Final ID: MP1358
Short-term Prognostic Value of Early Renal Microcirculatory Assessment Using Superb Microvascular Imaging in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Prospective Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Renal hemodynamics plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology and clinical trajectory of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). Superb Microvascular Imaging (SMI), an advanced Doppler technique with enhanced clutter suppression capabilities, enables detailed visualization of microvascular flow patterns. However, its prognostic utility in ADHF remains unexplored.
Methods:
We prospectively enrolled 85 consecutive patients admitted with ADHF who survived to discharge (mean age 80±12 years, 57% male). Renal ultrasound with SMI was performed 48 hours post-admission. The vascular index (VI) was quantified as the percentage of blood flow signal area within the region of interest (ROI). The intra-renal perfusion index (IRPI) was calculated as [(maximum VI - minimum VI)/maximum VI] over one cardiac cycle (Figure 1). The primary endpoint (CE) was a composite of all-cause mortality and unplanned hospitalization for worsening heart failure.
Results:
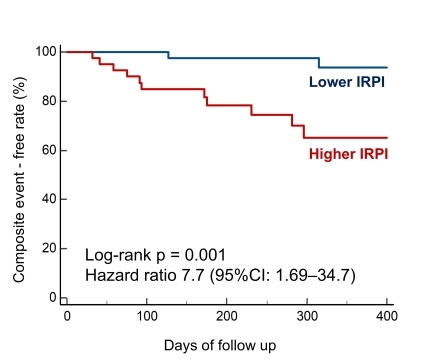
During a mean follow-up period of 296±184 days from discharge, 13 patients (15.3%) experienced the composite endpoint. Patients who experienced events had significantly higher prevalence of prior heart failure hospitalization and diabetes. Additionally, patients with CE demonstrated significantly higher creatinine (1.3±0.5 vs. 1.1±0.3 mg/dL, P=0.007) and IRPI values (0.78±0.18 vs. 0.59±0.24, P=0.008) measured 48 hours after admission compared to those without CE. No significant differences were observed in age, sex, laboratory parameters, or echocardiographic data. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for IRPI was 0.729 (95% CI: 0.621-0.819), which was superior to that of creatinine (AUC 0.670, 95% CI: 0.560-0.769). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that patients with elevated IRPI (>0.68, determined by ROC analysis) had significantly higher event risk (27.5% vs. 4.4%, log-rank p = 0.001) (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
Early assessment of renal microcirculatory dysfunction using SMI demonstrates short-term prognostic significance in ADHF patients. These findings suggest that renal hemodynamic evaluation in the early phase may help identify high-risk patients requiring more intensive monitoring and therapy.
Renal hemodynamics plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology and clinical trajectory of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). Superb Microvascular Imaging (SMI), an advanced Doppler technique with enhanced clutter suppression capabilities, enables detailed visualization of microvascular flow patterns. However, its prognostic utility in ADHF remains unexplored.
Methods:
We prospectively enrolled 85 consecutive patients admitted with ADHF who survived to discharge (mean age 80±12 years, 57% male). Renal ultrasound with SMI was performed 48 hours post-admission. The vascular index (VI) was quantified as the percentage of blood flow signal area within the region of interest (ROI). The intra-renal perfusion index (IRPI) was calculated as [(maximum VI - minimum VI)/maximum VI] over one cardiac cycle (Figure 1). The primary endpoint (CE) was a composite of all-cause mortality and unplanned hospitalization for worsening heart failure.
Results:
During a mean follow-up period of 296±184 days from discharge, 13 patients (15.3%) experienced the composite endpoint. Patients who experienced events had significantly higher prevalence of prior heart failure hospitalization and diabetes. Additionally, patients with CE demonstrated significantly higher creatinine (1.3±0.5 vs. 1.1±0.3 mg/dL, P=0.007) and IRPI values (0.78±0.18 vs. 0.59±0.24, P=0.008) measured 48 hours after admission compared to those without CE. No significant differences were observed in age, sex, laboratory parameters, or echocardiographic data. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for IRPI was 0.729 (95% CI: 0.621-0.819), which was superior to that of creatinine (AUC 0.670, 95% CI: 0.560-0.769). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that patients with elevated IRPI (>0.68, determined by ROC analysis) had significantly higher event risk (27.5% vs. 4.4%, log-rank p = 0.001) (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
Early assessment of renal microcirculatory dysfunction using SMI demonstrates short-term prognostic significance in ADHF patients. These findings suggest that renal hemodynamic evaluation in the early phase may help identify high-risk patients requiring more intensive monitoring and therapy.
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations of Ideal Cardiovascular Health and Its Change With Cardiovascular-Kidney Outcomes in Young Adults
Lee Hokyou, Lee Hyeok-hee, Jhee Jong Hyun, Kim Eun Jin, Kim Hyeon Chang, Lloyd-jones Donald
A RARE CARDIAC COMPLICATION OF LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE: LEFT VENTRICULAR APICAL THROMBUS WITH SEVERE CARDIOMYOPATHYRamalingam Archana, Shabnam Arshiya, Devi Reddy Akhila Reddy, Nookala Vinod