Final ID: MP1403
Efficacy and safety of antihypertensive drugs: Meta-analysis of 484 randomized double-blind trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objectives
To compare the efficacy and tolerability of antihypertensive drugs and their combinations.
Methods
We conducted meta-analyses of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers (BBs), calcium channel blockers (CCBs) and diuretics, with treatment duration 4 to 26 weeks. The primary outcomes were the placebo-corrected reduction in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and withdrawal of treatment due to adverse events (WDAEs), estimated using fixed-effects meta-analysis. Doses of drugs were standardized, and drug regimens were categorized as low, moderate and high efficacy for SBP reduction of <10, 10-19 and ≥20 mmHg from a baseline SBP 154 mmHg.
Results
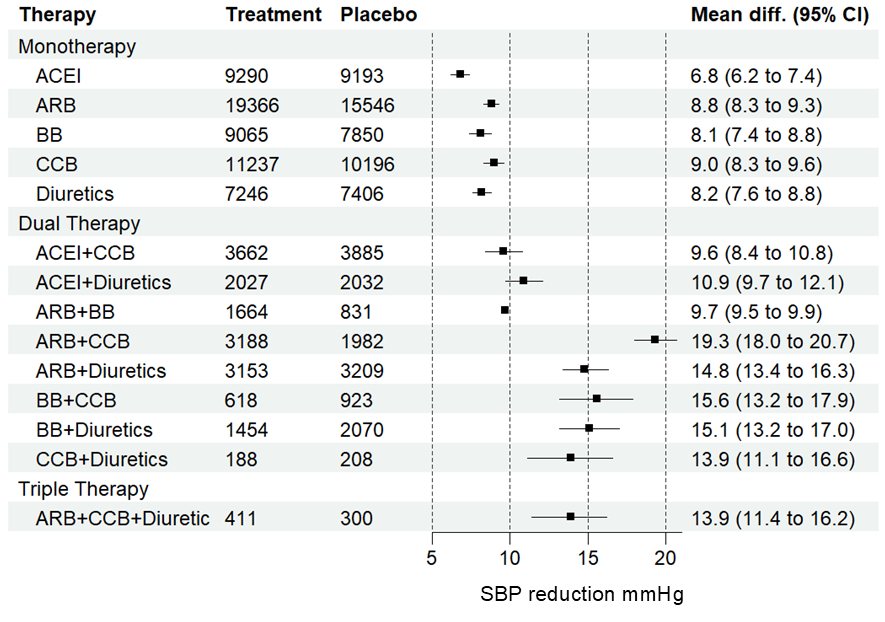
The efficacy analysis included 484 trials (104,176 participants, mean age 54 years, 45% women, baseline mean BP 154/100 mmHg). Standard-dose monotherapy reduced BP by 8.7/5.6 mmHg, and dose doubling reduced BP by 1.5/1.0 mmHg (Figure 1). Standard dose dual combinations reduced BP by 14.9/9.1 mmHg, and dose doubling reduced BP by 2.5/1.4 mmHg. BP reduction with monotherapies decreased by 1.3/0.9 mmHg for every 10 mmHg lower baseline BP, with variation across drug classes. Of 57 standard-dose monotherapies, 79% were low efficacy; of 189 dual combinations, 58% were moderate and 11% were high efficacy.
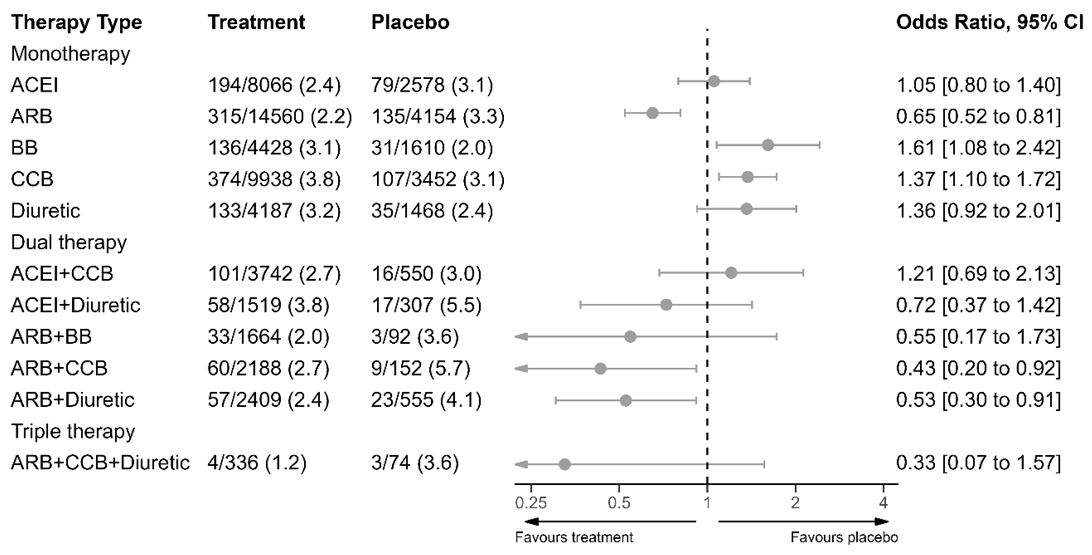
The tolerability analysis included 235 trials (68,412 participants, mean age 55 years, 39% women, baseline mean BP 154/99 mmHg). Compared to placebo, the odds of WDAEs with ACEIs, ARBs. BBs, CCBs, and thiazide diuretics, were 1.05 (0.80-1.40), 0.65 (0.52-0.81), 1.61 (1.08-2.42), 1.37 (1.10-1.72), 1.36 (0.92-2.01). There was a higher incidence of WDAEs with higher doses of CCBs. For dual combinations compared to placebo, all ARB-containing regimens had fewer WDAEs than placebo, which was significant for ARB-CCB and ARB+diuretics (Figure 2). The overall results for WDAEs reflected the net results of a decrease in headache for almost all regimens except CCBs, an increase in dizziness for all regimens, class-specific effects (eg. cough with ACEIs), and counterbalancing effects, such as ARBs reducing CCB-related peripheral edema.
Conclusions
Tolerability varies substantially across regimens, with no consistent evidence that combination therapy is less tolerable than monotherapy, whereas combination therapy is more efficacious. ARB monotherapy and ARB-containing combinations had fewer WDAEs than placebo.
To compare the efficacy and tolerability of antihypertensive drugs and their combinations.
Methods
We conducted meta-analyses of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers (BBs), calcium channel blockers (CCBs) and diuretics, with treatment duration 4 to 26 weeks. The primary outcomes were the placebo-corrected reduction in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and withdrawal of treatment due to adverse events (WDAEs), estimated using fixed-effects meta-analysis. Doses of drugs were standardized, and drug regimens were categorized as low, moderate and high efficacy for SBP reduction of <10, 10-19 and ≥20 mmHg from a baseline SBP 154 mmHg.
Results
The efficacy analysis included 484 trials (104,176 participants, mean age 54 years, 45% women, baseline mean BP 154/100 mmHg). Standard-dose monotherapy reduced BP by 8.7/5.6 mmHg, and dose doubling reduced BP by 1.5/1.0 mmHg (Figure 1). Standard dose dual combinations reduced BP by 14.9/9.1 mmHg, and dose doubling reduced BP by 2.5/1.4 mmHg. BP reduction with monotherapies decreased by 1.3/0.9 mmHg for every 10 mmHg lower baseline BP, with variation across drug classes. Of 57 standard-dose monotherapies, 79% were low efficacy; of 189 dual combinations, 58% were moderate and 11% were high efficacy.
The tolerability analysis included 235 trials (68,412 participants, mean age 55 years, 39% women, baseline mean BP 154/99 mmHg). Compared to placebo, the odds of WDAEs with ACEIs, ARBs. BBs, CCBs, and thiazide diuretics, were 1.05 (0.80-1.40), 0.65 (0.52-0.81), 1.61 (1.08-2.42), 1.37 (1.10-1.72), 1.36 (0.92-2.01). There was a higher incidence of WDAEs with higher doses of CCBs. For dual combinations compared to placebo, all ARB-containing regimens had fewer WDAEs than placebo, which was significant for ARB-CCB and ARB+diuretics (Figure 2). The overall results for WDAEs reflected the net results of a decrease in headache for almost all regimens except CCBs, an increase in dizziness for all regimens, class-specific effects (eg. cough with ACEIs), and counterbalancing effects, such as ARBs reducing CCB-related peripheral edema.
Conclusions
Tolerability varies substantially across regimens, with no consistent evidence that combination therapy is less tolerable than monotherapy, whereas combination therapy is more efficacious. ARB monotherapy and ARB-containing combinations had fewer WDAEs than placebo.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertension
Schlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael
Comparative effects of Single-Pill Combinations on Arterial Stiffness and Central Blood Pressure: A Randomized Trial in Indian Adults with HypertensionPatil Satish, Nabeel P M, Joseph Jayaraj, Mukherjee Somnath, Salwa Hyndavi, Christa Edmin, Lobo Ameeka, Kiru Gaia, Singh Kavita, Prabhakaran Dorairaj, Poulter Neil, Sayed Sumaiya, Katti Pooja, Hiremath Shankarayya, Aithal Kiran, Kaulgud Ram, Chandrasekaran Ambalam, Roy Ambuj, Khode Vitthal