Final ID: Mo2079
The Gut-Heart Axis: A Systematic Review of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction :Atherosclerosis, an immunoinflammatory disease of medium and large
arteries, involves endothelial cells, leukocytes, and smooth muscle cells, causing plaque formation and complications like myocardial infarction and strokes. While traditional risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and diabetes are established, emerging evidence highlights gut microbiota's role in atherosclerosis. Dysbiosis influences lipid metabolism, immune responses, and inflammation through metabolites like TMA and TMAO. This review explores evidence linking gut microbiota dysbiosis to atherosclerosis pathogenesis.
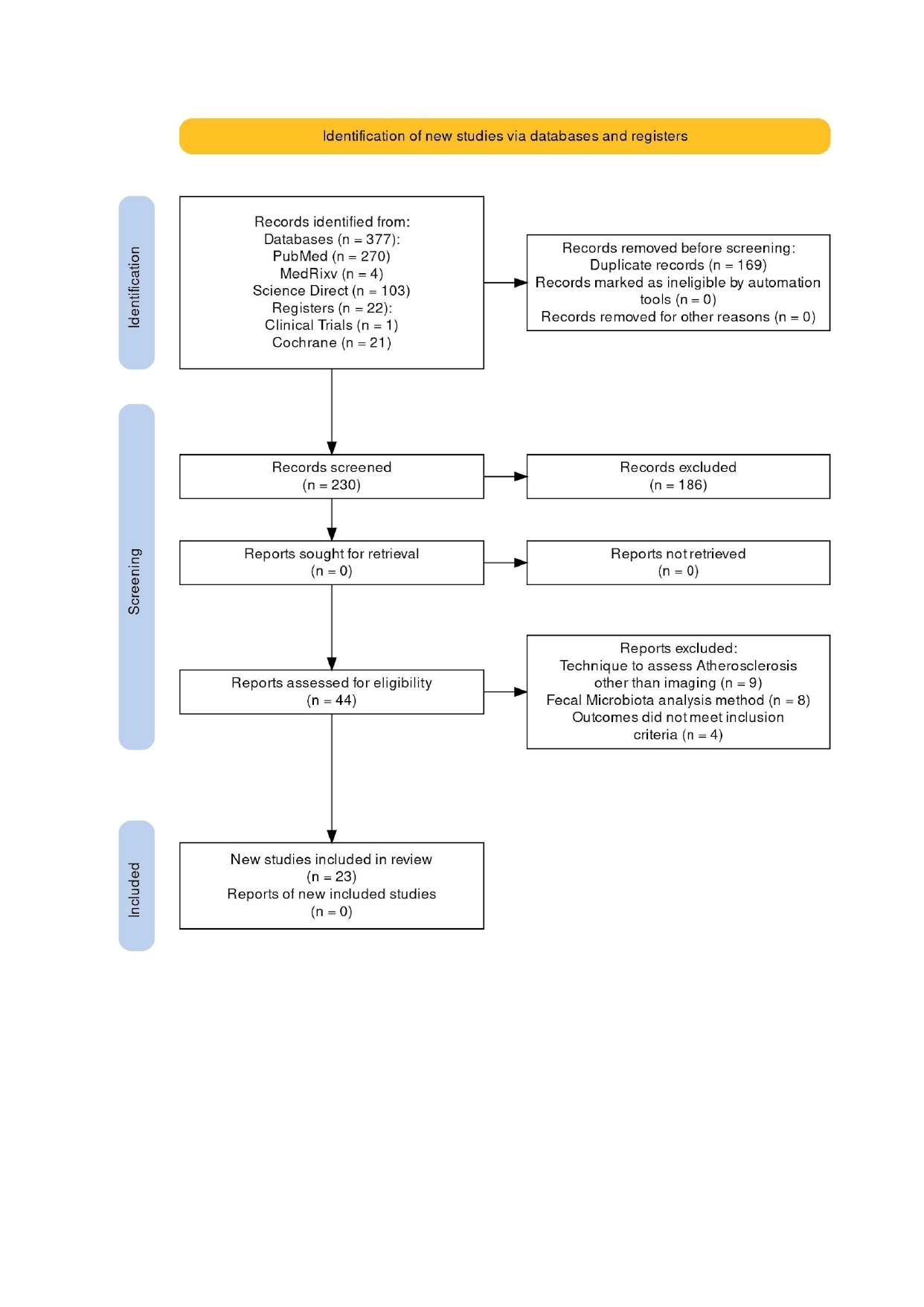
Methods: This systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines. Literature searches used
PubMed, medRxiv, ClinicalTrials.gov, ScienceDirect, and Cochrane databases with gut
microbiota and atherosclerosis keywords. Final search: May 4, 2023. Studies included
human participants, English reports, and CAD diagnosis via coronary imaging, excluding
preexisting CAD in controls. Multiple reviewers screened independently. Only peer-reviewed
literature included.
Results: 23 studies examined gut microbiota, microbial metabolites, and CAD. Most showed
dysbiosis correlated with atherosclerotic endpoints. In AMI patients, high gut-microbial
scores predicted twofold MACE risk over 3.2 years (HR 2.01; 95% CI 1.04–4.24) with higher
fecal acetate/butyrate and lower choline/carnitine versus controls. Lifestyle modification
reduced triglycerides 24% after 15 days and MetS prevalence 44.8% after 75 days, with
Akkermansia muciniphila enrichment. Elevated TMAO distinguished CHD patients (P <
0.001), highest in multivessel disease (P < 0.001), significant after risk factor adjustment (P
= 0.046). High-risk plaques (92.7% lipid-rich, 30.9% TCFA) associated with specific bacterial
enrichment. Phenylacetylglutamine independently predicted CAD (OR 1.17; P = 1.9×10^–3).
Conclusions: Gut microbiota and metabolites play crucial roles in CAD pathogenesis.
Dysbiosis correlates with inflammation, metabolic syndrome, and plaque development. Key
metabolites like TMAO present diagnostic and therapeutic targets. Further studies are needed to
establish causal relationships and develop microbiome-targeted cardiovascular
interventions.
arteries, involves endothelial cells, leukocytes, and smooth muscle cells, causing plaque formation and complications like myocardial infarction and strokes. While traditional risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and diabetes are established, emerging evidence highlights gut microbiota's role in atherosclerosis. Dysbiosis influences lipid metabolism, immune responses, and inflammation through metabolites like TMA and TMAO. This review explores evidence linking gut microbiota dysbiosis to atherosclerosis pathogenesis.
Methods: This systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines. Literature searches used
PubMed, medRxiv, ClinicalTrials.gov, ScienceDirect, and Cochrane databases with gut
microbiota and atherosclerosis keywords. Final search: May 4, 2023. Studies included
human participants, English reports, and CAD diagnosis via coronary imaging, excluding
preexisting CAD in controls. Multiple reviewers screened independently. Only peer-reviewed
literature included.
Results: 23 studies examined gut microbiota, microbial metabolites, and CAD. Most showed
dysbiosis correlated with atherosclerotic endpoints. In AMI patients, high gut-microbial
scores predicted twofold MACE risk over 3.2 years (HR 2.01; 95% CI 1.04–4.24) with higher
fecal acetate/butyrate and lower choline/carnitine versus controls. Lifestyle modification
reduced triglycerides 24% after 15 days and MetS prevalence 44.8% after 75 days, with
Akkermansia muciniphila enrichment. Elevated TMAO distinguished CHD patients (P <
0.001), highest in multivessel disease (P < 0.001), significant after risk factor adjustment (P
= 0.046). High-risk plaques (92.7% lipid-rich, 30.9% TCFA) associated with specific bacterial
enrichment. Phenylacetylglutamine independently predicted CAD (OR 1.17; P = 1.9×10^–3).
Conclusions: Gut microbiota and metabolites play crucial roles in CAD pathogenesis.
Dysbiosis correlates with inflammation, metabolic syndrome, and plaque development. Key
metabolites like TMAO present diagnostic and therapeutic targets. Further studies are needed to
establish causal relationships and develop microbiome-targeted cardiovascular
interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease
Jha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia
A murine model of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome demonstrates compromised limb function in the ischemic hind limbLotfollahzadeh Saran, Siracuse Jeffrey, Cabral Howard, Malikova Marina, Sayed Nazish, Chitalia Vipul