Final ID: Su4037
Distribution and clinical impact of polygenetic risk scores in younger subjects at uncertain coronary risk
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD) risk using risk scores and coronary artery calcium (CAC) is not predictive in younger individuals. Additionally, patients with hyperlipidemia and other factors known to increase CAD risk may desire additional evidence to support treatment recommendations. Emerging polygenic risk scores (PRS) have been proposed to address these challenges, but clinical experience is limited.
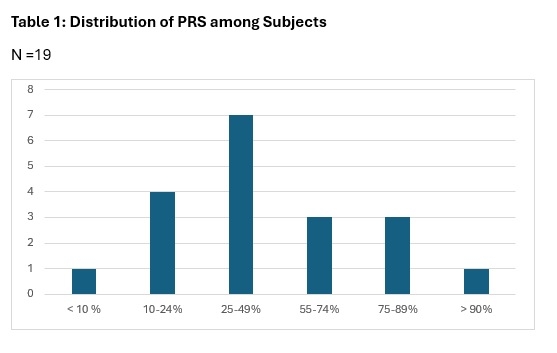
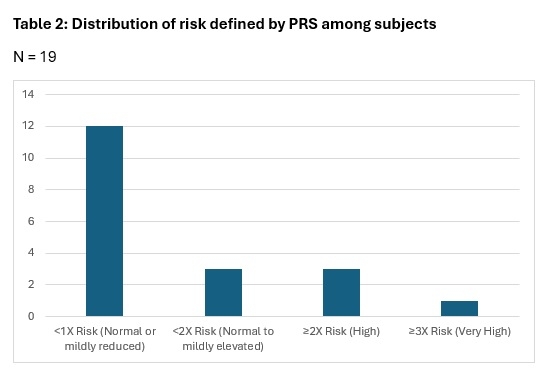
Methods: PRS testing (Allelica, San Francisco, California), obtained by buccal swab, was offered to appropriate patients at an advanced lipid clinic. Of the group who agreed to screening, we assessed the distribution of PRS percentiles and relative risk, the number treated with statin therapy and the influence PRS had on lipid-lowering recommendations. The PRS reports risk both by providing a percentile and relative risk (figures 1, 2). The relative risk varies by race and other factors. A 2-fold increased risk can be used as a risk-enhancing factor and a 3-fold increase risk as equivalent to CAD risk from familial hypercholesterolemia.
Results: The patient series included 22 individuals undergoing PRS to assist in therapeutic decision-making. Ages ranged from 19-65, with ten (45%) under the age of 40, and nine (41%) women. The average LDL was 152 mg/dL (range 37-230 mg/dL). Evaluation of coronary calcium was completed in 12 (55%) subjects, and nine of those (75%) had CAC=0. PRS results were returned for 19 (89%) subjects, with lack of payment in three. The distribution across percentages of relative risk is shown in figures 1 and 2. Three subjects were classified as high (> 2 x) risk and one at very high (> 3 x) risk. Statin therapy was prescribed for all four of these. Overall, 59% were prescribed statin therapy, and treatment recommendations were influenced by the PRS report (i.e., starting or not starting lipid lowering therapy or intensifying therapy) in ten (46%). All three who opted not to complete the evaluation were prescribed statin therapy.
Conclusions: In this initial consecutive case-series experience, applying PRS to better and earlier understand genetic predisposition vs. environmental risk for CAD, we found a broad distribution of genetic risk among PRS-tested individuals, which impacted lipid-lowering decision-making in a large percentage of individuals. The impact on outcomes using PRS will require large, randomized clinical trials with long-term follow-up.
Methods: PRS testing (Allelica, San Francisco, California), obtained by buccal swab, was offered to appropriate patients at an advanced lipid clinic. Of the group who agreed to screening, we assessed the distribution of PRS percentiles and relative risk, the number treated with statin therapy and the influence PRS had on lipid-lowering recommendations. The PRS reports risk both by providing a percentile and relative risk (figures 1, 2). The relative risk varies by race and other factors. A 2-fold increased risk can be used as a risk-enhancing factor and a 3-fold increase risk as equivalent to CAD risk from familial hypercholesterolemia.
Results: The patient series included 22 individuals undergoing PRS to assist in therapeutic decision-making. Ages ranged from 19-65, with ten (45%) under the age of 40, and nine (41%) women. The average LDL was 152 mg/dL (range 37-230 mg/dL). Evaluation of coronary calcium was completed in 12 (55%) subjects, and nine of those (75%) had CAC=0. PRS results were returned for 19 (89%) subjects, with lack of payment in three. The distribution across percentages of relative risk is shown in figures 1 and 2. Three subjects were classified as high (> 2 x) risk and one at very high (> 3 x) risk. Statin therapy was prescribed for all four of these. Overall, 59% were prescribed statin therapy, and treatment recommendations were influenced by the PRS report (i.e., starting or not starting lipid lowering therapy or intensifying therapy) in ten (46%). All three who opted not to complete the evaluation were prescribed statin therapy.
Conclusions: In this initial consecutive case-series experience, applying PRS to better and earlier understand genetic predisposition vs. environmental risk for CAD, we found a broad distribution of genetic risk among PRS-tested individuals, which impacted lipid-lowering decision-making in a large percentage of individuals. The impact on outcomes using PRS will require large, randomized clinical trials with long-term follow-up.
More abstracts on this topic:
Accumulation of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Marker of Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients With Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Undergoing Coronary Computed Tomography Angiograph
Ishikawa Hirotoshi, Kasayuki Noriaki, Fukuda Daiju, Otsuka Kenichiro, Sugiyama Takatoshi, Yamaura Hiroki, Hojo Kana, Kawa Yoshinori, Shintani Ako, Ito Asahiro, Yamazaki Takanori
A First-in-Class EV-miRNA Diagnostic System for Early Identification of IVIG-Resistant Kawasaki DiseaseNakaoka Hideyuki, Hirono Keiichi, Hara Akane, Tsuboi Kaori, Ibuki Keijiro, Ozawa Sayaka, Ichida Fukiko