Final ID: MP2184
Performance of the PREVENT ASCVD Risk Calculator Across Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and other Pacific Islander Individuals: The PANACHE Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Accurately predicting 10-year ASCVD risk is key to guide primary prevention, yet little is known about how the AHA PREVENT ASCVD equation performs in disaggregated Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and Pacific Islander (AANHPI) adults.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized the performance of the PREVENT ASCVD equations varies across contemporary AANHPI groups.
Goal: To evaluate discrimination and calibration of the PREVENT ASCVD equations in 8 major AANHPI groups (Chinese, Filipino, Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander [NH/PI], Japanese, Korean, South Asian, Vietnamese, other Southeast Asian) and Non-Hispanic Whites (NHW).
Methods: We identified all members aged 30-79 years of Kaiser Permanente (KP) Northern California and KP Hawaii integrated healthcare delivery systems from 2012-2022 who had no prior CVD and had complete data to estimate the PREVENT ASCVD risk using the base and full models. Incident ASCVD events (non-fatal and fatal MI and stroke) were identified through December 2023 using validated ICD-9/10 diagnosis codes in EHR and vital status data, and observed risk calculated using a cause-specific risk model that accounted for competing risk of non-ASCVD death. We examined model discrimination (C-index) and calibration (calibration plot and slope) by individual AANHPI group.
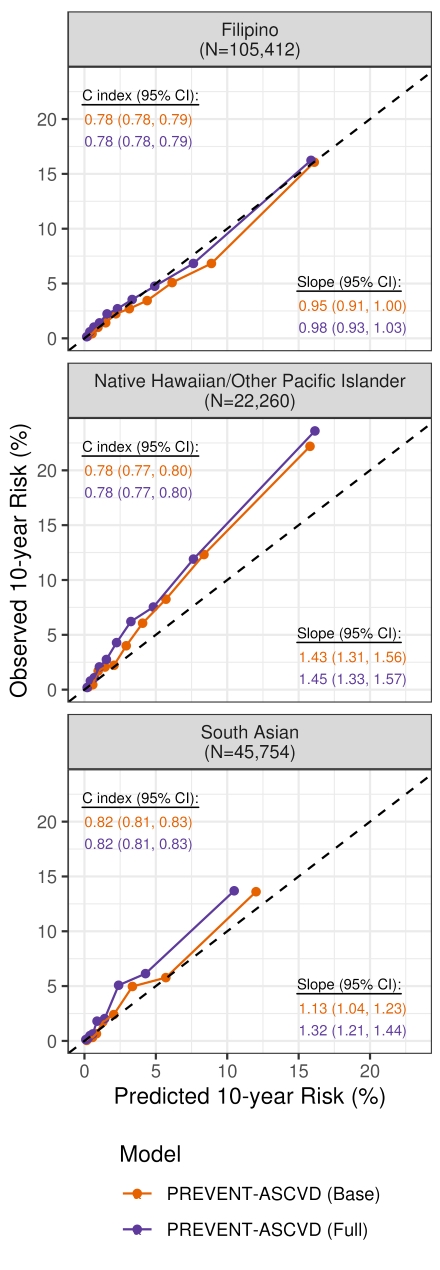
Results: We identified 1,219,255 eligible adults, with mean (SD) age ranging from 44.4 (13.2) years in South Asian to 61.0 (15.4) years in Japanese; 54.6% were women and there were higher proportions of women in Japanese, Korean, and NHW groups. Discrimination of the PREVENT base and full models was good overall and consistent across AANHPI individuals, with C statistics ranging from 0.77 (Japanese, Korean) to 0.82 (Chinese, South Asian) (Figure 1-3). However, calibration for the PREVENT base equation varied across AANHPI individuals, with underestimation of actual 10-year ASCVD risk in NH/PI, South Asian and other Southeast Asian adults, and overestimation in Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese adults. The PREVENT full equation lowered predicted ASCVD risk in all groups (Figure).
Conclusions: In a large, contemporary, primary prevention population of AANHPI and NHW adults in California and Hawaii, the PREVENT ASCVD equations had good discrimination but variable calibration across 8 major AANHPI individual groups. Given primary prevention decisions rely on predicted absolute risks, our findings support further optimizing ASCVD risk equations in targeted AANHPI groups.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized the performance of the PREVENT ASCVD equations varies across contemporary AANHPI groups.
Goal: To evaluate discrimination and calibration of the PREVENT ASCVD equations in 8 major AANHPI groups (Chinese, Filipino, Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander [NH/PI], Japanese, Korean, South Asian, Vietnamese, other Southeast Asian) and Non-Hispanic Whites (NHW).
Methods: We identified all members aged 30-79 years of Kaiser Permanente (KP) Northern California and KP Hawaii integrated healthcare delivery systems from 2012-2022 who had no prior CVD and had complete data to estimate the PREVENT ASCVD risk using the base and full models. Incident ASCVD events (non-fatal and fatal MI and stroke) were identified through December 2023 using validated ICD-9/10 diagnosis codes in EHR and vital status data, and observed risk calculated using a cause-specific risk model that accounted for competing risk of non-ASCVD death. We examined model discrimination (C-index) and calibration (calibration plot and slope) by individual AANHPI group.
Results: We identified 1,219,255 eligible adults, with mean (SD) age ranging from 44.4 (13.2) years in South Asian to 61.0 (15.4) years in Japanese; 54.6% were women and there were higher proportions of women in Japanese, Korean, and NHW groups. Discrimination of the PREVENT base and full models was good overall and consistent across AANHPI individuals, with C statistics ranging from 0.77 (Japanese, Korean) to 0.82 (Chinese, South Asian) (Figure 1-3). However, calibration for the PREVENT base equation varied across AANHPI individuals, with underestimation of actual 10-year ASCVD risk in NH/PI, South Asian and other Southeast Asian adults, and overestimation in Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese adults. The PREVENT full equation lowered predicted ASCVD risk in all groups (Figure).
Conclusions: In a large, contemporary, primary prevention population of AANHPI and NHW adults in California and Hawaii, the PREVENT ASCVD equations had good discrimination but variable calibration across 8 major AANHPI individual groups. Given primary prevention decisions rely on predicted absolute risks, our findings support further optimizing ASCVD risk equations in targeted AANHPI groups.
More abstracts on this topic:
A multifaceted family intervention for blood pressure management in rural China: an open label, parallel group, cluster randomized trial (Healthy Family Program)
Jiang Chao, Dong Jianzeng, Cai Jun, Anderson Craig, Du Xin, Tang Yangyang, Han Rong, Song Yanna, Wang Chi, Lin Xiaolei, Yi Yang, Rodgers Anthony, Ma Changsheng
A Risk Prediction Score for Shockable Sudden Cardiac Arrest: Validation in the Framingham Heart StudyTruyen Thien Tan Tri Tai, Lin Honghuang, Mathias Marco, Chugh Harpriya, Reinier Kyndaron, Benjamin Emelia, Chugh Sumeet