Final ID: 4364153
Cohort-scale automated patch clamp data improves variant classification and penetrance stratification for SCN5A-Brugada Syndrome
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Genetic data are transforming preventative cardiology by identifying individuals at risk of disease before sudden manifestations. Brugada Syndrome (BrS) is an inherited arrhythmia disorder that causes an elevated risk of sudden cardiac death. Approximately 20% of patients with BrS have rare variants in SCN5A, which encodes the cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5. Genetic workup of BrS, and analysis of secondary findings, is often complicated by SCN5A variants of uncertain significance (VUS) and/or incomplete penetrance.
Research Question: What is the additive value of variant functional testing when applied across a cohort of patients undergoing evaluation of potential BrS?
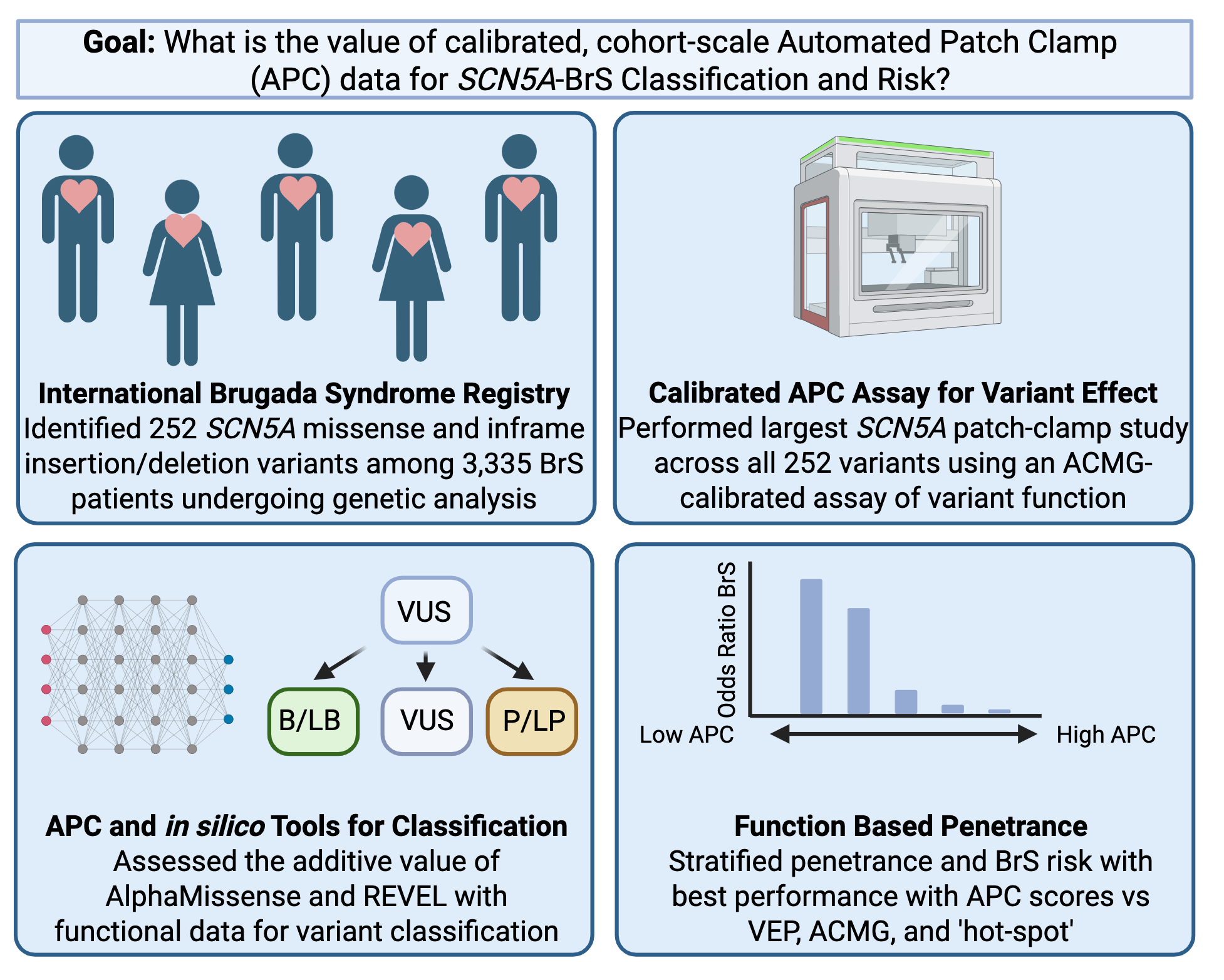
Methods: We comprehensively studied 252 missense and in-frame insertion/deletion SCN5A variants from a previously published large cohort of BrS cases (n=3,335 patients) using a calibrated high-throughput automated patch clamp (APC) assay. Variant functional Z-scores were assigned evidence levels ranging from BS3_moderate (normal function) to PS3_strong (loss-of-function), as defined by American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics criteria. Functional evidence was combined with population frequency, hot-spot, case counts, protein length changes, and in silico predictions. Odds ratios of BrS case-control enrichment and penetrance for BrS were calculated from variant frequencies in the BrS cohort and in gnomAD.
Results: Most variants (146/252) were functionally abnormal (Z ≤ -2), with 100 having severe loss-of-function (Z ≤ -4). Functional evidence enabled the reclassification of 110 of 225 VUS; 104 to likely pathogenic and 6 to likely benign. SCN5A variants with loss-of-function were mainly localized to the transmembrane domains, especially the regions comprising the central pore. SCN5A variant penetrance was proportional to the severity of loss-of-function; variants with Z ≤ -6 had penetrance of 24.5% (15.9 – 37.7% CI) and an odds ratio of 501 for BrS.
Conclusions: This cohort-scale APC dataset stratifies SCN5A variants found in BrS patients into normal function “bystander” variants that have a low risk for BrS and loss-of-function variants that have a high risk for BrS. Functional data can be integrated with other criteria to reclassify a substantial fraction of VUS and identifies variants with higher penetrance among a secondary findings population. We anticipate this dataset will improve the diagnosis and clinical management of BrS probands and their families.
Research Question: What is the additive value of variant functional testing when applied across a cohort of patients undergoing evaluation of potential BrS?
Methods: We comprehensively studied 252 missense and in-frame insertion/deletion SCN5A variants from a previously published large cohort of BrS cases (n=3,335 patients) using a calibrated high-throughput automated patch clamp (APC) assay. Variant functional Z-scores were assigned evidence levels ranging from BS3_moderate (normal function) to PS3_strong (loss-of-function), as defined by American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics criteria. Functional evidence was combined with population frequency, hot-spot, case counts, protein length changes, and in silico predictions. Odds ratios of BrS case-control enrichment and penetrance for BrS were calculated from variant frequencies in the BrS cohort and in gnomAD.
Results: Most variants (146/252) were functionally abnormal (Z ≤ -2), with 100 having severe loss-of-function (Z ≤ -4). Functional evidence enabled the reclassification of 110 of 225 VUS; 104 to likely pathogenic and 6 to likely benign. SCN5A variants with loss-of-function were mainly localized to the transmembrane domains, especially the regions comprising the central pore. SCN5A variant penetrance was proportional to the severity of loss-of-function; variants with Z ≤ -6 had penetrance of 24.5% (15.9 – 37.7% CI) and an odds ratio of 501 for BrS.
Conclusions: This cohort-scale APC dataset stratifies SCN5A variants found in BrS patients into normal function “bystander” variants that have a low risk for BrS and loss-of-function variants that have a high risk for BrS. Functional data can be integrated with other criteria to reclassify a substantial fraction of VUS and identifies variants with higher penetrance among a secondary findings population. We anticipate this dataset will improve the diagnosis and clinical management of BrS probands and their families.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute clinical outcomes following virtual reality implementation in the electrophysiology laboratory
Romano Letizia, Calvelli Pierangelo, Quirino Gianluca, Tomaselli Caterina, Talarico Antonello, Pasqua Pino, Curcio Antonio
A Case of Spike-on-T Phenomenon and Polymorphic Ventricular TachycardiaTran Brittany, Thimmiah Harun, Rosenthal Lawrence