Final ID: Su2019
Uncontrolled hypertension is associated with high healthcare resource utilization: Observations from the EnligHTN study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Despite the availability of various treatment options, uncontrolled hypertension (HTN) remains prevalent, significantly increasing risks of cardiorenal disease and mortality, and underscores the urgency of greater engagement from healthcare providers and burden for healthcare systems. We aimed to characterize healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) among patients with uncontrolled HTN across several countries.
Methods:
In this multi-country database cohort study, data from Telotròn (Spain (ESP)), IQVIA Ambulatory EMR linked with IQVIA PharMetrics® Plus claims (US), Clinical Practice Research Datalink (UK) and Meuhedet (Israel (ISR)) from 2018 to 2023 were used, with data anticipated from additional countries. Patients were included if they had a diagnosis of HTN and their first blood pressure (BP) measurement; were being treated with ≥2 antihypertensive medications for ≥30 days (index date) and were above the BP target (US: ≥130/80 mmHg; UK, ESP, and ISR: ≥140/90 mmHg), indicating uncontrolled HTN. Patient characteristics and all-cause HCRU were analyzed descriptively.
Results:
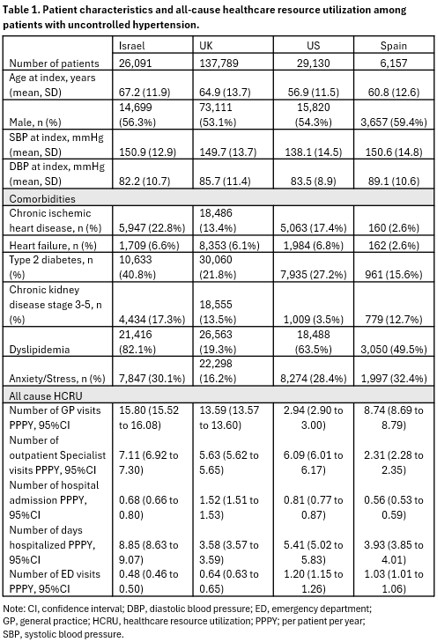
A total of 199,167 patients with uncontrolled HTN were included (Table 1). The mean age ranged from 56.9 – 67.2 years and 40.6% – 46.9% were female. Mean age was the highest in ISR (67.2 years; standard deviation (SD) 11.9) and lowest in the US (56.9 years; SD 11.5). General practice visit rates were highest in ISR, followed by the UK, ESP and the US. The number of outpatient specialist visits ranged from 2.31 (95%CI 2.28, 2.35) in ESP to 7.11 (6.92, 7.30) per person per year (PPPY) in ISR. The number of hospital admissions ranged between 0.56 (95%CI; 0.53, 0.59) in ESP and 1.52 in the UK (95%CI; 1.51, 1.53) PPPY with mean number of days hospitalized between 3.58 (95%CI; 3.57, 3.59) and 8.85 (95%CI; 8.63, 9.07) PPPY. Lastly, the number of emergency department visits varied the most between the US (1.20 (95%CI; 1.15, 1.26)) and ISR (0.48 (95%CI; 0.46, 0.50)).
Conclusions:
Uncontrolled HTN is associated with a substantial burden on healthcare resources. Patterns of HCRU varied across countries, likely reflecting differences in healthcare systems, clinical practice, definitions of uncontrolled HTN and patient demographics.
Despite the availability of various treatment options, uncontrolled hypertension (HTN) remains prevalent, significantly increasing risks of cardiorenal disease and mortality, and underscores the urgency of greater engagement from healthcare providers and burden for healthcare systems. We aimed to characterize healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) among patients with uncontrolled HTN across several countries.
Methods:
In this multi-country database cohort study, data from Telotròn (Spain (ESP)), IQVIA Ambulatory EMR linked with IQVIA PharMetrics® Plus claims (US), Clinical Practice Research Datalink (UK) and Meuhedet (Israel (ISR)) from 2018 to 2023 were used, with data anticipated from additional countries. Patients were included if they had a diagnosis of HTN and their first blood pressure (BP) measurement; were being treated with ≥2 antihypertensive medications for ≥30 days (index date) and were above the BP target (US: ≥130/80 mmHg; UK, ESP, and ISR: ≥140/90 mmHg), indicating uncontrolled HTN. Patient characteristics and all-cause HCRU were analyzed descriptively.
Results:
A total of 199,167 patients with uncontrolled HTN were included (Table 1). The mean age ranged from 56.9 – 67.2 years and 40.6% – 46.9% were female. Mean age was the highest in ISR (67.2 years; standard deviation (SD) 11.9) and lowest in the US (56.9 years; SD 11.5). General practice visit rates were highest in ISR, followed by the UK, ESP and the US. The number of outpatient specialist visits ranged from 2.31 (95%CI 2.28, 2.35) in ESP to 7.11 (6.92, 7.30) per person per year (PPPY) in ISR. The number of hospital admissions ranged between 0.56 (95%CI; 0.53, 0.59) in ESP and 1.52 in the UK (95%CI; 1.51, 1.53) PPPY with mean number of days hospitalized between 3.58 (95%CI; 3.57, 3.59) and 8.85 (95%CI; 8.63, 9.07) PPPY. Lastly, the number of emergency department visits varied the most between the US (1.20 (95%CI; 1.15, 1.26)) and ISR (0.48 (95%CI; 0.46, 0.50)).
Conclusions:
Uncontrolled HTN is associated with a substantial burden on healthcare resources. Patterns of HCRU varied across countries, likely reflecting differences in healthcare systems, clinical practice, definitions of uncontrolled HTN and patient demographics.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled Hypertension
Nandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan
A durable reduction in blood pressure by ultrasound renal denervation: A real-world, single center experienceKing Jordan, Gharib Wissam