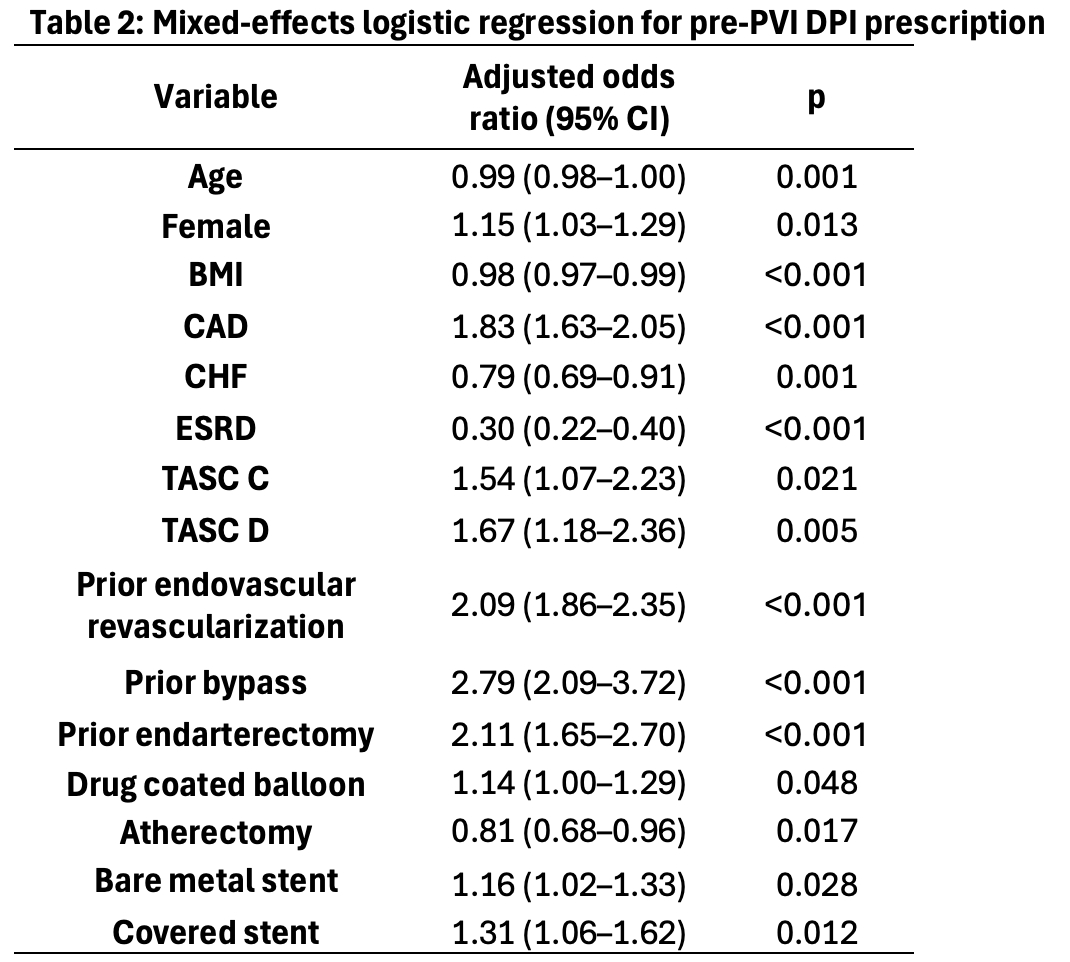
Post-PVI DPI prescription increased significantly over the study period from 0/20,075 (0%) in early 2022 to 742/9,200 (8.1%) in late 2024. Aspirin monotherapy decreased significantly (Figure 1b). Female sex, CAD, increased Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus (TASC) score, prior revascularization, drug coated balloon, and stent placement were associated with increased post-PVI DPI prescription. Increasing age and BMI, CHF, ESRD, and atherectomy were negatively associated with DPI prescription (Table 2). Physician accounted for 22.0% of variation in post-PVI DPI prescribing, whereas treating facility accounted for 12.6% for a total of 34.6%.
Conclusions: Pre and post-PVI DPI prescription was low in our cohort, although did increase significantly to 8.1% post-PVI during the study period. Physician and treating facility practice patterns accounted for one third of the variation in DPI prescribing.
Research Questions: What are the rates of and factors associated with pre and post-PVI DPI prescription in the Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI)?
Methods: We queried the VQI for PVI (2022-2024), excluding acute limb ischemia, aneurysmal disease, COVID+ patients, and those on full dose anticoagulation. DPI was defined as any antiplatelet therapy plus 2.5mg twice daily of rivaroxaban. Mann-Kendal tests evaluated pre- and post-PVI antithrombotic prescription trends. Mixed-effects logistic regression modeled factors associated with pre- and post-PVI DPI prescription, clustered by physician and treating facility, to evaluate the influence of provider and practice-level variation beyond patient characteristics.
Results: There were no significant changes in pre-PVI prescription patterns over the study period. DPI prescription increased non-significantly from 0/20,058 (0%) in early 2022 to 434/9,488 (4.6%) in late 2024 (Figure 1a). Female sex, Latinx ethnicity, CAD, statin, and prior revascularization were associated with increased pre-PVI DPI prescription. Increasing age and BMI, CHF, ESRD, current smoking, and tissue loss were negatively associated with pre-PVI DPI prescription (Table 1). Physician accounted for 17.4% of variation in pre-PVI DPI prescribing, while treating facility accounted for 14.4% for a total of 31.8%.
Post-PVI DPI prescription increased significantly over the study period from 0/20,075 (0%) in early 2022 to 742/9,200 (8.1%) in late 2024. Aspirin monotherapy decreased significantly (Figure 1b). Female sex, CAD, increased Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus (TASC) score, prior revascularization, drug coated balloon, and stent placement were associated with increased post-PVI DPI prescription. Increasing age and BMI, CHF, ESRD, and atherectomy were negatively associated with DPI prescription (Table 2). Physician accounted for 22.0% of variation in post-PVI DPI prescribing, whereas treating facility accounted for 12.6% for a total of 34.6%.
Conclusions: Pre and post-PVI DPI prescription was low in our cohort, although did increase significantly to 8.1% post-PVI during the study period. Physician and treating facility practice patterns accounted for one third of the variation in DPI prescribing.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bleeding risk with non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants versus single antiplatelet therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Baskaran Geethan, Conen David, Wang Michael, Razeghi Ghazal, Ma Richard, Park Louis, Tannu Manasi, Devereaux Pj, Mcintyre William, Healey Jeff
Association of Sleep and Exercise with Chronic Disease: Insights from Long-Term Wearable Data Among All of Us ParticipantsKalyanasundaram Asanish, Gerszten Robert, Rao Prashant, Barber Jacob, Mi Michael, Keyes Michelle, Tahir Usman, Robbins Jeremy, Peters Nicholas, Sofer Tamar, Kramer Daniel