Final ID: MP1165
Serum GUDCA Alleviates Cardiac Injury in Acute Myocardial Infarction by Promoting Regulatory T Cell Differentiation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) exert protective effects following acute myocardial infarction (AMI), yet their levels decline rapidly after injury. Although serum metabolites regulate various immune processes, it remains unclear whether specific metabolites can promote Treg expansion and mitigate post-AMI cardiac damage.
Methods
Serum non-targeted metabolomics was performed in ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients stratified by Treg levels: high (Tregs/CD4 T cells > 1.5%; n = 30) vs. low (Tregs/CD4 T cells < 0.25%; n = 30) at admission. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA), identified as a candidate metabolite, was validated by LC-MS and ELISA. In a murine model of AMI, GUDCA (50 mg/kg/day, oral gavage) was administered post-infarction. Treg levels were analyzed by flow cytometry on Day 3. Cardiac fibrosis and function were evaluated by Sirius Red staining and echocardiography on Day 7. In vitro, naïve CD4 T cells were treated with GUDCA (100 nM) for three days to assess Treg differentiation. Cytokine profiling and ELISA were used to determine involvement of key immunoregulatory cytokines.
Results
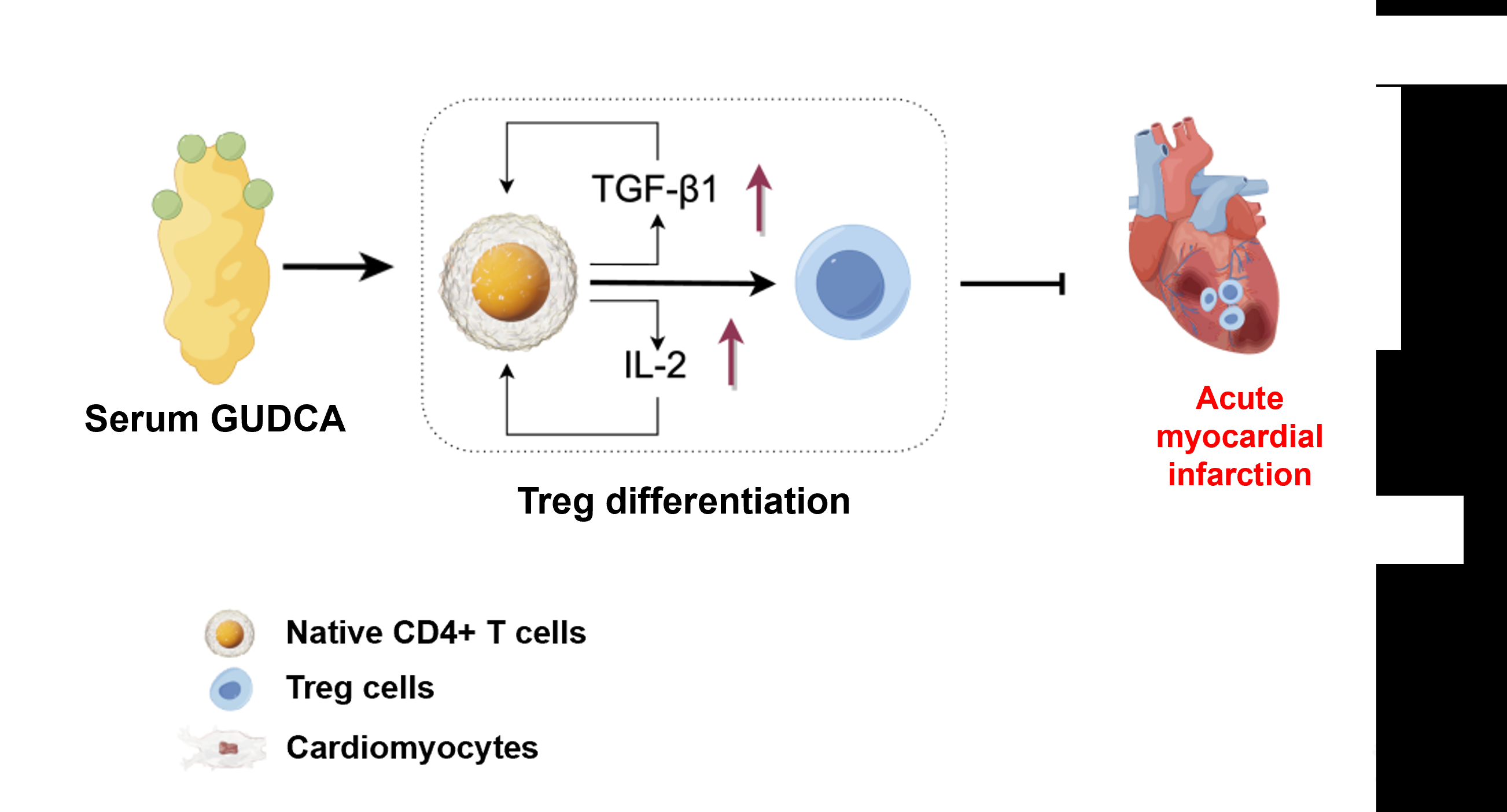
STEMI patients with higher Treg frequencies exhibited significantly elevated serum GUDCA levels. In vivo, GUDCA treatment increased Treg abundance, reduced myocardial fibrosis, and improved cardiac function post-AMI. In vitro, GUDCA directly promoted Treg differentiation from naive CD4 T cells. Mechanistically, GUDCA enhanced autocrine production of TGF-β1 and IL-2, two essential cytokines for Treg induction. Pharmacologic blockade of these cytokines abrogated GUDCA-mediated Treg differentiation.
Conclusions
GUDCA, a serum metabolite elevated in STEMI patients with higher Treg levels, promotes Treg differentiation and protects against cardiac injury following AMI. These findings highlight GUDCA’s potential as a novel immunometabolic therapeutic strategy for post-infarction cardiac remodeling.
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) exert protective effects following acute myocardial infarction (AMI), yet their levels decline rapidly after injury. Although serum metabolites regulate various immune processes, it remains unclear whether specific metabolites can promote Treg expansion and mitigate post-AMI cardiac damage.
Methods
Serum non-targeted metabolomics was performed in ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients stratified by Treg levels: high (Tregs/CD4 T cells > 1.5%; n = 30) vs. low (Tregs/CD4 T cells < 0.25%; n = 30) at admission. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA), identified as a candidate metabolite, was validated by LC-MS and ELISA. In a murine model of AMI, GUDCA (50 mg/kg/day, oral gavage) was administered post-infarction. Treg levels were analyzed by flow cytometry on Day 3. Cardiac fibrosis and function were evaluated by Sirius Red staining and echocardiography on Day 7. In vitro, naïve CD4 T cells were treated with GUDCA (100 nM) for three days to assess Treg differentiation. Cytokine profiling and ELISA were used to determine involvement of key immunoregulatory cytokines.
Results
STEMI patients with higher Treg frequencies exhibited significantly elevated serum GUDCA levels. In vivo, GUDCA treatment increased Treg abundance, reduced myocardial fibrosis, and improved cardiac function post-AMI. In vitro, GUDCA directly promoted Treg differentiation from naive CD4 T cells. Mechanistically, GUDCA enhanced autocrine production of TGF-β1 and IL-2, two essential cytokines for Treg induction. Pharmacologic blockade of these cytokines abrogated GUDCA-mediated Treg differentiation.
Conclusions
GUDCA, a serum metabolite elevated in STEMI patients with higher Treg levels, promotes Treg differentiation and protects against cardiac injury following AMI. These findings highlight GUDCA’s potential as a novel immunometabolic therapeutic strategy for post-infarction cardiac remodeling.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Cardioprotective Mechanism in Myocardial Reperfusion Injury: Dual Neutrophil Modulation and ROS/HOCl Scavenging by an Atypical Chemokine
Zwissler Leon, Bernhagen Juergen, Cabrera-fuentes Hector Alejandro, Hernandez Resendiz Sauri, Yap En Ping, Schindler Lisa, Zhang Zhishen, Dickerhof Nina, Hampton Mark, Liehn Elisa, Hausenloy Derek
A Potential Role for NKG2D, an NK cell receptor, in Accelerated CVD risk in African American Women Living in More Adverse Neighborhood Conditions: Data From the Step It Up Physical Activity Digital Health-Enabled, Community-Engaged InterventionBaez Andrew, Andrews Marcus, Sandler Dana, Aquino Peterson Elizabeth, Sharda Sonal, Tolentino Katherine Joy, Lopez De Leon Shirley, Seo Jein Eleanor, Cintron Manuel, Pita Mario, Tarfa Hannatu, Baumer Yvonne, Reger Robert, Childs Richard, Powell-wiley Tiffany, Dave Ayushi, Saurabh Abhinav, Mendelsohnl Laurel, Chen Long, Igboko Muna, Wells Ayanna, Marah Marie