Final ID: MP1310
Sex Differences in Oxidative Stress and Contributing Factors in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Oxidative stress, an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants, exacerbates metabolic syndrome and can worsen health outcomes. Females are at higher risk for inflammation, psychological stress, depressive symptoms, and obesity, all of which contribute to metabolic syndrome and elevated oxidative stress. However, sex differences in oxidative stress remain underexplored. We aimed to examine sex differences in oxidative stress and contributing factors in patients with metabolic syndrome.
Hypothesis: Females with metabolic syndrome have higher oxidative stress and contributing factors compared to males.
Methods: A secondary analysis of data from a randomized control trial was conducted to examine sex differences in oxidative stress (malondialdehyde, total antioxidant capacity) and contributing factors: inflammation (C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6), psychological stress (Perceived Stress Scale-10 (PSS-10)), depressive symptoms (patient health questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9)), and body mass index (BMI), using independent t-tests and Mann-Whitney U tests. Correlation and hierarchical linear regression were used to examine relationships between oxidative stress and potential contributing factors. To address the overrepresentation of females, we applied post-stratification weighting based on a standardized 50/50 sex distribution.
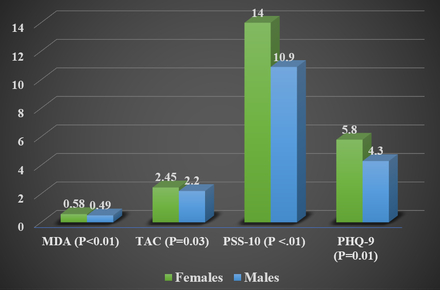
Results: Ninety-three participants with metabolic syndrome (61±12 years old, 71% female) were included. Females had higher malondialdehyde levels (0.58±0.17 vs 0.49±0.16, P<0.01), total antioxidant capacity (2.45±0.75 vs 2.20±0.76, P=0.03), PSS-10 (14.0±8.3 vs 10.9±5.6, P <0.01), and PHQ-9 (5.8±5.0 vs 4.3±3.2, P=0.01) compared to males. BMI and interleukin-6 had weak negative correlations with malondialdehyde (r=-.18, P=0.02 and r=-.19, P=0.02, respectively), while TNF-α had a moderate positive correlation with malondialdehyde (r=.25, P=0.003). Sex explained 7.4% of the variation of malondialdehyde values (P<0.001). The final regression model of sex, C-reactive protein, TNF-α, interleukin-6, BMI, PHQ-9, and PSS-10 explained 22.6% of the variation of malondialdehyde values (P=0.002).
Conclusion: Our findings reveal a disproportionately higher oxidative stress burden in females compared to males. Further longitudinal research is needed to investigate the sex-based differences and underlying mechanisms of oxidative stress across diverse populations.
Hypothesis: Females with metabolic syndrome have higher oxidative stress and contributing factors compared to males.
Methods: A secondary analysis of data from a randomized control trial was conducted to examine sex differences in oxidative stress (malondialdehyde, total antioxidant capacity) and contributing factors: inflammation (C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6), psychological stress (Perceived Stress Scale-10 (PSS-10)), depressive symptoms (patient health questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9)), and body mass index (BMI), using independent t-tests and Mann-Whitney U tests. Correlation and hierarchical linear regression were used to examine relationships between oxidative stress and potential contributing factors. To address the overrepresentation of females, we applied post-stratification weighting based on a standardized 50/50 sex distribution.
Results: Ninety-three participants with metabolic syndrome (61±12 years old, 71% female) were included. Females had higher malondialdehyde levels (0.58±0.17 vs 0.49±0.16, P<0.01), total antioxidant capacity (2.45±0.75 vs 2.20±0.76, P=0.03), PSS-10 (14.0±8.3 vs 10.9±5.6, P <0.01), and PHQ-9 (5.8±5.0 vs 4.3±3.2, P=0.01) compared to males. BMI and interleukin-6 had weak negative correlations with malondialdehyde (r=-.18, P=0.02 and r=-.19, P=0.02, respectively), while TNF-α had a moderate positive correlation with malondialdehyde (r=.25, P=0.003). Sex explained 7.4% of the variation of malondialdehyde values (P<0.001). The final regression model of sex, C-reactive protein, TNF-α, interleukin-6, BMI, PHQ-9, and PSS-10 explained 22.6% of the variation of malondialdehyde values (P=0.002).
Conclusion: Our findings reveal a disproportionately higher oxidative stress burden in females compared to males. Further longitudinal research is needed to investigate the sex-based differences and underlying mechanisms of oxidative stress across diverse populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abl1 kinase-deficient mouse hearts exhibit conduction disturbance and arrhythmia vulnerability to oxidative stress that are typically associated with age-related proarrhythmic remodeling
Choi Bum-rak, Bronk Peter, Li Xiaofei, Song Yi, Kim Tae Yun, Lu Yichun, Radice Glenn
Analysis of First Morning Urine Transcriptomes in Normotensive and Hypertensive Patients Identify Upregulated Inflammatory and Signaling Pathways Associated with HypertensionUmanath Kausik, Ortiz Pablo, Sohaney Ryann, Atchison Douglas, Abraham Emmy, Meng Ze, She Ruicong, Adrianto Indra, Levin Albert, Wu Andrew