Final ID: MP2116
Diagnostic Utility of Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) after an Abnormal or Non-diagnostic Stress Test
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is widely recognized as a valuable non-invasive tool for evaluating patients with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD). Patients with inconclusive or abnormal cardiac stress tests present a management challenge and can lead to unnecessary invasive procedures. This study aims to assess the diagnostic utility of CCTA in patients with abnormal or inconclusive stress tests and its impact on invasive coronary angiography (ICA) and revascularization rates.
Methods: This retrospective single center study included adults with no prior history of coronary artery disease who had an abnormal or inconclusive stress test result between January 2018 and December 2024. Among patients referred for CCTA after an abnormal or inconclusive stress test (CT arm), the diagnostic yield of CCTA for detecting coronary stenoses and the subsequent need for ICA and revascularization was evaluated and compared with patients who were not referred for a CCTA (non-CT arm).
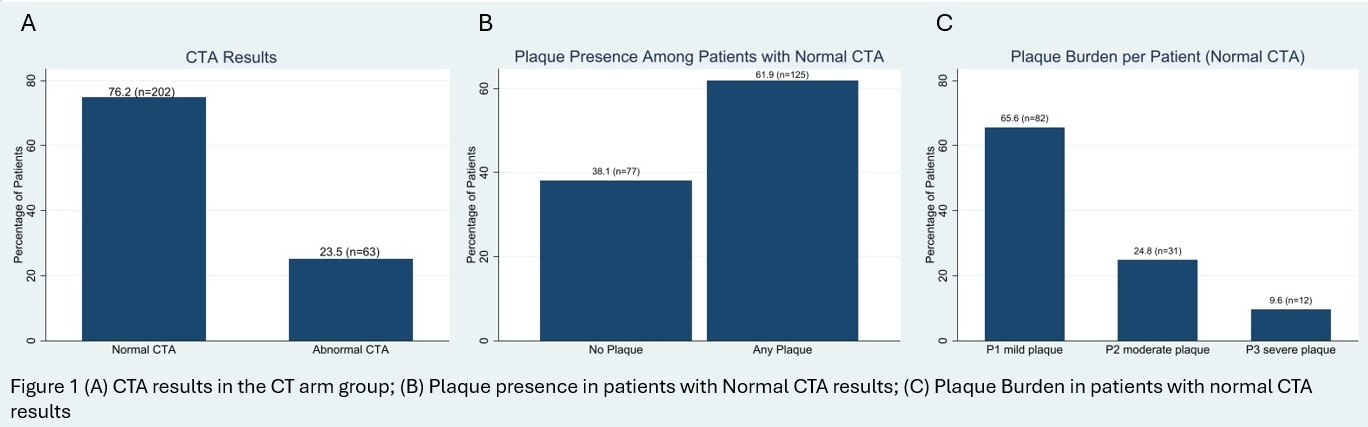
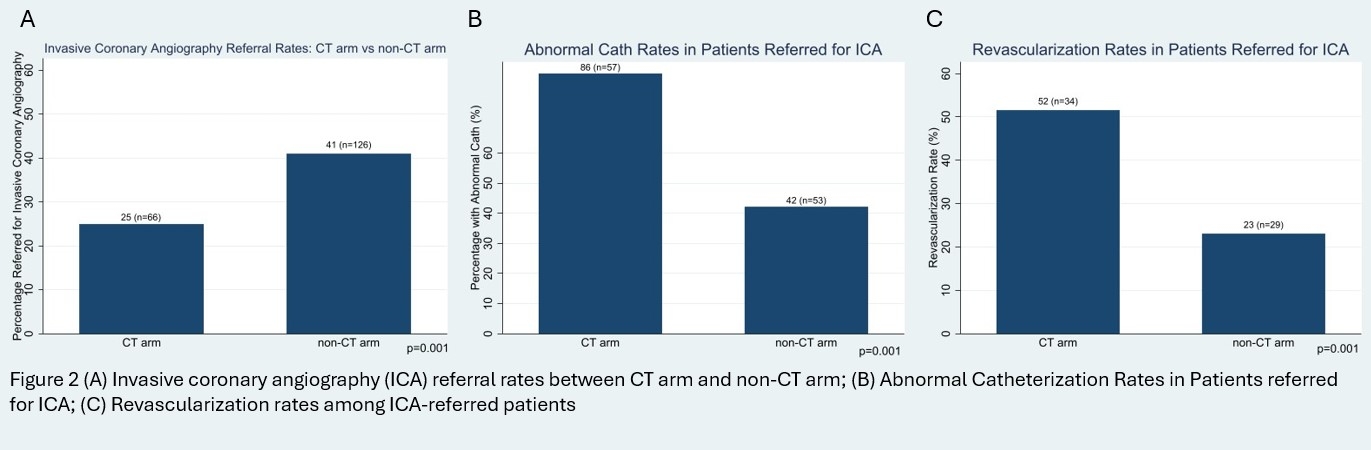
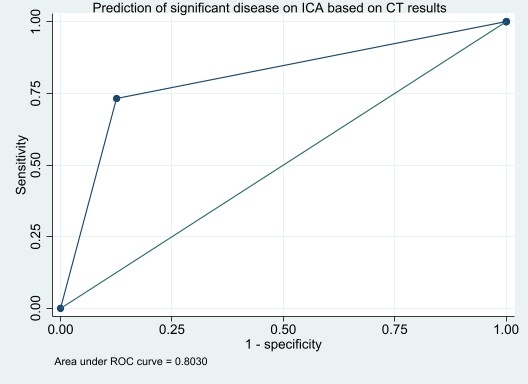
Results: A total of 573 patients (mean age:68±12.7) were included in the study. The majority of patients in both groups underwent SPECT or PET (74% (n=197) in CT arm and 88% (n= 272) in non-CT arm). Of the 265 patients in the CT arm, 76.2% (n=202) had a normal CTA result (Figure 1A). Among patients with normal CTA results, the presence of any plaque was detected in 61.9% (n=125) of patients (Figure 1B). ICA referral rates were significantly lower in the CT arm group compared to the non-CT arm group (25% (n=66) vs 41% (n=126), p=0.001) (Figure 2A). Among patients referred for ICA, 86% (n=57) in the CT arm group had abnormal coronary angiography results compared to 42% (n=53) in the non-CT arm group (p=0.001) (Figure 2B). Revascularization rates were significantly higher in the CT arm compared to the non-CT arm (52% (n=34) vs 23% (n=29), p=0.001) (Figure 2C). CCTA had excellent diagnostic performance in this patient population for detection of significant disease (>70% stenosis) on ICA with an AUC of 0.8 (Figure 3).
Conclusion: CCTA can serve as a gatekeeper to invasive coronary angiography reducing unnecessary procedures in patients with abnormal or inconclusive stress test results. CCTA continues to have excellent diagnostic performance for detection of significant disease on ICA in this patient population. Majority of patients referred for CCTA were found to have some degree of plaque, potentially prompting the initiation of preventive therapies.
Methods: This retrospective single center study included adults with no prior history of coronary artery disease who had an abnormal or inconclusive stress test result between January 2018 and December 2024. Among patients referred for CCTA after an abnormal or inconclusive stress test (CT arm), the diagnostic yield of CCTA for detecting coronary stenoses and the subsequent need for ICA and revascularization was evaluated and compared with patients who were not referred for a CCTA (non-CT arm).
Results: A total of 573 patients (mean age:68±12.7) were included in the study. The majority of patients in both groups underwent SPECT or PET (74% (n=197) in CT arm and 88% (n= 272) in non-CT arm). Of the 265 patients in the CT arm, 76.2% (n=202) had a normal CTA result (Figure 1A). Among patients with normal CTA results, the presence of any plaque was detected in 61.9% (n=125) of patients (Figure 1B). ICA referral rates were significantly lower in the CT arm group compared to the non-CT arm group (25% (n=66) vs 41% (n=126), p=0.001) (Figure 2A). Among patients referred for ICA, 86% (n=57) in the CT arm group had abnormal coronary angiography results compared to 42% (n=53) in the non-CT arm group (p=0.001) (Figure 2B). Revascularization rates were significantly higher in the CT arm compared to the non-CT arm (52% (n=34) vs 23% (n=29), p=0.001) (Figure 2C). CCTA had excellent diagnostic performance in this patient population for detection of significant disease (>70% stenosis) on ICA with an AUC of 0.8 (Figure 3).
Conclusion: CCTA can serve as a gatekeeper to invasive coronary angiography reducing unnecessary procedures in patients with abnormal or inconclusive stress test results. CCTA continues to have excellent diagnostic performance for detection of significant disease on ICA in this patient population. Majority of patients referred for CCTA were found to have some degree of plaque, potentially prompting the initiation of preventive therapies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Self-Resolving Pheochromocytoma-Induced Reverse Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Due to Tumor Hemorrhagic Conversion
Cedeno Serna Juan, Jayant Girish, Joseph Christy, Contreras Yametti Felipe, Lorenzatti Daniel, Mangeshkar Shaunak, Morales Nieves, Carruthers David, Sims Daniel
A Rare Case of Epicardial Cavernous Hemangioma with Coexisting Severe Mitral RegurgitationAbdallah Ala, Sutton Jenna, Houshmand Nazanin, Gupta Neelesh, Ahsan Chowdhury