Final ID: MP1526
High-Fidelity, Low-Cost Extraction of Valvular Disease Parameters from Echocardiography Reports Using Rule-Based NLP
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background:
Extraction of data from transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) reports is critical for cardiovascular research, particularly in valvular heart disease. While machine learning (ML) and large language models (LLMs) offer automated solutions, they remain computationally intensive, opaque and cost-prohibitive for many health systems. The AHA highlights the need for scalable and interpretable informatics tools to bridge these gaps.
Objective:
Building on our prior work demonstrating high-accuracy extraction from TTE reports, we developed and validated an enhanced rule-based natural language processing (NLP) pipeline that emphasizes the extraction of valvular heart disease variables including aortic valve (AV) stenosis from structured and free-text sections.
Methods:
We analyzed 1,405 adult TTE reports (1000 for all parameters with an additional 405 for AV parameters) between 09/2020–03/2023 from a tertiary academic center. Using iteratively refined regular expressions in R, we extracted and structured 20 variables across demographic, functional and structural domains, with a focus on AV parameters, including degree of stenosis, AV area, gradients and velocities. Improving on our prior model, this pipeline parses unstructured narrative text to extract manually typed variables relevant to valvular disease. Performance was validated via comparison to manually extracted data. The pipeline was further evaluated on 7,800 reports for computational performance on a single-core central processing unit (CPU).
Results:
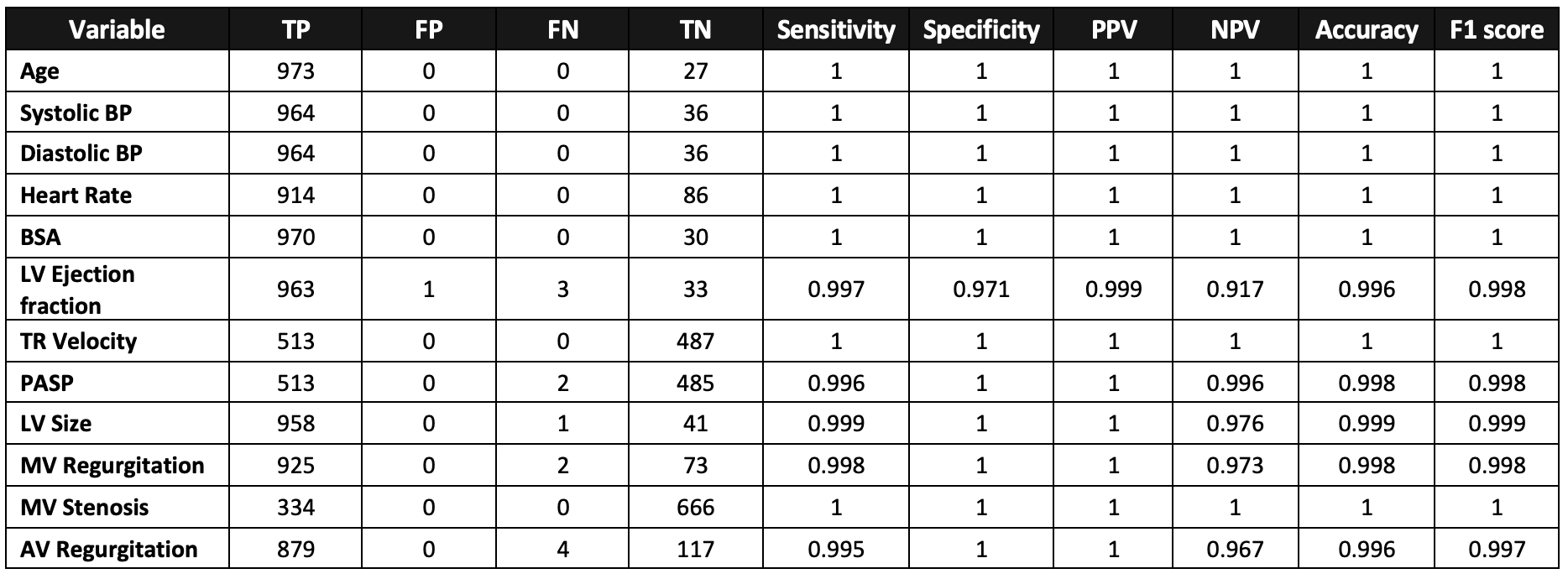
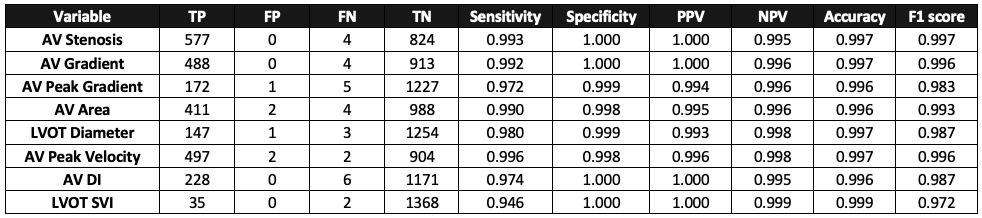
Overall mean extraction accuracy was 99.8% and 16 of 20 variables demonstrated 100% precision (PPV). AV area (PPV 99.5%, false positives [FP] 2) and AV peak velocity (PPV 99.6%, FP 2) showed slightly lower precision, whereas AV peak gradient (sensitivity [SN] 97.2%, false negatives [FN] 5) and AV dimensionless index (SN 97.4%, FN 6) showed lower sensitivity primarily due to formatting inconsistencies in free-text sections rather than extraction failure. An overall run-time of 14.5 mins for 7,800 reports, average inference time of 111.5 ms/report, throughput of 9 reports/second and max RAM usage of 47 MB per 1,000 reports.
Conclusion:
This rule-based NLP pipeline achieves near-perfect accuracy in extracting structured and free text variables from TTE reports, without the energy consumption, cost, or opacity of ML. This pipeline is scalable, interpretable and energy-efficient, making it an effective solution for real-world clinical data environments.
Background:
Extraction of data from transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) reports is critical for cardiovascular research, particularly in valvular heart disease. While machine learning (ML) and large language models (LLMs) offer automated solutions, they remain computationally intensive, opaque and cost-prohibitive for many health systems. The AHA highlights the need for scalable and interpretable informatics tools to bridge these gaps.
Objective:
Building on our prior work demonstrating high-accuracy extraction from TTE reports, we developed and validated an enhanced rule-based natural language processing (NLP) pipeline that emphasizes the extraction of valvular heart disease variables including aortic valve (AV) stenosis from structured and free-text sections.
Methods:
We analyzed 1,405 adult TTE reports (1000 for all parameters with an additional 405 for AV parameters) between 09/2020–03/2023 from a tertiary academic center. Using iteratively refined regular expressions in R, we extracted and structured 20 variables across demographic, functional and structural domains, with a focus on AV parameters, including degree of stenosis, AV area, gradients and velocities. Improving on our prior model, this pipeline parses unstructured narrative text to extract manually typed variables relevant to valvular disease. Performance was validated via comparison to manually extracted data. The pipeline was further evaluated on 7,800 reports for computational performance on a single-core central processing unit (CPU).
Results:
Overall mean extraction accuracy was 99.8% and 16 of 20 variables demonstrated 100% precision (PPV). AV area (PPV 99.5%, false positives [FP] 2) and AV peak velocity (PPV 99.6%, FP 2) showed slightly lower precision, whereas AV peak gradient (sensitivity [SN] 97.2%, false negatives [FN] 5) and AV dimensionless index (SN 97.4%, FN 6) showed lower sensitivity primarily due to formatting inconsistencies in free-text sections rather than extraction failure. An overall run-time of 14.5 mins for 7,800 reports, average inference time of 111.5 ms/report, throughput of 9 reports/second and max RAM usage of 47 MB per 1,000 reports.
Conclusion:
This rule-based NLP pipeline achieves near-perfect accuracy in extracting structured and free text variables from TTE reports, without the energy consumption, cost, or opacity of ML. This pipeline is scalable, interpretable and energy-efficient, making it an effective solution for real-world clinical data environments.
More abstracts on this topic:
6-Nitrodopamine potentiates the positive chronotopic and inotropic effect induced by noradrenaline in the rat isolated heart
Lima Antonio, Sobanski Joao Fernando, Antunes Edson, De Nucci Gilberto
A Rare Case of Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Cardiac MassMallipeddi Tarun, Rantanen Petra, Debakey Michael, Cheng Lily, Waheed Nida