Final ID: MP1819
SGLT2 Inhibitors Reduce Mortality and Improve Cardiac Biomarkers in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background:
Cardiac amyloidosis (CA), comprising transthyretin (ATTR) and light-chain (AL) subtypes, is an important yet underidentified mimic of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have proven benefits in general heart failure (HF) populations, but their role in CA remains unclear.
Objective:
We evaluated the impact of SGLT2i on clinical outcomes, renal and cardiac biomarkers in patients with CA, including a subgroup analysis of ATTR-CA.
Methods:
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted per PRISMA guidelines, including seven observational studies (N=9607). Patients with AL or ATTR CA receiving SGLT2i were compared to matched controls without SGLT2i. Outcomes analyzed included all-cause mortality, HF exacerbations, change in eGFR, and change in NT-proBNP levels. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and mean differences (MDs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic.
Results:
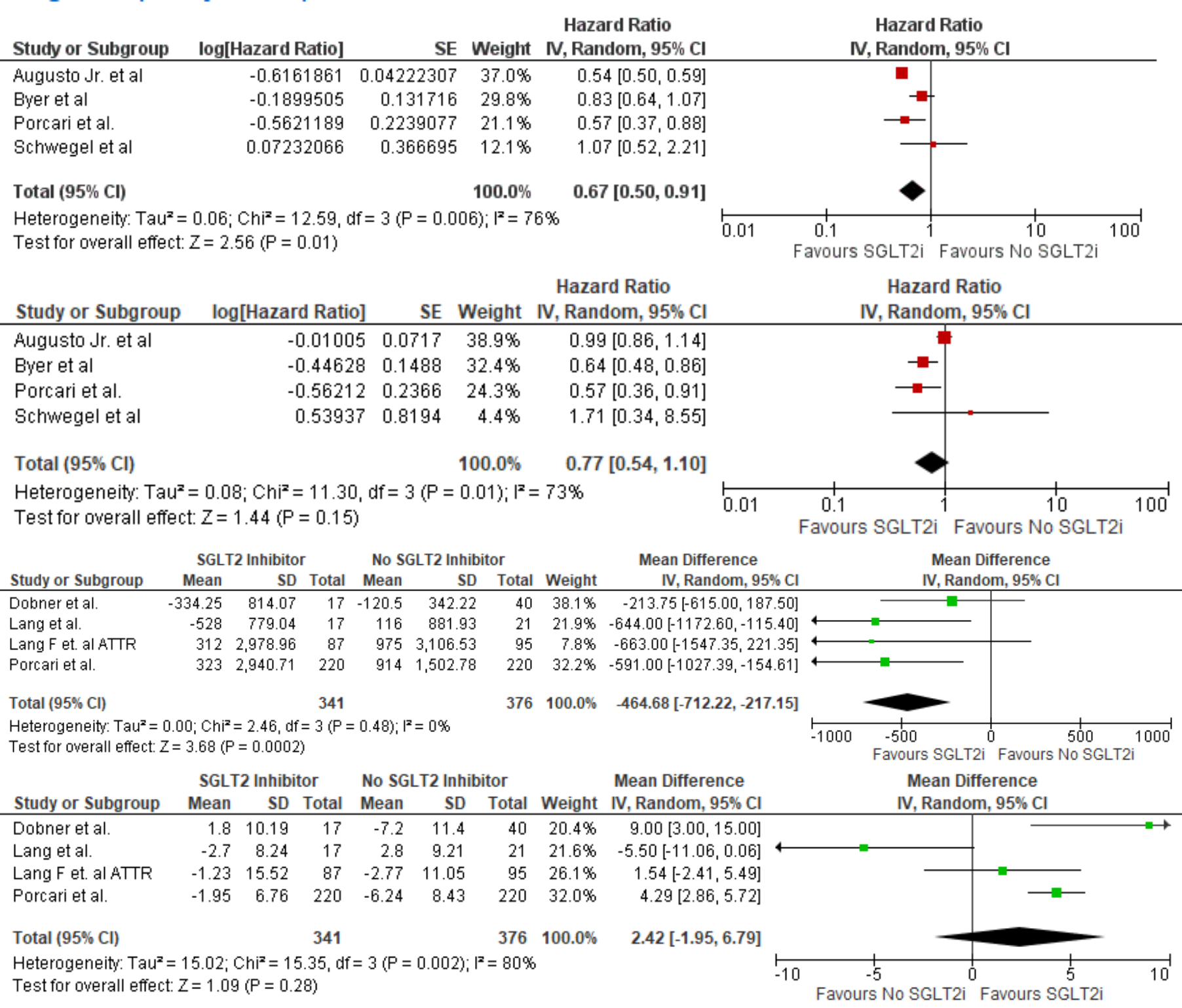
Among patients with CA (AL + ATTR), SGLT2i use was associated with a significant reduction in all-cause mortality (HR 0.67; 95% CI 0.50-0.91; p = 0.003) and NT-proBNP levels (MD: –464.68 pg/mL; 95% CI –712.22 to –217.15; p = 0.0002). There was a trend towards reduced HF exacerbations, although not statistically significant (HR 0.77; 95% CI 0.54–1.10; p = 0.15). Changes in eGFR did not differ significantly (MD: +2.42 mL/min/1.73m2; 95% CI –1.95 to 6.79; p = 0.28).
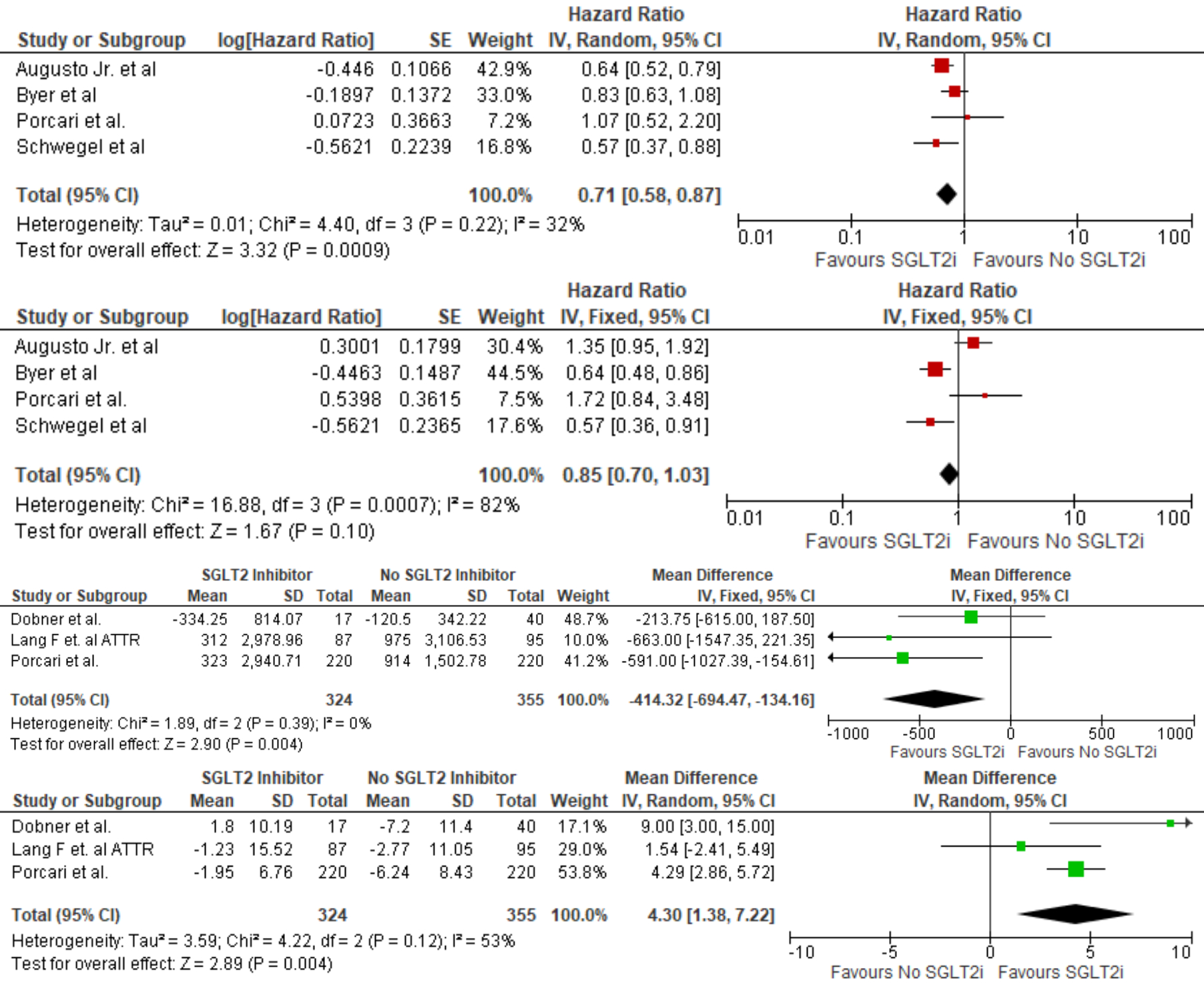
In the ATTR subgroup, SGLT2i use was associated with a significant reduction in all-cause mortality (HR 0.71; 95% CI 0.58–0.87; p = 0.0009) and NT-proBNP levels (MD: –414.32 pg/mL; 95% CI –694.47 to –134.16; p = 0.004). HF exacerbations in this subgroup showed a trend towards reduction (HR 0.85; 95% CI 0.70–1.03; p = 0.10), although not statistically significant. In this subgroup, a statistically significant improvement in eGFR was noted (mean difference +4.30 mL/min/1.73m2; 95% CI 1.38 to 7.22; p = 0.004).
Conclusions:
SGLT2 inhibitors are associated with a significant reduction in all-cause mortality and improvements in cardiac biomarkers in patients with CA, particularly in those with the ATTR subtype. While HF hospitalization trends were favorable, statistical significance was not reached. Renal benefits were more pronounced in ATTR-CA. These findings support the use of SGLT2i in CA, particularly in the ATTR subgroup. Further randomized trials are needed to confirm these observational findings.
Background:
Cardiac amyloidosis (CA), comprising transthyretin (ATTR) and light-chain (AL) subtypes, is an important yet underidentified mimic of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have proven benefits in general heart failure (HF) populations, but their role in CA remains unclear.
Objective:
We evaluated the impact of SGLT2i on clinical outcomes, renal and cardiac biomarkers in patients with CA, including a subgroup analysis of ATTR-CA.
Methods:
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted per PRISMA guidelines, including seven observational studies (N=9607). Patients with AL or ATTR CA receiving SGLT2i were compared to matched controls without SGLT2i. Outcomes analyzed included all-cause mortality, HF exacerbations, change in eGFR, and change in NT-proBNP levels. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and mean differences (MDs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic.
Results:
Among patients with CA (AL + ATTR), SGLT2i use was associated with a significant reduction in all-cause mortality (HR 0.67; 95% CI 0.50-0.91; p = 0.003) and NT-proBNP levels (MD: –464.68 pg/mL; 95% CI –712.22 to –217.15; p = 0.0002). There was a trend towards reduced HF exacerbations, although not statistically significant (HR 0.77; 95% CI 0.54–1.10; p = 0.15). Changes in eGFR did not differ significantly (MD: +2.42 mL/min/1.73m2; 95% CI –1.95 to 6.79; p = 0.28).
In the ATTR subgroup, SGLT2i use was associated with a significant reduction in all-cause mortality (HR 0.71; 95% CI 0.58–0.87; p = 0.0009) and NT-proBNP levels (MD: –414.32 pg/mL; 95% CI –694.47 to –134.16; p = 0.004). HF exacerbations in this subgroup showed a trend towards reduction (HR 0.85; 95% CI 0.70–1.03; p = 0.10), although not statistically significant. In this subgroup, a statistically significant improvement in eGFR was noted (mean difference +4.30 mL/min/1.73m2; 95% CI 1.38 to 7.22; p = 0.004).
Conclusions:
SGLT2 inhibitors are associated with a significant reduction in all-cause mortality and improvements in cardiac biomarkers in patients with CA, particularly in those with the ATTR subtype. While HF hospitalization trends were favorable, statistical significance was not reached. Renal benefits were more pronounced in ATTR-CA. These findings support the use of SGLT2i in CA, particularly in the ATTR subgroup. Further randomized trials are needed to confirm these observational findings.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial Intelligence Assisted Characterization of HFpEF in Patients with Indeterminate Diastolic Function
Papadogiannis Alexander, Karnik Amogh, Tang Maxine, Hussain Kifah, Kansal Preeti, Narang Akhil
β1 Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies Promote Heart Failure Though Activation of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP1/Phosphodiesterase 4B PathwayCao Ning, Qiu Hui, Li Hongwei