Final ID: Mo4084
In Vivo and Clinical Evidence of HDL Electronegativity in Atherogenicity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is classically recognized for its atheroprotective functions, including facilitating reverse cholesterol transport and reducing vascular inflammation and oxidative stress. However, growing evidence reveals that HDL is functionally heterogeneous. Human plasma HDL can be fractionated chromatographically into five subfractions (H1-H5), with increasing electronegativity and progressively impaired protective functions. H5, the most electronegative subfraction, is associated with increased inflammation, impaired cholesterol efflux capacity, and other features suggestive of a potential atherogenic role.
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical and mechanistic relevance of H5 in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), we performed a translational study integrating human data with in vivo mouse experiments. Given the elevated ASCVD risk among individuals with metabolic syndrome (MetS), we investigated correlations between H5 levels, the number of MetS criteria met, and key ASCVD-related risk indicators. We hypothesized that H5 enrichment contributes directly to vascular pathology.
Methods
Asymptomatic individuals (n=83) who met diagnostic criteria for MetS and exhibited at least one ASCVD risk factor were enrolled. Carotid artery ultrasonography was used to measure stenosis as a surrogate of subclinical ASCVD. To explore causality, purified human H5 was intravenously administered to C57BL/6J mice. H1, the least electronegative HDL subfraction, and saline served as controls. Aortic lipid deposition and fibrosis were assessed via Oil Red O and Picro-Sirius Red staining, respectively.
Results
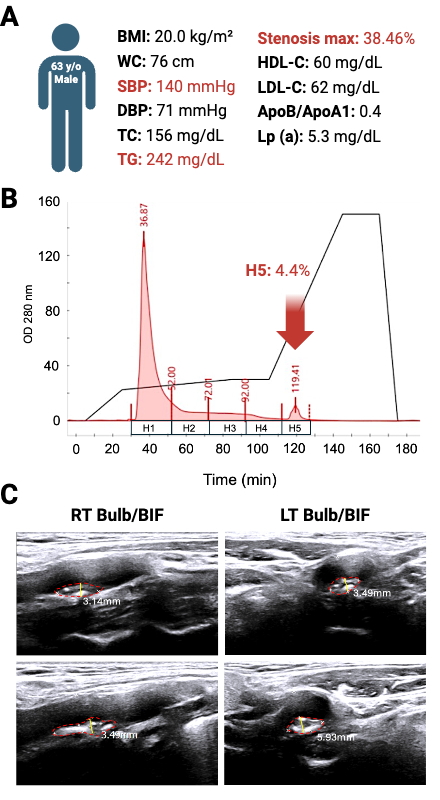
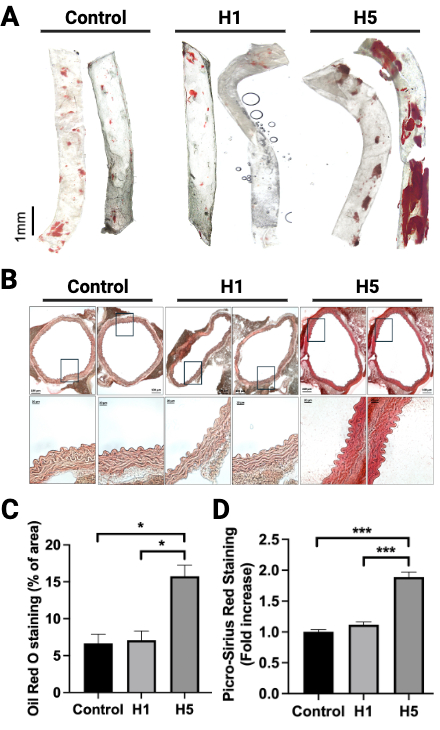
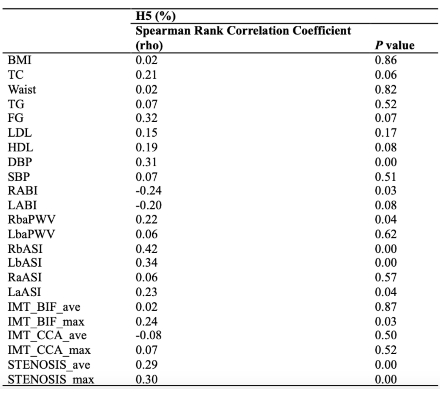
Plasma H5% positively correlated with systolic blood pressure, ankle-brachial index (ABI), and carotid artery stenosis (Table 1). A representative case of a 63-year-old male with T2DM and a MetS history—yet otherwise favorable lipid profile—revealed 38.46% carotid stenosis associated with elevated H5 (4.4%), despite no history of statin use (Figure 1). In vivo, H5-treated mice exhibited marked lipid-rich aortic plaques and increased collagen deposition, while H1 and saline controls showed minimal pathology (Figure 2).
Conclusion
This study provides both clinical and experimental evidence that electronegative HDL, specifically H5, contributes to vascular dysfunction and ASCVD progression. H5 may serve as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target, enabling more refined cardiovascular risk stratification and personalized preventive strategies.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is classically recognized for its atheroprotective functions, including facilitating reverse cholesterol transport and reducing vascular inflammation and oxidative stress. However, growing evidence reveals that HDL is functionally heterogeneous. Human plasma HDL can be fractionated chromatographically into five subfractions (H1-H5), with increasing electronegativity and progressively impaired protective functions. H5, the most electronegative subfraction, is associated with increased inflammation, impaired cholesterol efflux capacity, and other features suggestive of a potential atherogenic role.
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical and mechanistic relevance of H5 in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), we performed a translational study integrating human data with in vivo mouse experiments. Given the elevated ASCVD risk among individuals with metabolic syndrome (MetS), we investigated correlations between H5 levels, the number of MetS criteria met, and key ASCVD-related risk indicators. We hypothesized that H5 enrichment contributes directly to vascular pathology.
Methods
Asymptomatic individuals (n=83) who met diagnostic criteria for MetS and exhibited at least one ASCVD risk factor were enrolled. Carotid artery ultrasonography was used to measure stenosis as a surrogate of subclinical ASCVD. To explore causality, purified human H5 was intravenously administered to C57BL/6J mice. H1, the least electronegative HDL subfraction, and saline served as controls. Aortic lipid deposition and fibrosis were assessed via Oil Red O and Picro-Sirius Red staining, respectively.
Results
Plasma H5% positively correlated with systolic blood pressure, ankle-brachial index (ABI), and carotid artery stenosis (Table 1). A representative case of a 63-year-old male with T2DM and a MetS history—yet otherwise favorable lipid profile—revealed 38.46% carotid stenosis associated with elevated H5 (4.4%), despite no history of statin use (Figure 1). In vivo, H5-treated mice exhibited marked lipid-rich aortic plaques and increased collagen deposition, while H1 and saline controls showed minimal pathology (Figure 2).
Conclusion
This study provides both clinical and experimental evidence that electronegative HDL, specifically H5, contributes to vascular dysfunction and ASCVD progression. H5 may serve as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target, enabling more refined cardiovascular risk stratification and personalized preventive strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Genome-wide CRISPRi Screen Implicates Coronary Artery Disease GWAS Genes as Key Regulators of Adventitial Fibroblast Proliferation
Jackson William, Zhu Ashley, Gu Wenduo, Berezowitz Alexa, Iyer Meghana, Cheng Paul
Additive Value of Lipoprotein(a), Remnant Cholesterol, and Inflammation for Risk Stratification of Myocardial Infarction: Evidence from the UK BiobankKazibwe Richard, Schaich Christopher, Kingsley Jeffrey, Rikhi Rishi, Namutebi Juliana, Chevli Parag, Mirzai Saeid, Shapiro Michael