Final ID: MP131
Independent Associations of Mitral Valve Prolapse Volume and LV Remodeling with Ventricular Ectopic Burden: A CMR Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Qualitative phenotypic features of arrhythmogenic mitral valve prolapse (MVP) have been described. We sought to determine the association of prolapse volume (PV) and left ventricular end-diastolic volume index (LVEDVi) with ventricular ectopic (VE) burden.
Research Question:
Are LVEDVi and PV associated with increased VE burden in patients with MVP?
Methods:
We evaluated 88 patients diagnosed with MVP who underwent cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging and Holter monitoring at the Cleveland Clinic between 2020 and 2024. The primary VE burden metric was a weighted composite of VE burden, defined as PVC burden > 5% (1 point) or sustained ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation (VT/VF) (2 points). Clinical and CMR features were included in a logistic regression models, including abnormal LVEDVi status (> 93 mL/m2 for females, > 107 mL/m2 for males), PV, late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) status, mitral annular disjunction (MAD) single vs bileaflet prolapse, age, and gender. To evaluate the association between CMR variables and VE burden, we developed two Multivariate models. Incremental model performance assessed using the C-index (AUC).
Results:
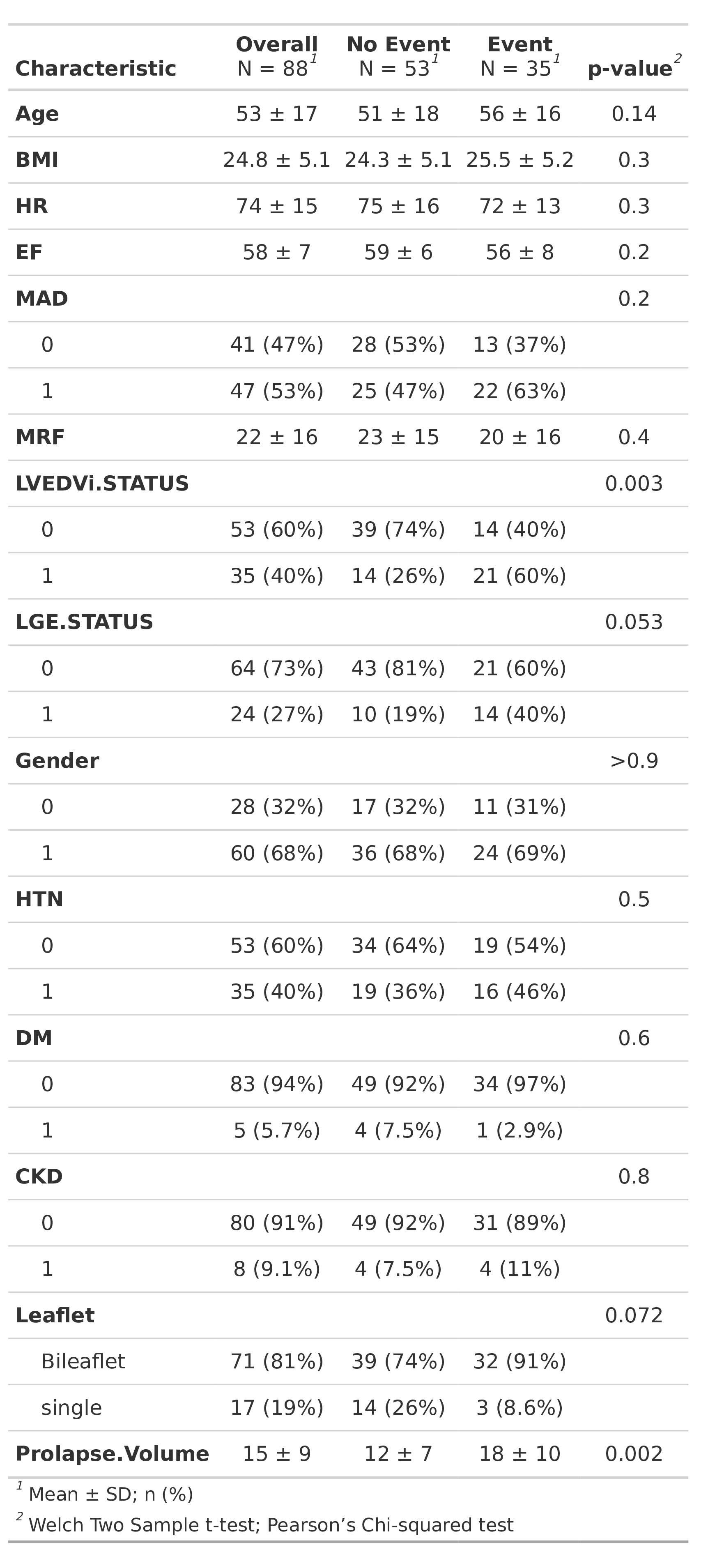
Of the 88 MVP patients, 35 (40%) exhibited an elevated VE burden, including 9 (26%) with sustained VT/VF and 26 (74%) with a PVC burden >5%. Those with events had higher mean PV (18 ± 10 cm3 vs. 12 ± 7 cm3; p = 0.0002) and a greater prevalence of abnormal LVEDVi (60% vs. 26%; p = 0.003) (Table 1).
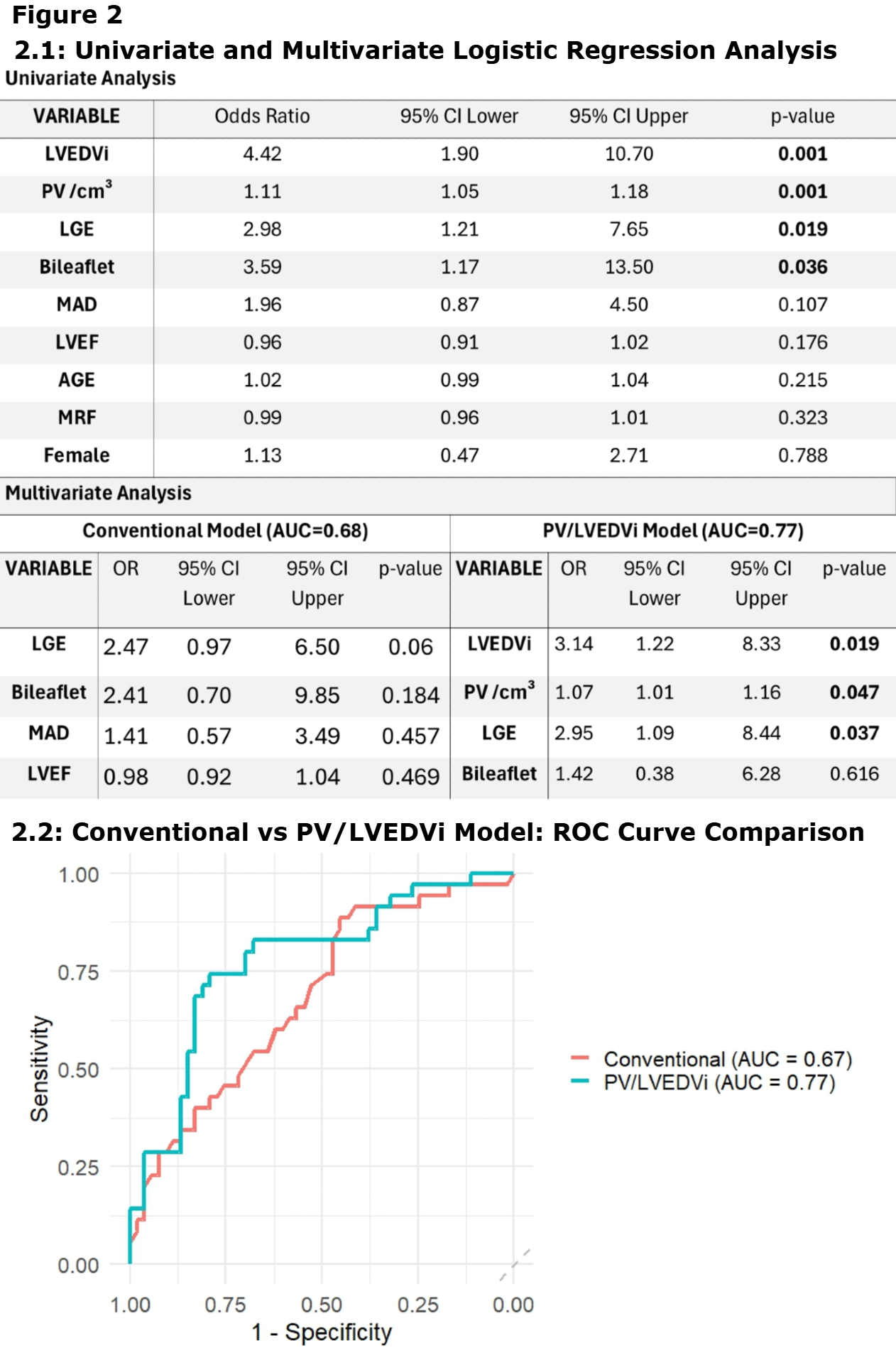
The first model, referred to as the conventional model, included variables previously associated with ventricular arrhythmogenicity in MVP: LGE, MAD, leaflet status, and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). This model achieved a C-index of 0.68.
The second model, PV/LVEDVi model, was derived from univariate significance and relevance to structural remodeling. This final model achieved a C-index of 0.77. In this model abnormal LVEDVi (OR = 3.14; 95% CI 1.22–8.33; p = 0.019), PV (OR = 1.07 per cm3; 95% CI 1.01–1.16; p = 0.048), and LGE (OR = 2.95; 95% CI 1.09–8.44; p = 0.037) were independently associated with increased VE burden (Table 2).
Conclusion:
LVEDVi and PV were independently associated with VE Burden in MVP, even after adjusting for LGE. CMR–derived structural features provide further phenotypic insights regarding arrhythmogenic MVP.
Qualitative phenotypic features of arrhythmogenic mitral valve prolapse (MVP) have been described. We sought to determine the association of prolapse volume (PV) and left ventricular end-diastolic volume index (LVEDVi) with ventricular ectopic (VE) burden.
Research Question:
Are LVEDVi and PV associated with increased VE burden in patients with MVP?
Methods:
We evaluated 88 patients diagnosed with MVP who underwent cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging and Holter monitoring at the Cleveland Clinic between 2020 and 2024. The primary VE burden metric was a weighted composite of VE burden, defined as PVC burden > 5% (1 point) or sustained ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation (VT/VF) (2 points). Clinical and CMR features were included in a logistic regression models, including abnormal LVEDVi status (> 93 mL/m2 for females, > 107 mL/m2 for males), PV, late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) status, mitral annular disjunction (MAD) single vs bileaflet prolapse, age, and gender. To evaluate the association between CMR variables and VE burden, we developed two Multivariate models. Incremental model performance assessed using the C-index (AUC).
Results:
Of the 88 MVP patients, 35 (40%) exhibited an elevated VE burden, including 9 (26%) with sustained VT/VF and 26 (74%) with a PVC burden >5%. Those with events had higher mean PV (18 ± 10 cm3 vs. 12 ± 7 cm3; p = 0.0002) and a greater prevalence of abnormal LVEDVi (60% vs. 26%; p = 0.003) (Table 1).
The first model, referred to as the conventional model, included variables previously associated with ventricular arrhythmogenicity in MVP: LGE, MAD, leaflet status, and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). This model achieved a C-index of 0.68.
The second model, PV/LVEDVi model, was derived from univariate significance and relevance to structural remodeling. This final model achieved a C-index of 0.77. In this model abnormal LVEDVi (OR = 3.14; 95% CI 1.22–8.33; p = 0.019), PV (OR = 1.07 per cm3; 95% CI 1.01–1.16; p = 0.048), and LGE (OR = 2.95; 95% CI 1.09–8.44; p = 0.037) were independently associated with increased VE burden (Table 2).
Conclusion:
LVEDVi and PV were independently associated with VE Burden in MVP, even after adjusting for LGE. CMR–derived structural features provide further phenotypic insights regarding arrhythmogenic MVP.
More abstracts on this topic:
Electrocardiographic Right Ventricular Hypertrophy Enhances Contemporary Risk Stratification in Predicting All-Cause Mortality in Mitral Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair
Young Kirsten, Skaf Sabah, Makar Moody, Chakravarty Tarun, Makkar Raj, Mirocha James, Siegel Robert, Chonde Meshe, Chyu Kuang-yuh, Wangmang Felix, Richards Donald, Dhillon Manvir, Torbati Tina, Shechter Alon, Kaewkes Danon, Patel Vivek, Koren Ofir
Association of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome with Cardiovascular Events after Mitral Transcatheter Edge-to-edge RepairMannina Carlo, Sharma Samin, Kini Annapoorna, Lerakis Stamatios, Sharma Akarsh, Carbone Andreina, Bossone Eduardo, Tuttolomondo Antonino, Argulian Edgar, Neibart Eric, Halperin Jonathan, Dangas George