Final ID: MP945
The Novel ErbB4 Agonist JK07 Modulates Gene Expression in Key Cardiac Cells. Insights from Single-Nuclei Transcriptomics in a Murine Heart Failure Model
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Heart failure (HF) involves complex interactions among cardiac cell types that drive disease progression. The neuregulin (NRG-1)/ErbB pathway is critical for cardiac repair, but clinical use of NRG-1 is limited by poor stability and receptor specificity. JK07, a fusion of an anti-ErbB3 antibody and the EGF-like domain, selectively activates ErbB4 while blocking ErbB3 activation to reduce side effects. While JK07 has demonstrated early promise in the treatment of HF clinically, its cellular mechanisms underpinning these effects remain unclear. This study explores how JK07 impact on gene expression across key cardiac cell populations.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that JK07 modulates gene expression in key cardiac cell types, inducing distinct molecular responses depending on treatment duration.
Methods: BALB/c mice with MI-induced HF (EF<40%) received either a single or four weekly doses of JK07 (1 mg/kg) or vehicle. Hearts were collected 1 and 7 days after treatment for the single-dose experiments, or 7 and 28 days after the last dose for the four-dose experiments. Assessments included echocardiography, heart weight, histology, and single-nuclei RNA sequencing.
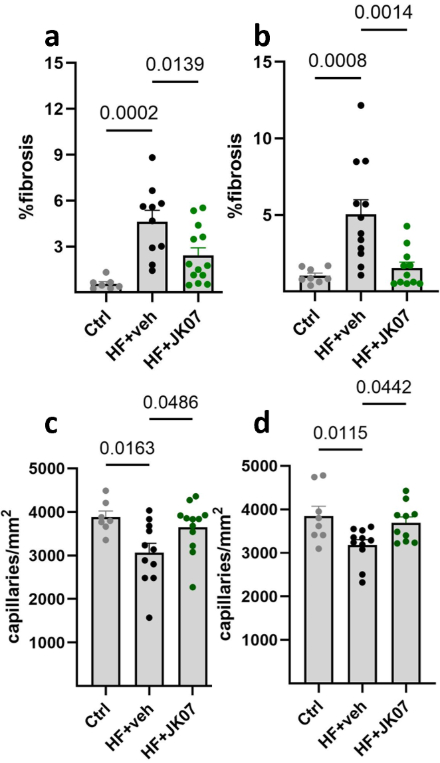
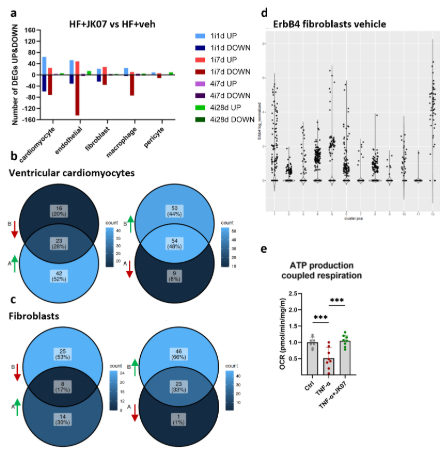
Results: JK07 promoted cardiac recovery by reducing interstitial fibrosis and increasing capillary density in multi-dose groups. NT-proBNP levels decreased 7 days post-treatment in both protocols. Single-nuclei transcriptomics showed significant JK07-induced changes in cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, macrophages, and endothelial cells, most prominently 1 and 7 days after a single dose. In cardiomyocytes, JK07 partially reversed HF-associated gene expression and enhanced mitochondrial and metabolic pathways, with confirmation in vitro via Seahorse mito stress test. In fibroblasts, JK07 altered key HF-related genes, including upregulation of Htra3 and downregulation of Igfbp7, implicating the Htra3–TGFβ–Igfbp7 axis in antifibrotic effects. Further subclustering revealed an ErbB4-high fibroblast subtype with high expression of WNT pathway genes and potential roles in cell interactions. In endothelial cells, JK07 activated angiogenic, cytoskeletal, and repair pathways.
Conclusion: JK07 promotes cardiac repair by driving cell-type-specific transcriptional programs that support metabolic adaptation in cardiomyocytes, modulate ErbB4-high fibroblast functions, and enhance endothelial regeneration. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of JK07 as a disease-modifying agent in HF.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that JK07 modulates gene expression in key cardiac cell types, inducing distinct molecular responses depending on treatment duration.
Methods: BALB/c mice with MI-induced HF (EF<40%) received either a single or four weekly doses of JK07 (1 mg/kg) or vehicle. Hearts were collected 1 and 7 days after treatment for the single-dose experiments, or 7 and 28 days after the last dose for the four-dose experiments. Assessments included echocardiography, heart weight, histology, and single-nuclei RNA sequencing.
Results: JK07 promoted cardiac recovery by reducing interstitial fibrosis and increasing capillary density in multi-dose groups. NT-proBNP levels decreased 7 days post-treatment in both protocols. Single-nuclei transcriptomics showed significant JK07-induced changes in cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, macrophages, and endothelial cells, most prominently 1 and 7 days after a single dose. In cardiomyocytes, JK07 partially reversed HF-associated gene expression and enhanced mitochondrial and metabolic pathways, with confirmation in vitro via Seahorse mito stress test. In fibroblasts, JK07 altered key HF-related genes, including upregulation of Htra3 and downregulation of Igfbp7, implicating the Htra3–TGFβ–Igfbp7 axis in antifibrotic effects. Further subclustering revealed an ErbB4-high fibroblast subtype with high expression of WNT pathway genes and potential roles in cell interactions. In endothelial cells, JK07 activated angiogenic, cytoskeletal, and repair pathways.
Conclusion: JK07 promotes cardiac repair by driving cell-type-specific transcriptional programs that support metabolic adaptation in cardiomyocytes, modulate ErbB4-high fibroblast functions, and enhance endothelial regeneration. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of JK07 as a disease-modifying agent in HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Antagonistic and Cooperative Dynamics of Irx3 and Irx4 in Ventricular Compaction
Abid Rimshah, Puviindran Vijitha, Van Eede Matthijs, Henkelman Mark, Miquerol Lucile, Bruneau Benoit, Hui Chi-chung, Kim Kyoung-han, Oh Yena, Liu Wei Fan, Bakr Marwan, Yin Wen Chi, Zhou Yu-qing, Zhang Xiaoyun, Kim Riyoun, Mo Rong
4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal Alters Alternative Polyadenylation to Regulate mRNA Isoform Diversity in the Transition from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts to MyofibroblastsNatarajan Kartiga, Neupane Rahul, Yalamanchili Hari Krishna, Palaniyandi Suresh, Wagner Eric, Guha Ashrith, Amirthalingam Thandavarayan Rajarajan