Final ID: 4139038
Ibrutinib Increases Phosphorylation of the Src-Erk1/2 Signaling Pathway in Human Atrial-Specific Cardiomyocytes Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has revolutionized treatment for B-cell malignancies but increases the incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) compared with conventional chemotherapy. Reports indicate that ibrutinib-mediated AF does not result from inhibition of BTK, but from off-target inhibition of a different kinase, C-terminal Src kinase (CSK). The signaling pathway by which CSK inhibition results in AF is unknown and may represent a novel molecular mechanism for AF.
Objective:
To identify kinase pathways that promote atrial fibrillation downstream from CSK.
Methods:
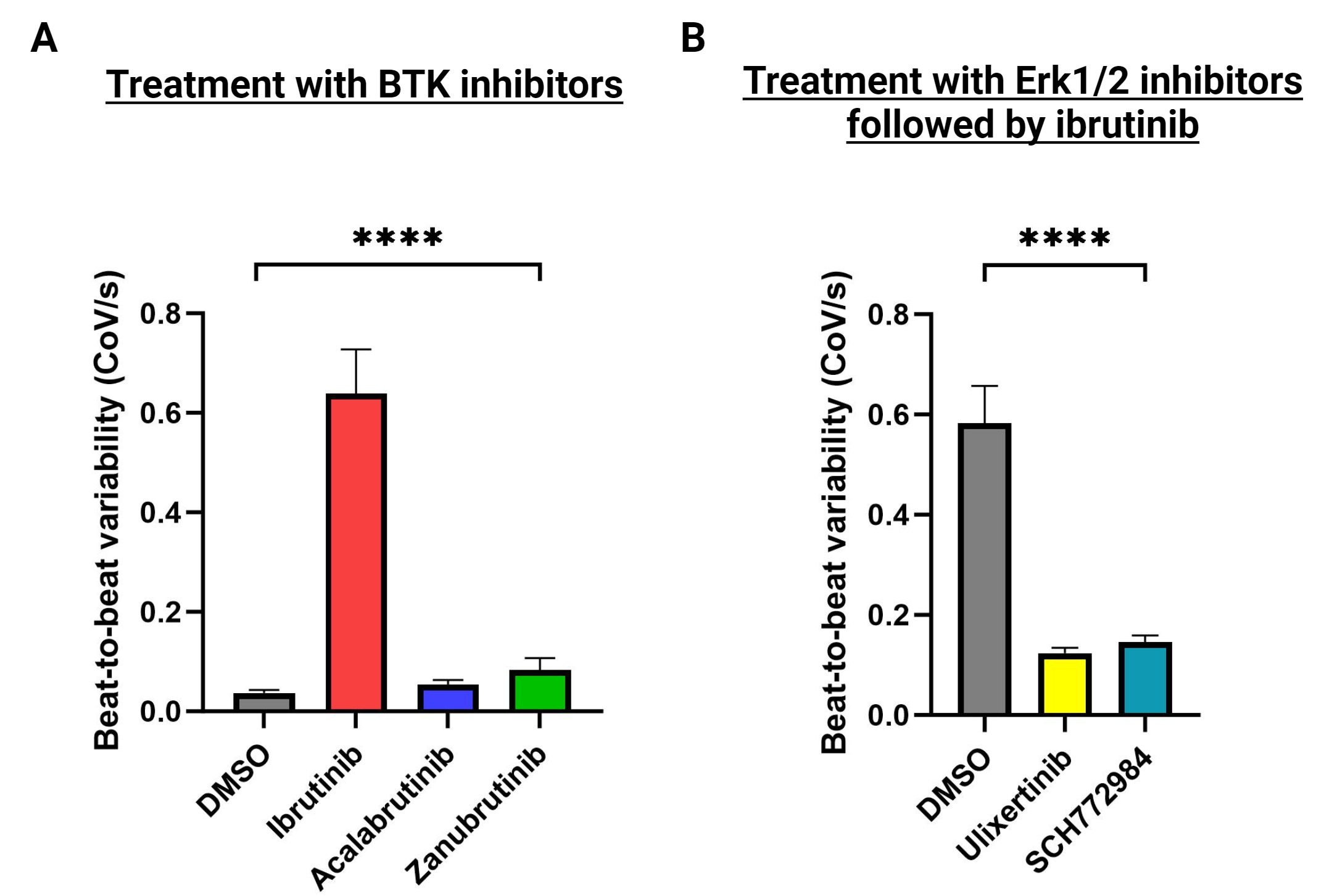
Studies were performed in human atrial-specific cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-aCMs) derived from population control induced pluripotent stem cells. Extracellular field potentials (EFPs) with the Nanion CardioExcyte 96 system demonstrated marked increased spontaneous beat-to-beat variability, an in vitro correlate of arrhythmogenic behavior, with exposure to ibrutinib but not to second-generation BTK inhibitors, which are less associated with AF (Figure 1A). Human phospho-kinase arrays determined the relative phosphorylation of 37 kinases in hiPSC-aCMs treated with ibrutinib or vehicle.
Results:
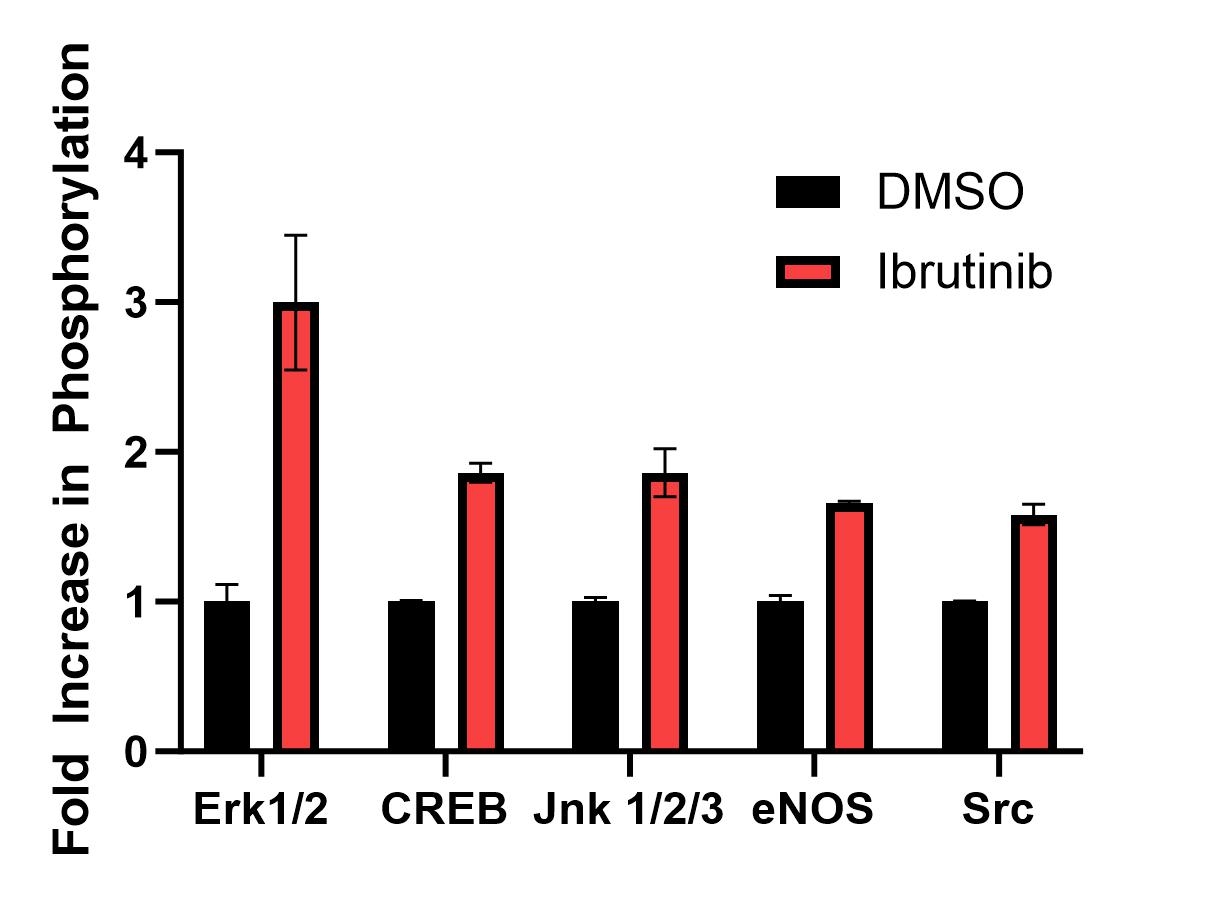
Treatment with ibrutinib increased phosphorylation of multiple kinases (Src, Erk1/2, CREB) in the Src-Erk1/2 pathway (Figure 2); the biggest increase was with Erk1/2 phosphorylation (3-fold). Pre-treatment of hiPSC-aCMs with the Erk1/2 inhibitors ulixertinib and SCH772984 inhibited the EFP arrhythmogenic signal seen with ibrutinib (Figure 1B).
Conclusion:
In hiPSC-aCMs, inhibition of CSK by ibrutinib results in increased arrhythmogenic behavior through Erk1/2-dependent phosphorylation. The downstream mechanisms by which this occurs remain unknown and represent novel potential target(s) for AF therapeutics.
The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has revolutionized treatment for B-cell malignancies but increases the incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) compared with conventional chemotherapy. Reports indicate that ibrutinib-mediated AF does not result from inhibition of BTK, but from off-target inhibition of a different kinase, C-terminal Src kinase (CSK). The signaling pathway by which CSK inhibition results in AF is unknown and may represent a novel molecular mechanism for AF.
Objective:
To identify kinase pathways that promote atrial fibrillation downstream from CSK.
Methods:
Studies were performed in human atrial-specific cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-aCMs) derived from population control induced pluripotent stem cells. Extracellular field potentials (EFPs) with the Nanion CardioExcyte 96 system demonstrated marked increased spontaneous beat-to-beat variability, an in vitro correlate of arrhythmogenic behavior, with exposure to ibrutinib but not to second-generation BTK inhibitors, which are less associated with AF (Figure 1A). Human phospho-kinase arrays determined the relative phosphorylation of 37 kinases in hiPSC-aCMs treated with ibrutinib or vehicle.
Results:
Treatment with ibrutinib increased phosphorylation of multiple kinases (Src, Erk1/2, CREB) in the Src-Erk1/2 pathway (Figure 2); the biggest increase was with Erk1/2 phosphorylation (3-fold). Pre-treatment of hiPSC-aCMs with the Erk1/2 inhibitors ulixertinib and SCH772984 inhibited the EFP arrhythmogenic signal seen with ibrutinib (Figure 1B).
Conclusion:
In hiPSC-aCMs, inhibition of CSK by ibrutinib results in increased arrhythmogenic behavior through Erk1/2-dependent phosphorylation. The downstream mechanisms by which this occurs remain unknown and represent novel potential target(s) for AF therapeutics.
More abstracts on this topic:
1-Year Outcomes After Cardioversion With and Without Anticoagulation in Patients With Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Propensity-Matched Analysis
Thangjui Sittinun, Trongtorsak Angkawipa, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Thyagaturu Harshith, Watson Hangyu, Mensah Samuel, Balla Sudarshan, Navaravong Leenhapong
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisIbrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.