Final ID: Mo4067
Using a proteomics-based test to assess cardiovascular risk in individuals with clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) is an age-related phenomenon associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk, independent of traditional risk factors, which can make risk stratification a challenge. The residual cardiovascular risk (RCVR) test is a recently developed 27-protein model that has been shown to predict 4-year risk of a CV event (myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attack, heart failure hospitalization, death) in independent replication cohorts of at-risk populations.
Objectives: The goal of this analysis was to evaluate whether the RCVR test could detect significant differences in CV risk between CHIP+ and CHIP- sub-populations using data from the CANTOS trial (NCT01327846), a study that enrolled subjects with a history of cardiovascular disease that were evaluated for their CHIP status.
Methods: RCVR test scores were generated from SomaScan v4.1 assay data on EDTA plasma samples from the CANTOS trial. Baseline analysis compared mean RCVR test scores in CHIP+ (n=174) and CHIP- (n=1794) subjects who were either randomized into the placebo or canakinumab treated arms. A linear model of RCVR distributed by CHIP status, with fixed effects of treatment arm, age, and sex was evaluated in a Type III ANOVA to determine covariate adjusted between group differences in RCVR test scores.
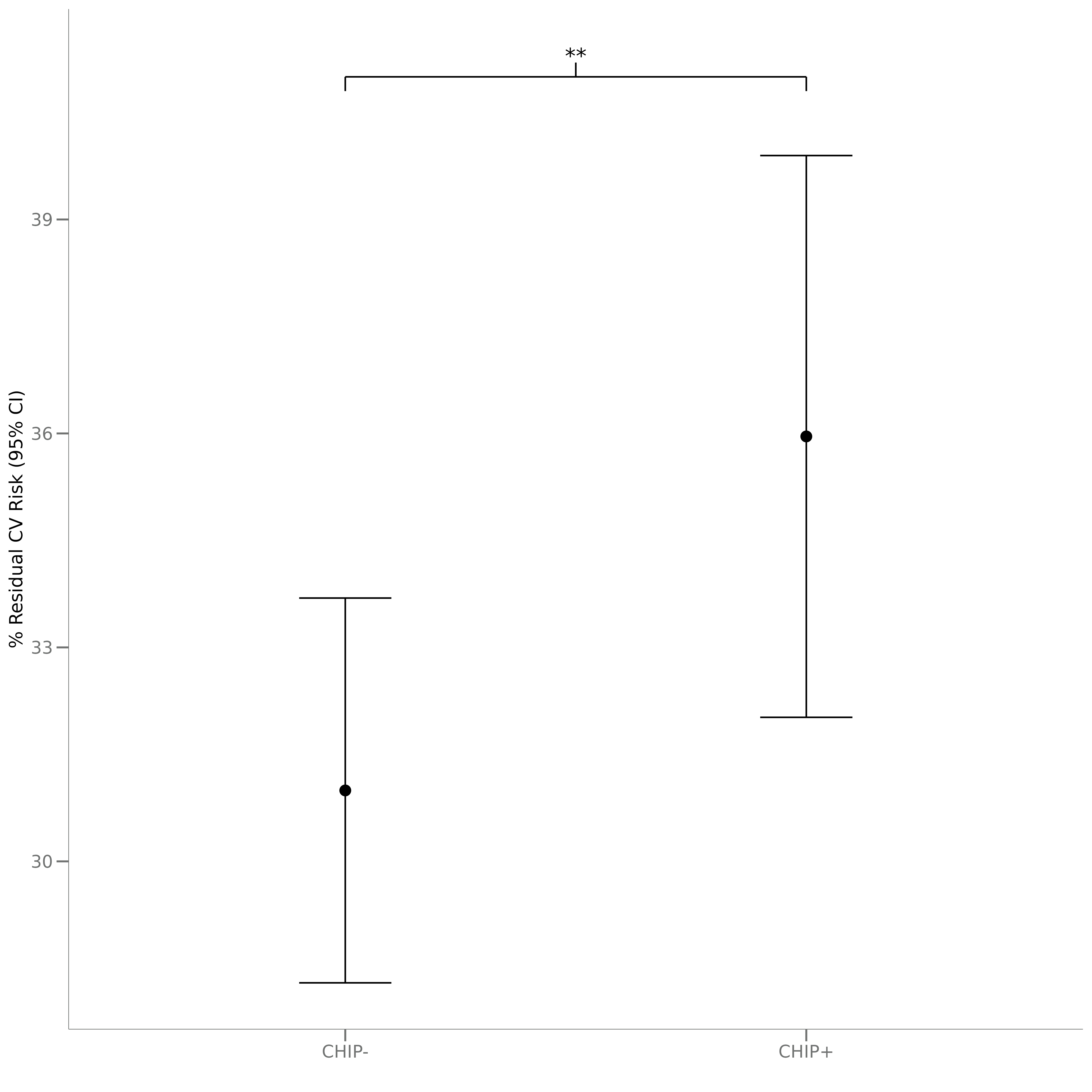
Results: The mean predicted RCVR test score was 4.96% greater at baseline for CHIP+ subjects compared to CHIP- subjects after adjusting for covariates (p=2.07e-3).
Conclusions: The RCVR test predicted that the absolute risk of a cardiovascular event within four years is significantly greater for CHIP+ individuals. These results suggest RCVR may be able to capture the increased CV risk conferred by novel risk factors like CHIP status and highlight the potential utility of multi-protein-based prognostic test as a tool for CV risk assessment. Further analysis of longitudinal time points from the placebo arm of the trial are planned to assess whether cardiovascular risk increases at a different rate in CHIP+ and CHIP- individuals over time.
Objectives: The goal of this analysis was to evaluate whether the RCVR test could detect significant differences in CV risk between CHIP+ and CHIP- sub-populations using data from the CANTOS trial (NCT01327846), a study that enrolled subjects with a history of cardiovascular disease that were evaluated for their CHIP status.
Methods: RCVR test scores were generated from SomaScan v4.1 assay data on EDTA plasma samples from the CANTOS trial. Baseline analysis compared mean RCVR test scores in CHIP+ (n=174) and CHIP- (n=1794) subjects who were either randomized into the placebo or canakinumab treated arms. A linear model of RCVR distributed by CHIP status, with fixed effects of treatment arm, age, and sex was evaluated in a Type III ANOVA to determine covariate adjusted between group differences in RCVR test scores.
Results: The mean predicted RCVR test score was 4.96% greater at baseline for CHIP+ subjects compared to CHIP- subjects after adjusting for covariates (p=2.07e-3).
Conclusions: The RCVR test predicted that the absolute risk of a cardiovascular event within four years is significantly greater for CHIP+ individuals. These results suggest RCVR may be able to capture the increased CV risk conferred by novel risk factors like CHIP status and highlight the potential utility of multi-protein-based prognostic test as a tool for CV risk assessment. Further analysis of longitudinal time points from the placebo arm of the trial are planned to assess whether cardiovascular risk increases at a different rate in CHIP+ and CHIP- individuals over time.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Contemporary Machine Learning-Based Risk Stratification for Mortality and Hospitalization in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Multimodal Real-World Data
Fudim Marat, Weerts Jerremy, Patel Manesh, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Torres Francisco, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Rigolli Marzia, Kessler Paul, Touzot Maxime, Lund Lars, Van Empel Vanessa, Pradhan Aruna, Butler Javed, Zehnder Tobias, Sauty Benoit, Esposito Christian, Balazard Félix, Mayer Imke, Hallal Mohammad, Loiseau Nicolas
A Potential Role for NKG2D, an NK cell receptor, in Accelerated CVD risk in African American Women Living in More Adverse Neighborhood Conditions: Data From the Step It Up Physical Activity Digital Health-Enabled, Community-Engaged InterventionBaez Andrew, Andrews Marcus, Sandler Dana, Aquino Peterson Elizabeth, Sharda Sonal, Tolentino Katherine Joy, Lopez De Leon Shirley, Seo Jein Eleanor, Cintron Manuel, Pita Mario, Tarfa Hannatu, Baumer Yvonne, Reger Robert, Childs Richard, Powell-wiley Tiffany, Dave Ayushi, Saurabh Abhinav, Mendelsohnl Laurel, Chen Long, Igboko Muna, Wells Ayanna, Marah Marie