Final ID: MP2035
Trends and Disparities in Stroke-Related Mortality among Heart Failure Patients in the United States, 1999-2020.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Stroke is a leading cause of death in patients with heart failure (HF), but national trends and disparities in stroke-related mortality within this population remain poorly defined. This study aims to evaluate temporal trends and demographic disparities in stroke-related mortality among HF patients from 1999 to 2020.
Methods: The CDC-WONDER’s (Center for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research) mortality data were used to retrospectively analyze stroke-related mortality in HF patients from 1999 to 2020 and calculate annual age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 with stratification by demographics (sex and race). Stroke-related deaths were defined as those with stroke (ICD-10 I60–I69) as the underlying cause and heart failure listed as a contributing condition. Annual percent changes (APC) were calculated using the JoinPoint regression model.
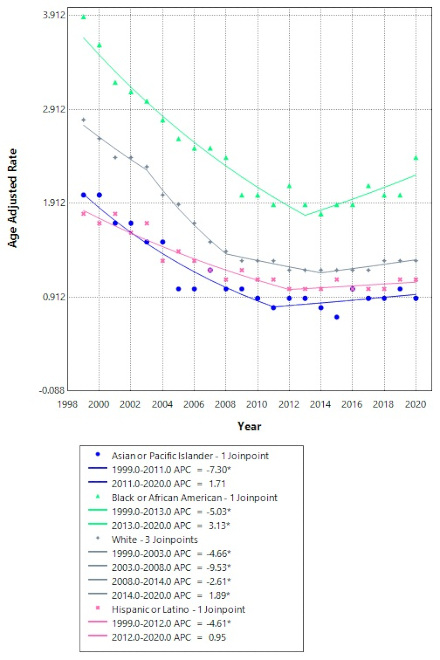
Results: A total of 121,192 stroke-related deaths occurred in HF patients between the years 1999 and 2020 with an overall AAMR of 1.6 per 100,000. AAMR declined consistently from 2.9 in 1999 to 1.4 in 2010 (APC -7.1, p<0.001); thereafter, rates plateaued, remaining 1.4 in 2020 (APC +0.3%, p=0.2). Among female patients, AAMR initially declined from 2.8 in 1999 to 1.4 in 2010 (APC -6.9, p<0.001) and remained relatively constant thereafter (APC -0.5, p=0.3). AAMR in males declined from 2.9 in 1999 to 1.3 in 2009 (APC -7.5, p<0.001), followed by a relatively stable period until 2016 when AAMR was 1.3 (APC -0.7, p=0.7); afterwards, AAMR increased to 1.5 in 2020 (APC 3.7, p=0.003). AAMRs were highest among NH Black patients (3.9 in 1999 and 2.4 in 2020), with an initial decline to 1.9 in 2013 (APC –5.0%, p<0.001), followed by an increase to 2.4 by 2020 (APC +3.1%, p=0.004).
Conclusion: Stroke-related AAMR in HF patients declined from 1999 to 2010 and remained relatively stable in the 2010s. Female and male patients had similar AAMRs over time. NH Black patients with HF had the highest stroke-related mortality, with an upward trend since 2013, highlighting persistent disparities.
Methods: The CDC-WONDER’s (Center for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research) mortality data were used to retrospectively analyze stroke-related mortality in HF patients from 1999 to 2020 and calculate annual age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 with stratification by demographics (sex and race). Stroke-related deaths were defined as those with stroke (ICD-10 I60–I69) as the underlying cause and heart failure listed as a contributing condition. Annual percent changes (APC) were calculated using the JoinPoint regression model.
Results: A total of 121,192 stroke-related deaths occurred in HF patients between the years 1999 and 2020 with an overall AAMR of 1.6 per 100,000. AAMR declined consistently from 2.9 in 1999 to 1.4 in 2010 (APC -7.1, p<0.001); thereafter, rates plateaued, remaining 1.4 in 2020 (APC +0.3%, p=0.2). Among female patients, AAMR initially declined from 2.8 in 1999 to 1.4 in 2010 (APC -6.9, p<0.001) and remained relatively constant thereafter (APC -0.5, p=0.3). AAMR in males declined from 2.9 in 1999 to 1.3 in 2009 (APC -7.5, p<0.001), followed by a relatively stable period until 2016 when AAMR was 1.3 (APC -0.7, p=0.7); afterwards, AAMR increased to 1.5 in 2020 (APC 3.7, p=0.003). AAMRs were highest among NH Black patients (3.9 in 1999 and 2.4 in 2020), with an initial decline to 1.9 in 2013 (APC –5.0%, p<0.001), followed by an increase to 2.4 by 2020 (APC +3.1%, p=0.004).
Conclusion: Stroke-related AAMR in HF patients declined from 1999 to 2010 and remained relatively stable in the 2010s. Female and male patients had similar AAMRs over time. NH Black patients with HF had the highest stroke-related mortality, with an upward trend since 2013, highlighting persistent disparities.
More abstracts on this topic:
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting Ferroptosis
Jiang Meng, Guo Xinning
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate OrgansChiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin