Final ID: Sa4029
RUNX2, IBSP, and SPP1 as Key Molecular Nodes in Calcific Aortic Stenosis: Transcriptomic Diagnostics and Emerging Therapeutic Targets.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Calcific aortic stenosis (CAS) is the most common valvular disease in the elderly, with no approved pharmacological treatment to slow or reverse its progression. This study combined a systematic literature review (38 human-only studies, PRISMA criteria) with transcriptomic analysis of publicly available datasets (GSE51472 and GSE12644), including 35 human aortic valve samples (15 control, 15 calcified, 5 sclerotic). Differential expression was assessed using the Limma package, applying FDR correction (padj < 0.01) and fold change threshold (|FC| ≥ 1).
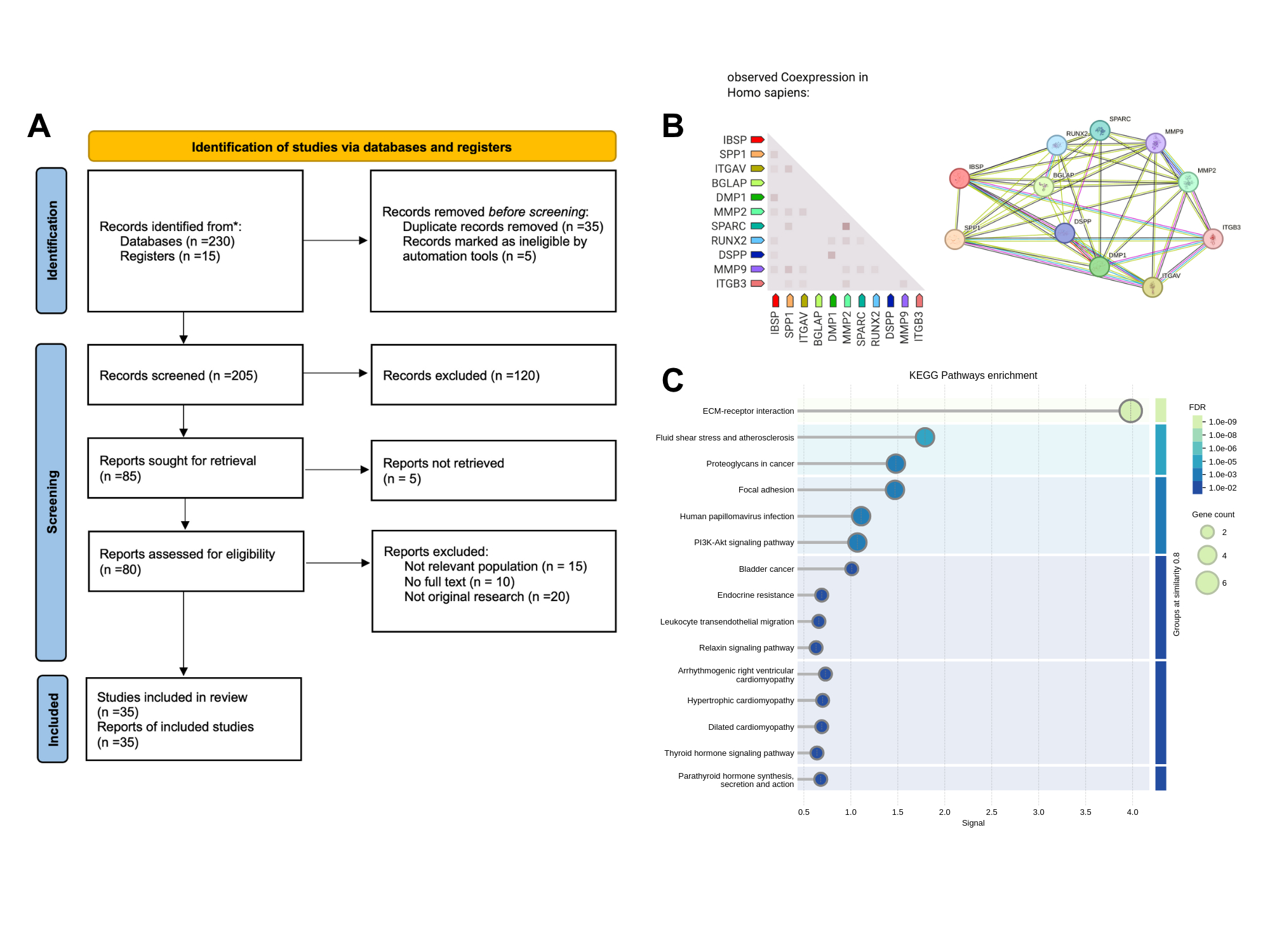
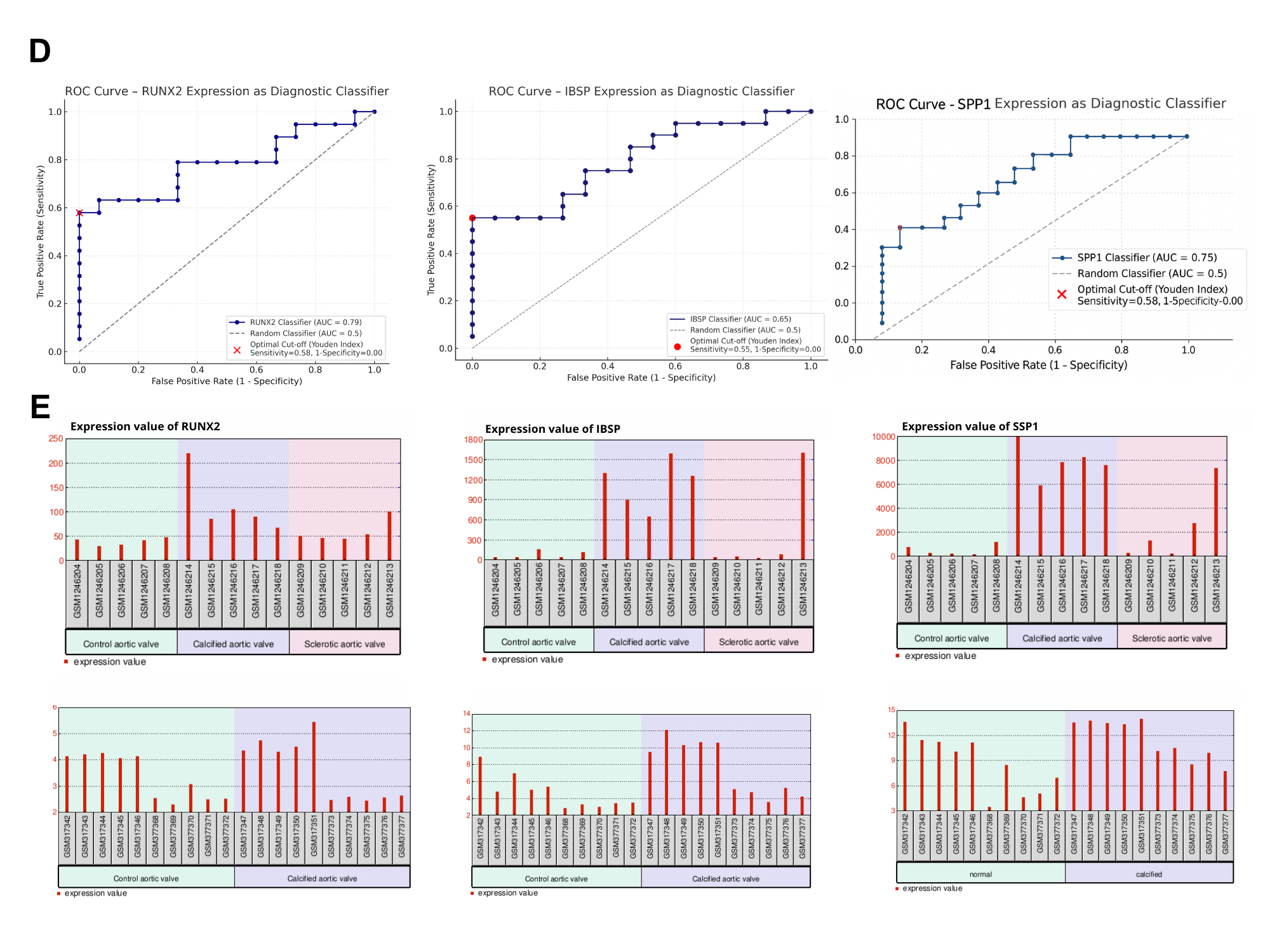
Key genes were identified based on significant overexpression and biological relevance. RUNX2, IBSP, and SPP1 emerged as central regulators linked to osteogenic transdifferentiation, immune modulation, and extracellular matrix remodeling. KEGG pathway analysis showed enrichment in ECM-receptor interaction, PI3K-Akt signaling. Coexpression and protein-protein interaction networks revealed strong functional clustering of these genes. ROC curve analysis yielded high diagnostic performance: AUC values were 0.79 (RUNX2), 0.65 (IBSP), and 0.75 (SPP1), indicating robust classification of diseased versus normal tissue. Expression levels rose progressively across control, calcified, and sclerotic valve samples.
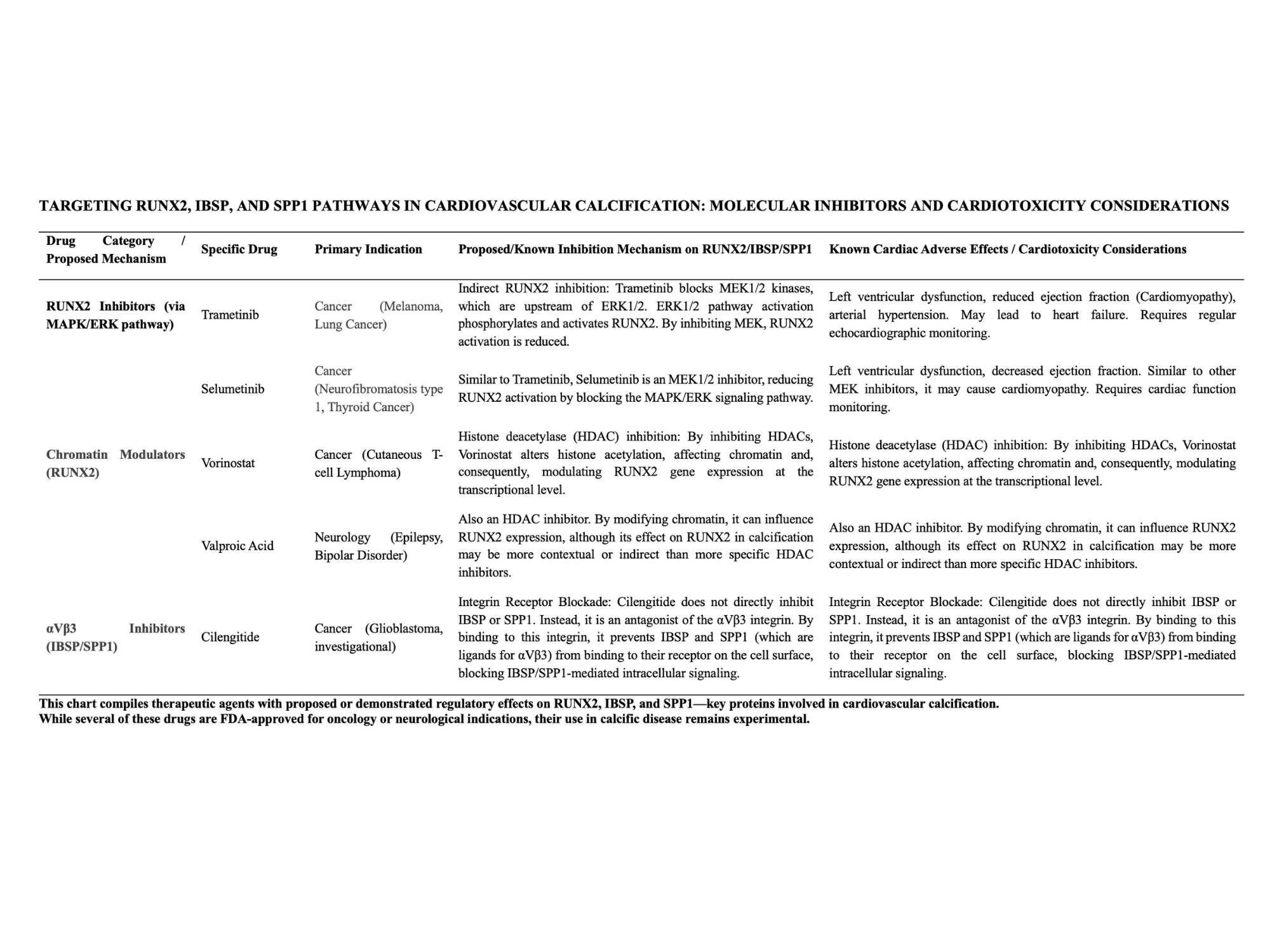
Drug repurposing candidates were identified targeting these molecules. MEK inhibitors (trametinib, selumetinib) downregulate RUNX2 via MAPK/ERK pathway inhibition. Epigenetic modulators (vorinostat, valproic acid) could suppress RUNX2 transcriptionally. The integrin antagonist cilengitide blocks αvβ3, disrupting IBSP/SPP1-mediated signaling. While these agents are approved for oncology or neurology, their utility in valve calcification remains investigational.
In summary, this study highlights RUNX2, IBSP, and SPP1 as transcriptomic biomarkers and actionable therapeutic targets in CAS. Their expression profiles, biological roles, and druggability make them high-priority candidates for future diagnostic tools and targeted interventions in a disease currently reliant on surgical replacement.
Key genes were identified based on significant overexpression and biological relevance. RUNX2, IBSP, and SPP1 emerged as central regulators linked to osteogenic transdifferentiation, immune modulation, and extracellular matrix remodeling. KEGG pathway analysis showed enrichment in ECM-receptor interaction, PI3K-Akt signaling. Coexpression and protein-protein interaction networks revealed strong functional clustering of these genes. ROC curve analysis yielded high diagnostic performance: AUC values were 0.79 (RUNX2), 0.65 (IBSP), and 0.75 (SPP1), indicating robust classification of diseased versus normal tissue. Expression levels rose progressively across control, calcified, and sclerotic valve samples.
Drug repurposing candidates were identified targeting these molecules. MEK inhibitors (trametinib, selumetinib) downregulate RUNX2 via MAPK/ERK pathway inhibition. Epigenetic modulators (vorinostat, valproic acid) could suppress RUNX2 transcriptionally. The integrin antagonist cilengitide blocks αvβ3, disrupting IBSP/SPP1-mediated signaling. While these agents are approved for oncology or neurology, their utility in valve calcification remains investigational.
In summary, this study highlights RUNX2, IBSP, and SPP1 as transcriptomic biomarkers and actionable therapeutic targets in CAS. Their expression profiles, biological roles, and druggability make them high-priority candidates for future diagnostic tools and targeted interventions in a disease currently reliant on surgical replacement.
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations of Long-Chain and Very-Long-Chain Saturated Fatty Acids with Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Li Jason, Brody Jennifer, Wiggins Kerri, Swenson Brenton, Jensen Paul, Bockus Lee, Lemaitre Rozenn, Sootedehnia Nona
AI-driven Aortic Valve Calcification Measurement in Coronary Artery Calcium Scan Detects Aortic Stenosis Comparably to Human Experts: An AI-CVD Study within the Framingham Heart StudyNaghavi Morteza, Atlas Kyle, Zhang Chenyu, Reeves Anthony, Atlas Thomas, Wasserthal Jakob, Yankelevitz David, Henschke Claudia, Wong Nathan