Final ID: MP1249
Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of a Novel Low-Dose Triple Single-Pill Combination for the Treatment of Hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
A new low-dose triple single-pill combination (SPC) of antihypertensive drugs (GMRx2, in three strengths: ¼, ½, and standard, containing telmisartan/amlodipine/indapamide [10/1.25/0.625 mg, 20/2.5/1.25 mg, and 40/5/2.5 mg]) has demonstrated superior blood pressure (BP)-lowering efficacy compared to placebo and dual combinations in double-blind, short-term trials.
Objectives
To evaluate the long-term BP-lowering efficacy and safety of GMRx2-based treatment for BP lowering when used in usual clinical care.
Methods
After a 4-week double-blind placebo-controlled randomized phase, participants from Sri Lanka and Nigeria were enrolled into an open-label extension (OLE) phase with follow-up to one year. The randomized phase compared GMRx2 ¼ dose vs. GMRx2 ½ dose vs. placebo in a 2:2:1 ratio. In the OLE phase, participants were switched to GMRx2 ¼, then, if needed, up-titrated to higher doses of GMRx2, and then by the addition of telmisartan 40 mg and amlodipine 5 mg SPC, and finally the addition of spironolactone 25 mg to achieve a target home BP <130/80 mmHg. The primary outcome was the percentage of participants with home BP control (<130/80 mmHg) at week 52.
Results
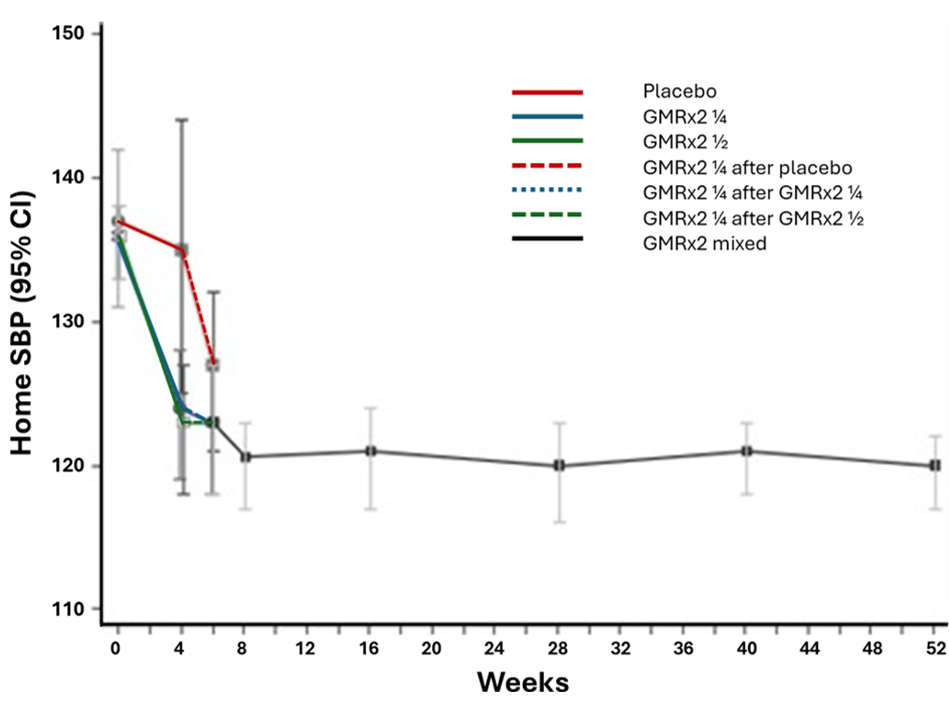
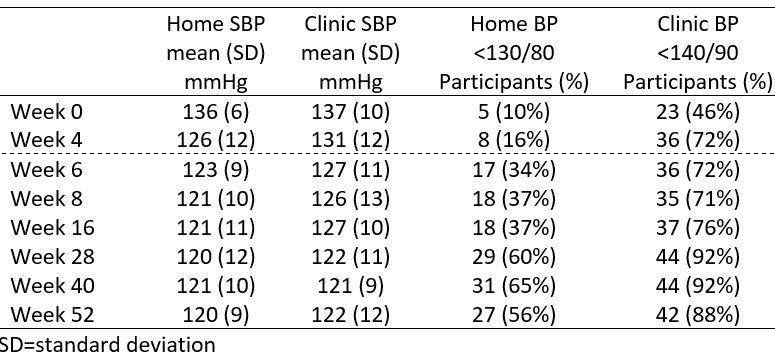
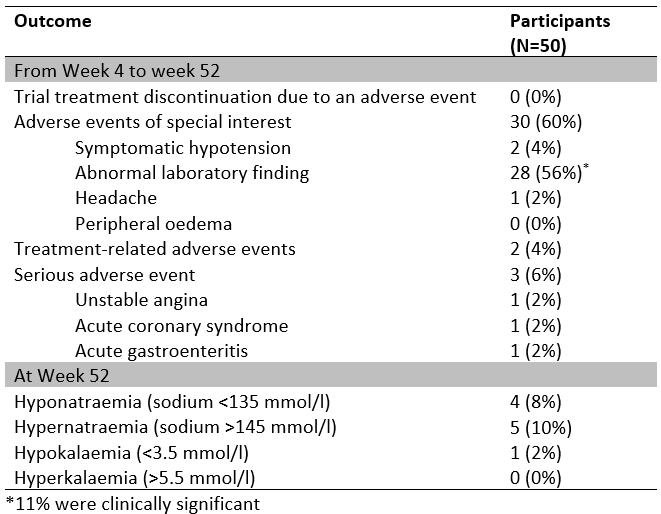
From 21 August 2023 to 20 August 2024, 50 participants participated in the OLE phase, of whom 48 (96%) completed it. The mean age of participants was 49 years, and 60% were female. At baseline entry to the randomized phase, with all participants on no active treatment, mean home and clinic BP levels were 137/85 mmHg and 136/85 mmHg. At entry to the OLE phase, with 4/5 of the participants receiving treatment, baseline mean home and clinic BP were 129/79 mmHg and 131/83 mmHg, respectively. Mean home BP was reduced to 121/78 mmHg 4 weeks into the OLE and was 120/78 at week 52 (Figures 1 and 2). For clinic BP, the corresponding values were 126/79 mmHg and 122/77 mmHg. At one year, home BP control (<130/80 mmHg) was 56%, and clinic BP control (<140/90 mmHg) was 88%. At week 52, the proportions of participants receiving GMRx2 ¼, GMRx2 ½, and GMRx2 standard doses were 53%, 27%, and 22%, respectively, and only three (6%) participants required add-on therapy. Tolerability was good (Figure 3), and none of the participants discontinued trial treatment due to an adverse event.
Conclusions
In a population with mild-to-moderate hypertension, long-term therapy with GMRx2-based treatment achieved high levels of sustained BP control out to one year, with good tolerability and low treatment discontinuation.
A new low-dose triple single-pill combination (SPC) of antihypertensive drugs (GMRx2, in three strengths: ¼, ½, and standard, containing telmisartan/amlodipine/indapamide [10/1.25/0.625 mg, 20/2.5/1.25 mg, and 40/5/2.5 mg]) has demonstrated superior blood pressure (BP)-lowering efficacy compared to placebo and dual combinations in double-blind, short-term trials.
Objectives
To evaluate the long-term BP-lowering efficacy and safety of GMRx2-based treatment for BP lowering when used in usual clinical care.
Methods
After a 4-week double-blind placebo-controlled randomized phase, participants from Sri Lanka and Nigeria were enrolled into an open-label extension (OLE) phase with follow-up to one year. The randomized phase compared GMRx2 ¼ dose vs. GMRx2 ½ dose vs. placebo in a 2:2:1 ratio. In the OLE phase, participants were switched to GMRx2 ¼, then, if needed, up-titrated to higher doses of GMRx2, and then by the addition of telmisartan 40 mg and amlodipine 5 mg SPC, and finally the addition of spironolactone 25 mg to achieve a target home BP <130/80 mmHg. The primary outcome was the percentage of participants with home BP control (<130/80 mmHg) at week 52.
Results
From 21 August 2023 to 20 August 2024, 50 participants participated in the OLE phase, of whom 48 (96%) completed it. The mean age of participants was 49 years, and 60% were female. At baseline entry to the randomized phase, with all participants on no active treatment, mean home and clinic BP levels were 137/85 mmHg and 136/85 mmHg. At entry to the OLE phase, with 4/5 of the participants receiving treatment, baseline mean home and clinic BP were 129/79 mmHg and 131/83 mmHg, respectively. Mean home BP was reduced to 121/78 mmHg 4 weeks into the OLE and was 120/78 at week 52 (Figures 1 and 2). For clinic BP, the corresponding values were 126/79 mmHg and 122/77 mmHg. At one year, home BP control (<130/80 mmHg) was 56%, and clinic BP control (<140/90 mmHg) was 88%. At week 52, the proportions of participants receiving GMRx2 ¼, GMRx2 ½, and GMRx2 standard doses were 53%, 27%, and 22%, respectively, and only three (6%) participants required add-on therapy. Tolerability was good (Figure 3), and none of the participants discontinued trial treatment due to an adverse event.
Conclusions
In a population with mild-to-moderate hypertension, long-term therapy with GMRx2-based treatment achieved high levels of sustained BP control out to one year, with good tolerability and low treatment discontinuation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A pilot study of an intervention for self-management of blood pressure among refugees fleeing war and resettled in the United States
Behnam Rawnaq, Godino Job, Celis Deisy, Anderson Cheryl, Al-rousan Tala
Chronotherapy in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of the Cardiovascular Effects of Bedtime Versus Morning Antihypertensive AdministrationLee Yebon, Riaz Minahil, Ajaz Hareem, Muhammad Daniyal Shaikh, Fahim Syeda, Aftab Zunaira, Tauiqr Habiba, Ashraf Danish Ali, Sarwar Mahwish, Noor Amna, Batool Fizza, Murad Khatoon Naveen