Final ID: MP505
Long-Term Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Hematologic Malignancy Patients Treated with CAR-T Therapy: A TriNetX Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis
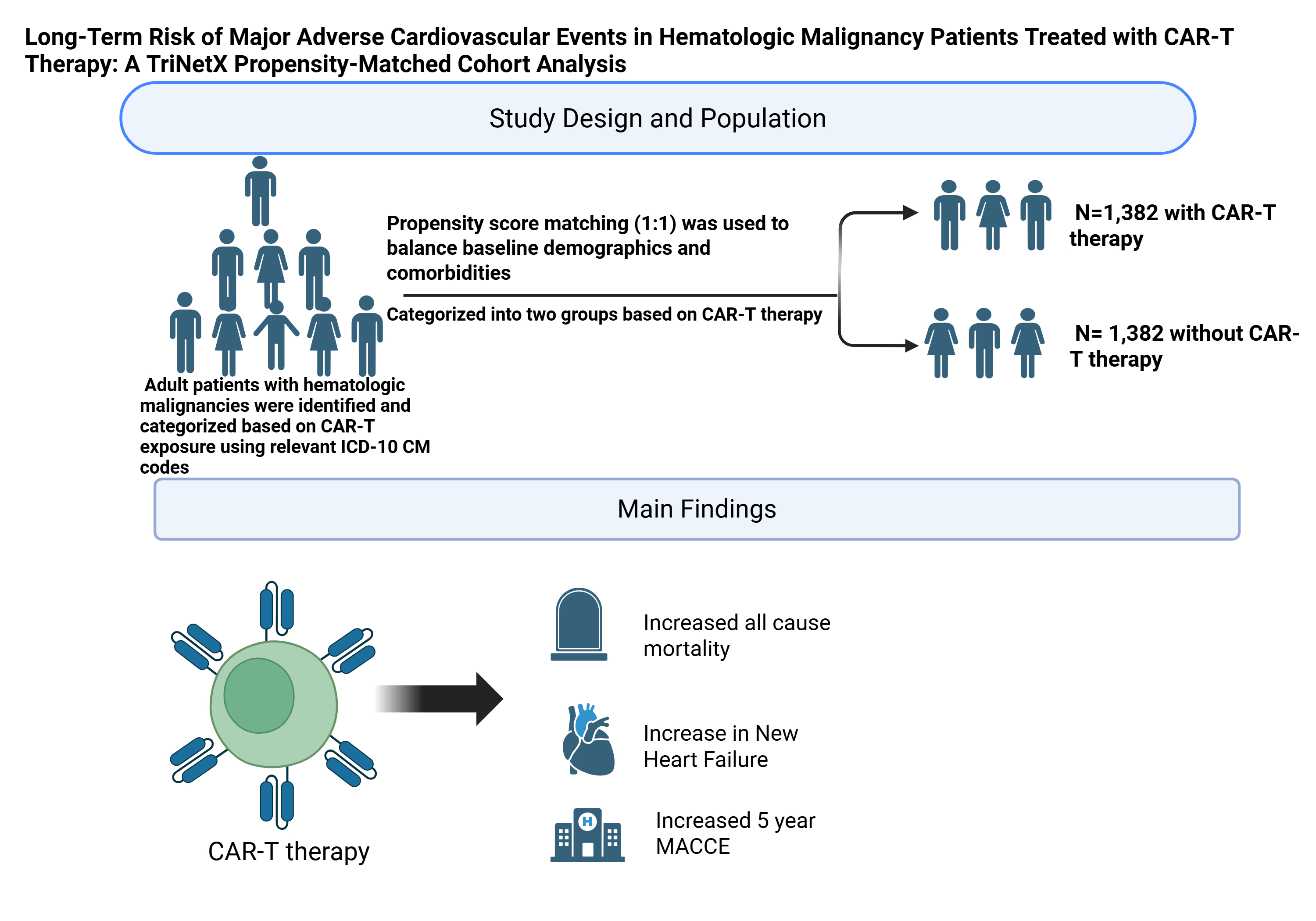
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is an innovative treatment for hematologic malignancies. However, its long-term cardiovascular safety profile remains understudied. Understanding its impact on cardiovascular outcomes is essential for holistic survivorship care. We aimed to evaluate the 5-year incidence of MACE and other cardiovascular outcomes in patients with hematologic malignancies who received CAR-T therapy compared to those who did not, using real-world data.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the TriNetX network. Adult patients with hematologic malignancies were identified and categorized based on CAR-T exposure using relevant ICD-10 CM codes. Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance baseline demographics and comorbidities. The primary outcome was 5-year MACE. Secondary outcomes included myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and all-cause mortality. Hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. A two-tailed p less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: After matching (N=1,382 in each group), baseline characteristics were balanced. Statistically significance were seen in Major Adverse Cardiac Cerebrovascular Events (MACCE) (HR 1.623, 95% CI 1.414-1.862), all cause mortality (HR 1.680, 95% CI 1.466-1.924), new Heart Failure (HR 1.366, 95% CI 1.063-1.755), Major Adverse Kidney Events (HR 2.022, 95% CI 1.670-2.448). No statistical significance were seen in MI (HR 1.147, 95% CI (O.761-1.730), cardiac arrest (HR 1.729, 95% CI 0.973-3.072), new Afib/flutter (HR 1.575, 95% CI 1.214-2.043).
Conclusions: CAR-T therapy was associated with a significantly increased 5-year risk of MACCE, mortality, heart failure, MAKE rates. Ongoing cardiovascular monitoring may be warranted in long-term CAR-T survivors.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the TriNetX network. Adult patients with hematologic malignancies were identified and categorized based on CAR-T exposure using relevant ICD-10 CM codes. Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance baseline demographics and comorbidities. The primary outcome was 5-year MACE. Secondary outcomes included myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and all-cause mortality. Hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. A two-tailed p less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: After matching (N=1,382 in each group), baseline characteristics were balanced. Statistically significance were seen in Major Adverse Cardiac Cerebrovascular Events (MACCE) (HR 1.623, 95% CI 1.414-1.862), all cause mortality (HR 1.680, 95% CI 1.466-1.924), new Heart Failure (HR 1.366, 95% CI 1.063-1.755), Major Adverse Kidney Events (HR 2.022, 95% CI 1.670-2.448). No statistical significance were seen in MI (HR 1.147, 95% CI (O.761-1.730), cardiac arrest (HR 1.729, 95% CI 0.973-3.072), new Afib/flutter (HR 1.575, 95% CI 1.214-2.043).
Conclusions: CAR-T therapy was associated with a significantly increased 5-year risk of MACCE, mortality, heart failure, MAKE rates. Ongoing cardiovascular monitoring may be warranted in long-term CAR-T survivors.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Vitamin D Normalization on Major Adverse Cardiovascular-Related Events Among Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: The TARGET-D Trial
May Heidi, Colipi Dominique, Whiting Tyler, Muhlestein Joseph, Le Viet, Anderson Jeffrey, Babcock Daniel, Wayman Libby, Bair Tami, Knight Stacey, Knowlton Kirk, Iverson Leslie
A Polypill Strategy for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: The POLY-HF TrialPandey Ambarish, Wang Thomas, Keshvani Neil, Rizvi Syed Kazim, Jain Anand, Coellar Juan David, Drazner Mark, Gupta Deepak, Chandra Alvin, Zaha Vlad