Final ID: MP765
Improved Spatial Stability with a Flexible Tip Ablation Catheter in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Optimal catheter-tissue contact during radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with improved ablation success. In preclinical models, catheter-tissue contact stability is improved with a flexible tip ablation catheter (FTAC, TactiFlex, Abbott, Inc.) compared to a conventional tip ablation catheter (CTAC, TactiCath, Abbott, Inc.). The impact of the FTAC on catheter stability during AF ablation is unknown.
Objective: To investigate catheter stability and procedural lesion parameters of FTAC compared to those of CTAC.
Methods: Lesion characteristics and ablation outcomes of 16 consecutive patients undergoing first-time radiofrequency ablation for AF with FTAC were retrospectively compared to 16 consecutive patients undergoing ablation with CTAC between June 2022 and December 2023 in our center. Spatial position of the ablation catheter sampled at 100 Hz during radiofrequency application was extracted from the mapping system (Ensite X, Abbott, Inc.). Average catheter excursion for all ablation lesions during a single procedure was determined for each patient. The average values of lesion contact force and maximum temperature were also calculated for each patient.
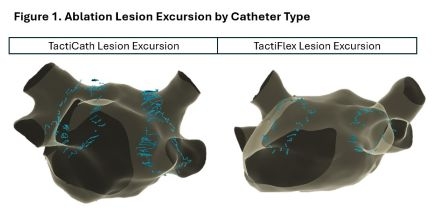
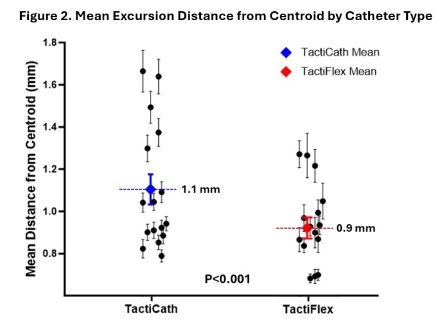
Results: A total of 2,109 FTAC and 3,556 CTAC ablation lesions were analyzed. Representative catheter movement during ablation for each catheter is shown in Figure 1. Mean excursion distance from lesion centroid was smaller for the FTAC lesions than CTAC lesions (0.9 vs 1.1 mm, p<0.001), representing an 18% decrease in mean excursion distance with FTAC (Figure 2). Mean excursion distance greater than 1 mm from lesion centroid occurred in 1,476/3,556 (41.5%) CTAC lesions compared to 574/2,109 (27.2%) FTAC lesions (p<0.001). For FTAC lesions compared to CTAC lesions, mean contact force was greater (14.8 vs 12.7 g, p<0.001) and maximum temperature was lower (30.2 vs 34.2 °C, p<0.001). At one year follow-up, freedom from AF recurrence occurred in 13/16 (81.3%) cases in the FTAC group and 13/16 (81.3%) cases in the CTAC group.
Conclusions: Spatial stability and contact force parameters were significantly more favorable with FTAC compared to those of CTAC during AF ablation. Benefits of FTAC observed during RF ablation may be applicable to future utilization of FTAC for pulsed field ablation. Future studies are required to determine the relationship between catheter spatial stability and freedom from atrial arrythmia recurrence.
Objective: To investigate catheter stability and procedural lesion parameters of FTAC compared to those of CTAC.
Methods: Lesion characteristics and ablation outcomes of 16 consecutive patients undergoing first-time radiofrequency ablation for AF with FTAC were retrospectively compared to 16 consecutive patients undergoing ablation with CTAC between June 2022 and December 2023 in our center. Spatial position of the ablation catheter sampled at 100 Hz during radiofrequency application was extracted from the mapping system (Ensite X, Abbott, Inc.). Average catheter excursion for all ablation lesions during a single procedure was determined for each patient. The average values of lesion contact force and maximum temperature were also calculated for each patient.
Results: A total of 2,109 FTAC and 3,556 CTAC ablation lesions were analyzed. Representative catheter movement during ablation for each catheter is shown in Figure 1. Mean excursion distance from lesion centroid was smaller for the FTAC lesions than CTAC lesions (0.9 vs 1.1 mm, p<0.001), representing an 18% decrease in mean excursion distance with FTAC (Figure 2). Mean excursion distance greater than 1 mm from lesion centroid occurred in 1,476/3,556 (41.5%) CTAC lesions compared to 574/2,109 (27.2%) FTAC lesions (p<0.001). For FTAC lesions compared to CTAC lesions, mean contact force was greater (14.8 vs 12.7 g, p<0.001) and maximum temperature was lower (30.2 vs 34.2 °C, p<0.001). At one year follow-up, freedom from AF recurrence occurred in 13/16 (81.3%) cases in the FTAC group and 13/16 (81.3%) cases in the CTAC group.
Conclusions: Spatial stability and contact force parameters were significantly more favorable with FTAC compared to those of CTAC during AF ablation. Benefits of FTAC observed during RF ablation may be applicable to future utilization of FTAC for pulsed field ablation. Future studies are required to determine the relationship between catheter spatial stability and freedom from atrial arrythmia recurrence.
More abstracts on this topic:
Closing the Gap: Improved Survival with Early Catheter Ablation in Sustained VT – A Multicenter Real-World Study
Napon Geoffroy, Roy Shubha Deep, Jain Varun, Huebner Miranda, Wolfe Brandon, Gupta Tejasva, Aiyer Aishwarya, Rayapureddi Karthik
Air Pollution Induces Atrial Fibrosis via CARD9-Mediated Immune ResponseCui Yuqi, Ma Xiaochun, Patel Sheevang, Mraiyan Mohamed, Liu Zhenguo