Final ID: 4366136
Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Suppressed Mitochondrial Fuel Metabolism in HFpEF Myocardium
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a growing clinical challenge frequently associated with obesity and diabetes. While systemic metabolic abnormalities are known, myocardial-specific impairments in substrate metabolism remain poorly characterized.
Hypothesis: HFpEF myocardium exhibits coordinated suppression of mitochondrial fuel oxidation—including fatty acids (FA), ketones, branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), and anaplerotic pathways.
Methods: We analyzed myocardial tissue from HFpEF patients and non-failing (NF) controls using bulk RNA-seq (41 HFpEF, 24 NF), targeted metabolomics (38 HFpEF, 20 NF), and Western blotting for key metabolic enzymes.
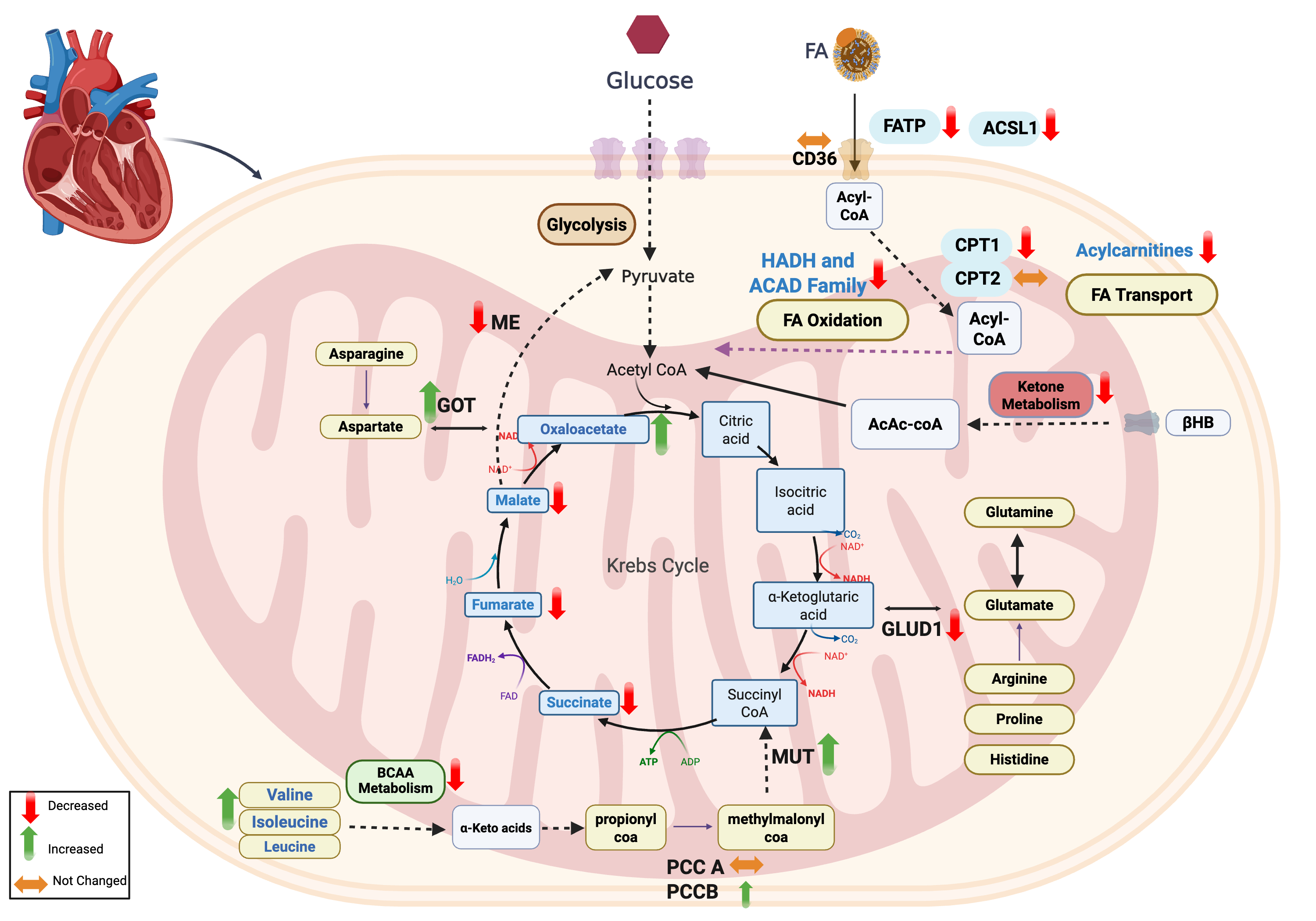
Results: Metabolomics revealed reduced medium- and long-chain acylcarnitines in HFpEF, suggesting impaired FA oxidation. Bulk RNA-seq showed downregulation of FA transport genes (CD36, FATP4, ACSL family, CPT1A). Protein analysis confirmed decreased FA transporters: CPT1A (P=0.0002), CPT1B (P=0.005), ACSL1 (P=0.002), FATPs, and β-oxidation enzymes (ACADs, HADHs), with unchanged CPT2—indicating defects in both FA transport and oxidation. While myocardial and plasma β-hydroxybutyrate (3-HBA) were unchanged, downstream C4-OH β-hydroxybutyryl was significantly reduced. Ketone oxidation enzymes BDH1 and ACAT1 were lower (P=1.2e-6, P=1e-6), despite preserved or elevated transcripts. SLC16A1 was unchanged at both mRNA and protein levels, suggesting intact ketone uptake but impaired oxidation. In BCAA metabolism, myocardial leucine, valine, and isoleucine were elevated in HFpEF, while downstream catabolites were lower. BCAT2 protein was significantly reduced (P=5.6e-7), while total and phosphorylated BCKDH and BCKDK were unchanged, suggesting a bottleneck in BCAA-to-keto-acid conversion. Despite BCAA accumulation, phosphorylation of mTOR effectors (p70S6K, AKT) was unchanged. In the TCA cycle, fumarate, malate, and succinate were reduced, while oxaloacetate was elevated; TCA enzyme transcripts were unchanged, suggesting impaired anaplerosis. GLUD1, ME1, and GOT1 proteins were decreased (P=0.003, P=4.7e-7, P=0.0002), while PCCB and MMUT proteins were increased (P=4.5e-5, P=0.02), suggesting enhanced compensatory propionyl-CoA–derived succinyl-CoA input.
Conclusions: HFpEF myocardium shows coordinated suppression of mitochondrial substrate use at gene, protein, and metabolite levels. Targeting these bottlenecks may offer therapeutic opportunities.
Hypothesis: HFpEF myocardium exhibits coordinated suppression of mitochondrial fuel oxidation—including fatty acids (FA), ketones, branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), and anaplerotic pathways.
Methods: We analyzed myocardial tissue from HFpEF patients and non-failing (NF) controls using bulk RNA-seq (41 HFpEF, 24 NF), targeted metabolomics (38 HFpEF, 20 NF), and Western blotting for key metabolic enzymes.
Results: Metabolomics revealed reduced medium- and long-chain acylcarnitines in HFpEF, suggesting impaired FA oxidation. Bulk RNA-seq showed downregulation of FA transport genes (CD36, FATP4, ACSL family, CPT1A). Protein analysis confirmed decreased FA transporters: CPT1A (P=0.0002), CPT1B (P=0.005), ACSL1 (P=0.002), FATPs, and β-oxidation enzymes (ACADs, HADHs), with unchanged CPT2—indicating defects in both FA transport and oxidation. While myocardial and plasma β-hydroxybutyrate (3-HBA) were unchanged, downstream C4-OH β-hydroxybutyryl was significantly reduced. Ketone oxidation enzymes BDH1 and ACAT1 were lower (P=1.2e-6, P=1e-6), despite preserved or elevated transcripts. SLC16A1 was unchanged at both mRNA and protein levels, suggesting intact ketone uptake but impaired oxidation. In BCAA metabolism, myocardial leucine, valine, and isoleucine were elevated in HFpEF, while downstream catabolites were lower. BCAT2 protein was significantly reduced (P=5.6e-7), while total and phosphorylated BCKDH and BCKDK were unchanged, suggesting a bottleneck in BCAA-to-keto-acid conversion. Despite BCAA accumulation, phosphorylation of mTOR effectors (p70S6K, AKT) was unchanged. In the TCA cycle, fumarate, malate, and succinate were reduced, while oxaloacetate was elevated; TCA enzyme transcripts were unchanged, suggesting impaired anaplerosis. GLUD1, ME1, and GOT1 proteins were decreased (P=0.003, P=4.7e-7, P=0.0002), while PCCB and MMUT proteins were increased (P=4.5e-5, P=0.02), suggesting enhanced compensatory propionyl-CoA–derived succinyl-CoA input.
Conclusions: HFpEF myocardium shows coordinated suppression of mitochondrial substrate use at gene, protein, and metabolite levels. Targeting these bottlenecks may offer therapeutic opportunities.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.
Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong
Acetylation of Electron Transfer Flavoprotein Alpha Is a Possible Regulatory Mechanism of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Diabetic HeartsTatekoshi Yuki, Yano Masaki, Hosoda Ryusuke, Saga Yukika, Kuno Atsushi