Final ID: Sa3054
Colchicine Reduces Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Increased High-sensitivity C-reactive protein
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Atherosclerosis is increasingly recognized as a chronic inflammatory process. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) is a well-established predictor of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). Colchicine has shown cardiovascular benefit in chronic CAD and post myocardial infarction. However, baseline hs-CRP was not used to guide colchicine therapy in prior trials, and its utility as a predictive biomarker remains unclear. We hypothesize that colchicine’s cardioprotective effect varies by baseline hs-CRP levels in patients with inflammatory gout.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study of patients with inflammatory gout treated at Kaiser Permanente Southern California from January 2010 to June 2024. Colchicine users were propensity score-matched 1:2 to non-users based on demographics, comorbidities, and medication use. The primary outcome was MACCE, defined as a composite of acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, stroke, percutaneous coronary intervention, arrhythmia, and all-cause mortality. Conditional logistic regression was used to estimate adjusted odds ratios. Effect modification by baseline hs-CRP was assessed using stratified analysis across predefined hs-CRP categories.
Results
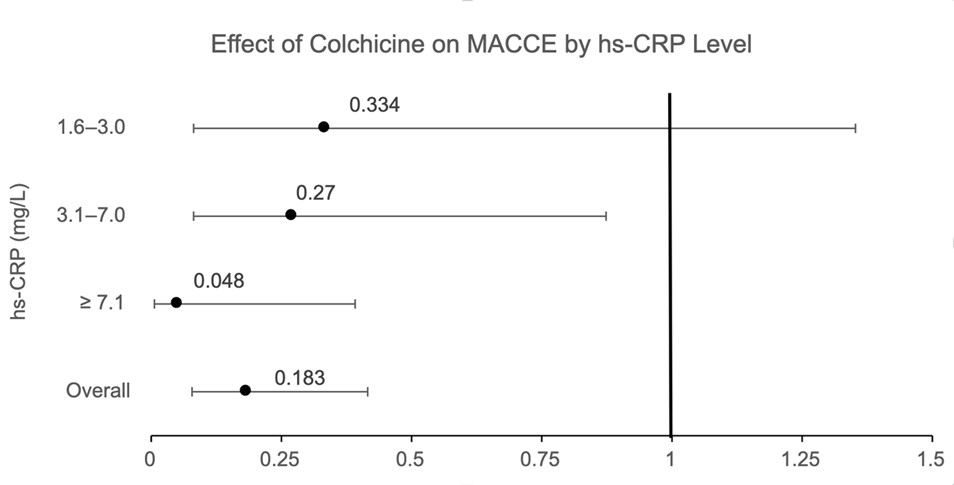
Among 2,367 matched patients (867 colchicine users, 1,500 non-users), MACCE occurred in 0.92% of users versus 4.33% of non-users. Colchicine use was associated with significantly lower MACCE risk (adjusted OR 0.183, 95% CI 0.080–0.417, p<0.0001). The strongest effect was observed in patients with hs-CRP ≥7.1 mg/L (OR 0.048, 95% CI 0.006–0.392, p=0.005). Protective effects persisted in the 3.1–7.0 mg/L group (OR 0.270, 95% CI 0.083–0.876, p=0.029), but were not significant in the 1.6–3.0 mg/L group.
Conclusion
Colchicine use significantly reduced MACCE in patients with inflammatory gout, with the greatest benefit seen in those with elevated hs-CRP. These findings highlight hs-CRP as a potential biomarker to guide anti-inflammatory therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Background
Atherosclerosis is increasingly recognized as a chronic inflammatory process. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) is a well-established predictor of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). Colchicine has shown cardiovascular benefit in chronic CAD and post myocardial infarction. However, baseline hs-CRP was not used to guide colchicine therapy in prior trials, and its utility as a predictive biomarker remains unclear. We hypothesize that colchicine’s cardioprotective effect varies by baseline hs-CRP levels in patients with inflammatory gout.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study of patients with inflammatory gout treated at Kaiser Permanente Southern California from January 2010 to June 2024. Colchicine users were propensity score-matched 1:2 to non-users based on demographics, comorbidities, and medication use. The primary outcome was MACCE, defined as a composite of acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, stroke, percutaneous coronary intervention, arrhythmia, and all-cause mortality. Conditional logistic regression was used to estimate adjusted odds ratios. Effect modification by baseline hs-CRP was assessed using stratified analysis across predefined hs-CRP categories.
Results
Among 2,367 matched patients (867 colchicine users, 1,500 non-users), MACCE occurred in 0.92% of users versus 4.33% of non-users. Colchicine use was associated with significantly lower MACCE risk (adjusted OR 0.183, 95% CI 0.080–0.417, p<0.0001). The strongest effect was observed in patients with hs-CRP ≥7.1 mg/L (OR 0.048, 95% CI 0.006–0.392, p=0.005). Protective effects persisted in the 3.1–7.0 mg/L group (OR 0.270, 95% CI 0.083–0.876, p=0.029), but were not significant in the 1.6–3.0 mg/L group.
Conclusion
Colchicine use significantly reduced MACCE in patients with inflammatory gout, with the greatest benefit seen in those with elevated hs-CRP. These findings highlight hs-CRP as a potential biomarker to guide anti-inflammatory therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction.
More abstracts on this topic:
84 Immune checkpoint profiling in major aortic diseases leads to identification of potential roles of CD155-CD206 pathway in suppressing inflammation and immune responses
Shao Ying, Saaoud Fatma, Xu Keman, Lu Yifan, Jiang Xiaohua, Wang Hong, Yang Xiaofeng
A Site-by-Site Comparison of CT Attenuation, Effective Atomic Numbers, and Electron Densities of Focal Pericoronary Adipose Tissue and Its Relationship to Adjacent Coronary Plaques on Contrast Enhanced Spectral CTKaneko Aya, Sakaguchi Yamato, Funabashi Nobusada