Final ID: 4363403
The Effect of Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide on Post-Operative Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetics Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Post-operative cardiovascular outcomes after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) in patients with type 2 diabetes pose unique and significant clinical challenges. Although both tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist, and semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, have demonstrated cardiovascular benefits in diabetic patients, their comparative effectiveness in this population post-CABG remains unclear- a gap this study aims to address.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that tirzepatide provides superior protection against post-operative complications compared to semaglutide in diabetic patients post-CABG based on the premise that dual agonism may offer enhanced metabolic benefits beyond GLP-1 receptor activation alone.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX global federated health research network (2022-2024), we analyzed 3,667 propensity score-matched pairs of type 2 diabetic adults (≥18 years old) on either tirzepatide or semaglutide after undergoing CABG. Outcomes measured at 6 months and 3 years included post-operative complications, cardiovascular outcomes, cerebrovascular outcomes, and healthcare utilization.
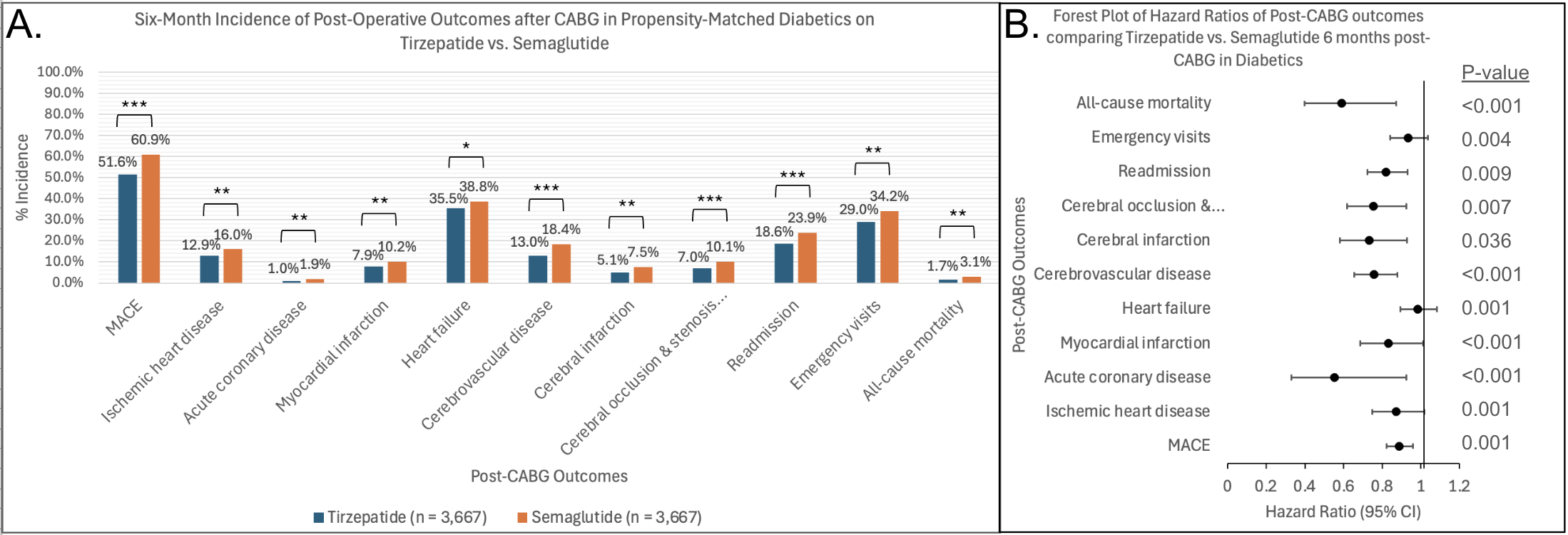
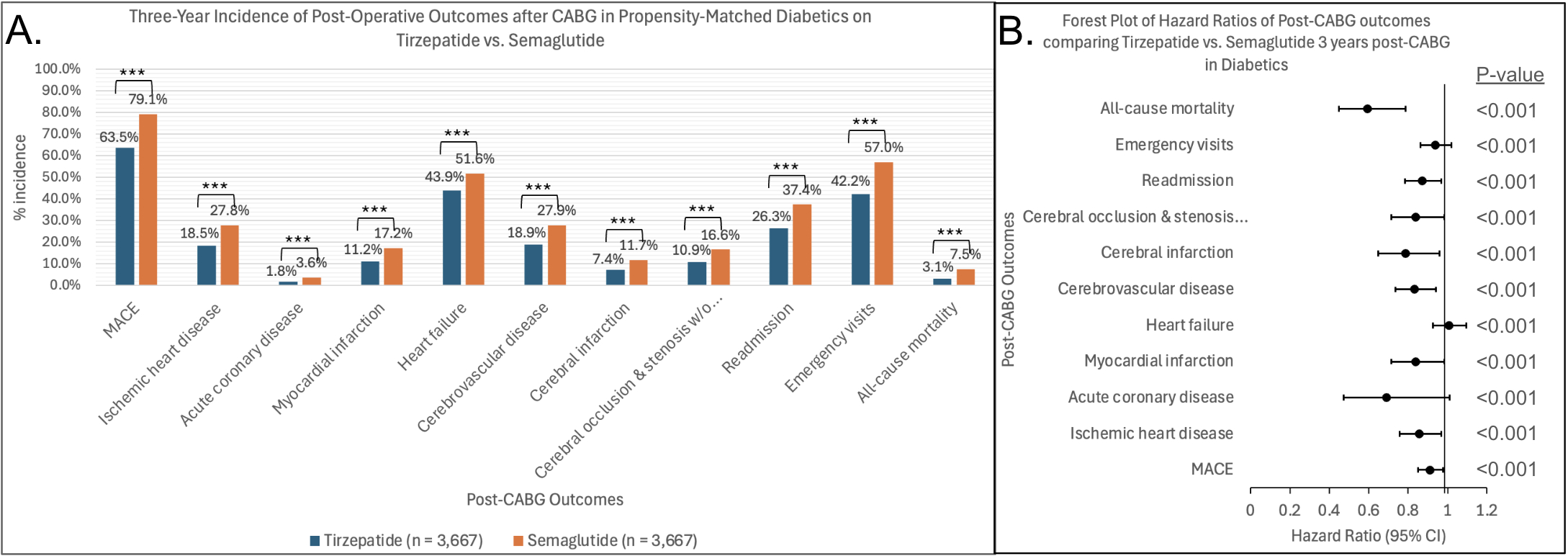
Results: At 6 months following CABG, tirzepatide use decreased adverse cardiovascular outcomes such as myocardial infarction (7.9% vs. 10.2%, HR=0.833, 95%CI=0.686-1.012, p=0.007) and MACE (51.6% vs. 60.9%, HR=0.889, 95%CI=0.822-0.960, p<0.001) compared to semaglutide. Statistical significance was maintained at 3 years post-CABG in MACE outcomes (63.7% vs. 79.1%, HR=0.911, 95%CI=0.850-0.976, p<0.001). Superior cerebrovascular protection with tirzepatide was also seen at 6 months following CABG with lower rates of cerebral infarction (5.1% vs. 7.5%, HR=0.733, 95%CI=0.580-0.927, p=0.001) and cerebrovascular disease (13.0% vs. 18.4%, HR=0.758, 95%CI=0.645-0.879, p<0.001) compared to semaglutide and sustained at 3 years. Both time points also showed tirzeptide use to have decreased readmissions, emergency visits, and all-cause mortality (3.1% vs. 7.5% at 3 years, HR=0.595, 95%CI=0.449-0.787, p<0.001).
Conclusions: Tirzepatide demonstrates superior cardiovascular and cerebrovascular protection, reduced healthcare utilization, and lower mortality compared to semaglutide in diabetic patients after CABG. These findings highlight the postoperative potential of GLP-1/GIP receptor agonism in this high-risk population.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that tirzepatide provides superior protection against post-operative complications compared to semaglutide in diabetic patients post-CABG based on the premise that dual agonism may offer enhanced metabolic benefits beyond GLP-1 receptor activation alone.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX global federated health research network (2022-2024), we analyzed 3,667 propensity score-matched pairs of type 2 diabetic adults (≥18 years old) on either tirzepatide or semaglutide after undergoing CABG. Outcomes measured at 6 months and 3 years included post-operative complications, cardiovascular outcomes, cerebrovascular outcomes, and healthcare utilization.
Results: At 6 months following CABG, tirzepatide use decreased adverse cardiovascular outcomes such as myocardial infarction (7.9% vs. 10.2%, HR=0.833, 95%CI=0.686-1.012, p=0.007) and MACE (51.6% vs. 60.9%, HR=0.889, 95%CI=0.822-0.960, p<0.001) compared to semaglutide. Statistical significance was maintained at 3 years post-CABG in MACE outcomes (63.7% vs. 79.1%, HR=0.911, 95%CI=0.850-0.976, p<0.001). Superior cerebrovascular protection with tirzepatide was also seen at 6 months following CABG with lower rates of cerebral infarction (5.1% vs. 7.5%, HR=0.733, 95%CI=0.580-0.927, p=0.001) and cerebrovascular disease (13.0% vs. 18.4%, HR=0.758, 95%CI=0.645-0.879, p<0.001) compared to semaglutide and sustained at 3 years. Both time points also showed tirzeptide use to have decreased readmissions, emergency visits, and all-cause mortality (3.1% vs. 7.5% at 3 years, HR=0.595, 95%CI=0.449-0.787, p<0.001).
Conclusions: Tirzepatide demonstrates superior cardiovascular and cerebrovascular protection, reduced healthcare utilization, and lower mortality compared to semaglutide in diabetic patients after CABG. These findings highlight the postoperative potential of GLP-1/GIP receptor agonism in this high-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Baseline Prevalence and Patterns of Dementia in Older Adults Referred for Coronary Revascularization after an Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Multicenter Study from an Integrated Healthcare System
Shin Edward, Damluji Abdulla, Yang Janine, Shah Ahmed, Krishnaswami Ashok, Jain Amanda, Ha Richard-tien, Canio Wynnelena, Romero Alicia, Gilsanz Paola, Dinh Howard, Aggarwal Neelum, Mielke Michelle
A Pilot Study of Post-Discharge Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Mobile Electrocardiography Monitoring DeviceIribarne Alexander, Kramer Robert, Moquete Ellen, Hupf Jonathan, Duncan Prezley, Mihelis Efstathia, Borger Michael, Muir Andrew, Starnes Vaughn, Edegran Albin, Fenton Kathleen, Patel Nirav, Taddei-peters Wendy, Moskowitz Alan, Ogara Patrick, Gelijns Annetine, Alexander John, Gillinov A, Bagiella Emilia, D'alessandro David, Dimaio John, Bhavnani Sanjeev, Badhwar Vinay, Sengupta Partho, Johnson Linda, Gajewska-dendek Elzbieta