Final ID: MP591
Retrospective Analysis of the Accuracy and Clinical Utility of Predictive Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Event Risk Assessment : PACE Study
Predictive analytics powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing cardiovascular risk assessment. Accurate prediction of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is critical for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk and guiding therapeutic decisions. This study evaluates deep learning (DL) models for LDL-C prediction in patients with prior cardiovascular events, comparing their performance against traditional ML methods and established LDL-C estimation formulas.
Methods:
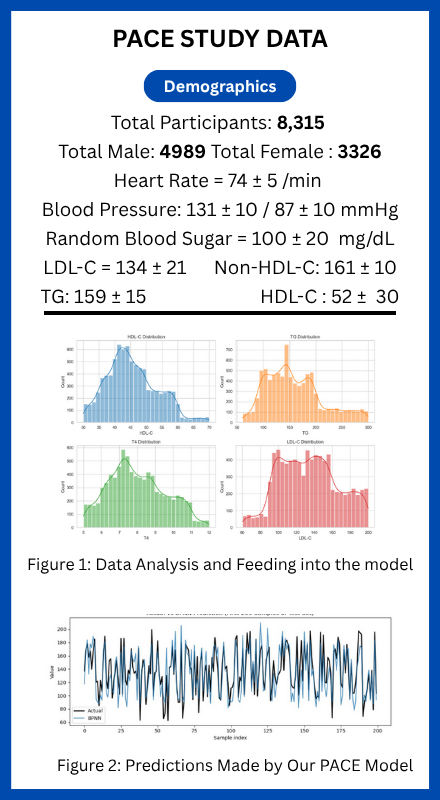
We retrospectively analyzed data from 8,315 patients with documented cardiovascular events from Rhythm Heart and Critical Care. Key lipid parameters included LDL-C, triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Patient CVD history was blinded during model training to ensure unbiased prediction. DL models tested included Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, and a Transformer-based architecture. These were benchmarked against Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) models and LDL-C formulas by Sampson and Martin. Model performance was assessed using Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE).
Results:
The models generated LDL-C predictions for 5,132 patients (61% of the cohort). The Transformer-based model achieved the highest accuracy with an RMSE of 10.58 mg/dL and MAPE of 7.35%, significantly outperforming BPNN (RMSE 17.16 mg/dL; MAPE 11.01%), RNN (RMSE 32.47 mg/dL), and LSTM (RMSE 32.51 mg/dL). Deep learning models also surpassed traditional LDL-C formulas in accuracy. Partial Dependence Plots (PDP) of the Transformer model revealed clinically meaningful relationships between LDL-C and predictors such as HDL-C, BMI, and thyroid hormones, supporting physiological validity and interpretability.
Conclusion:
This study demonstrates that DL models, particularly the Transformer-based approach, significantly outperform conventional methods in predicting LDL-C levels among patients with cardiovascular events. The model’s superior accuracy and interpretability offer a promising clinical tool for personalized risk assessment, early detection, and optimized management of CVD. Incorporation of such AI-driven models into clinical workflows could improve patient outcomes and resource allocation in cardiovascular care.
- Ma, Hongwei ( The University of Sydney , Sydney , New South Wales , Australia )
- Ch, Rahul ( Sri Ramachandra Medical College and Research Institute , Chennai , India )
- Biswas, Shankar ( Ivano-Frankivsk National Medical Un , Meerut , India )
- Kaste, Ritik ( government medical college & hospital , Jammu , India )
- Nandakishor, Nanditha ( JJM medical college , Davanagere , India )
- Karnasula, Varuni ( Rohan hospital , Hyderabad , Telangana , India )
- Narula, Aman ( GMERS Medical college and hospital , Gandhinagar , India )
- Tahir, Okasha ( khyber medical university , Peshawar , Pakistan )
- Reddy A, Likhitha ( madras medical college , Chennai , India )
- Sesham, John ( alluri sitarama raju academy of medical sciences , Vishakapatnam , India )
- Juneja, Manish ( Rhythm Heart and Critical Care , Nagpur , India )
- Gao, Junbin ( The University of Sydney , Sydney , New South Wales , Australia )
- Karande, Harsh ( Rhythm Heart and Critical Care , Nagpur , India )
- Jolly, Ivin ( Anhui Medical University , Hefei , Anhui , China )
- Ramteke, Harshawardhan Dhanraj ( Rhythm Heart and Critical Care , Nagpur , India )
- Khan, Rakhshanda ( Ayaan institute of medical sciences , Moinabad , India )
- Qianyi, Yang ( Anhui University , Hefei , Anhui , China )
- Farooqi, Sumayya ( Dr vrk womens medical college , Hyderabad , India )
- Banda, Susmitha ( government medical college nizamabad , Nizamabad , India )
- Rawat, Akash ( himalayan institute of medical sciences , Dehradun , India )
- Chilakala, Teja Vardhan ( Narayana medical college , Nellore , India )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
From Development to Deployment: Best Practices for Validating AI/ML Models in Healthcare
Saturday, 11/08/2025 , 01:45PM - 02:55PM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Adejumo Philip, Pedroso Aline, Khera Rohan
AI-Derived Retinal Vasculature Features Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from the CRIC StudyDhamdhere Rohan, Modanwal Gourav, Rahman Mahboob, Al-kindi Sadeer, Madabhushi Anant
More abstracts from these authors:
Ramteke Harshawardhan Dhanraj, Chaudhari Rucha, Malaiyappan Surya, Verma Pranav, Karnasula Varuni, Banda Susmitha, Juneja Manish, Jolly Ivin, Khan Rakhshanda, Gulzar Junaid, Makineni Karthik Sai, Bellam Manognya, Gill Jonty, Narula Aman, Bhattacharjee Mridula, Verma Bhanu
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, and Treatment: A Meta-Analysis of 45 StudiesQianyi Yang, Ramteke Harshawardhan Dhanraj, Khan Rakhshanda, Jolly Ivin, Juneja Manish