Final ID: MP1498
Impact of LDL-C and Apolipoprotein B Discordance and Associated Lipoprotein Particle Changes on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in a Large Primary Prevention Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Emerging evidence suggests that ApoB outperforms LDL-C in predicting cardiovascular risk, especially in cases of discordance with the two. However, the specific type and composition of lipoprotein particles in this situation remain unclear. Therefore, our study aimed to assess cardiovascular risk in individuals with discordant LDL-C and ApoB levels and explore the associated changes in lipoprotein particles.
Research Question: What are the associated changes in lipoprotein particle composition in individuals with discordant ApoB and LDL-C levels?
Methods: 274,243 individuals were enrolled from the UK Biobank without baseline cardiovascular disease, not on lipid-lowering therapy, and with available lipid nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data. Based on whether the absolute difference in baseline percentile of LDL-C and ApoB level was over 10 units, participants were categorized into concordant group, discordantly high ApoB group (ApoB percentile rank minus LDL-C percentile rank > 10 units), and discordantly low ApoB group (LDL-C percentile rank minus ApoB percentile rank > 10 units). The median follow-up duration was 10.9 years, with major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) as the primary endpoint.
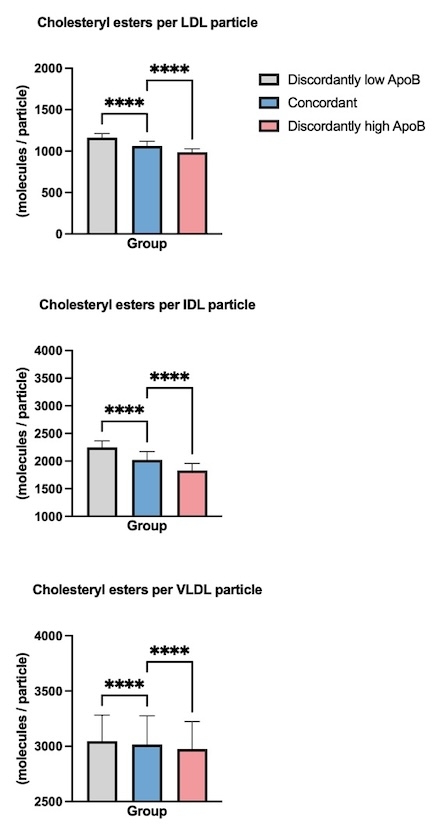
Results: Cox regression analysis (Image 1) showed that the risk of MACE was increased in the discordantly high ApoB group (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.10-1.21; P < 0.001) and reduced in the discordantly low ApoB group (HR, 0.75; 95% CI:0.71-0.81; P < 0.001). Compared to the other two groups, the discordantly high ApoB group exhibited the highest concentrations of VLDL-C, VLDL cholesteryl ester (CE), and VLDL particles. However, the CE content per LDL, IDL, and VLDL particle was lower in this group (Image 2). Mediation analysis (Image 3) revealed that VLDL-C and VLDL particle concentration mediated 41.13% and 25.46% of the MACE risk, respectively, in the discordantly high ApoB group (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: ApoB is a more comprehensive marker of cardiovascular risk, with increased ApoB in discordant group mainly driven by VLDL particles, highlighting the importance of VLDL management in individuals with discordant LDL-C and ApoB levels.
Research Question: What are the associated changes in lipoprotein particle composition in individuals with discordant ApoB and LDL-C levels?
Methods: 274,243 individuals were enrolled from the UK Biobank without baseline cardiovascular disease, not on lipid-lowering therapy, and with available lipid nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data. Based on whether the absolute difference in baseline percentile of LDL-C and ApoB level was over 10 units, participants were categorized into concordant group, discordantly high ApoB group (ApoB percentile rank minus LDL-C percentile rank > 10 units), and discordantly low ApoB group (LDL-C percentile rank minus ApoB percentile rank > 10 units). The median follow-up duration was 10.9 years, with major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) as the primary endpoint.
Results: Cox regression analysis (Image 1) showed that the risk of MACE was increased in the discordantly high ApoB group (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.10-1.21; P < 0.001) and reduced in the discordantly low ApoB group (HR, 0.75; 95% CI:0.71-0.81; P < 0.001). Compared to the other two groups, the discordantly high ApoB group exhibited the highest concentrations of VLDL-C, VLDL cholesteryl ester (CE), and VLDL particles. However, the CE content per LDL, IDL, and VLDL particle was lower in this group (Image 2). Mediation analysis (Image 3) revealed that VLDL-C and VLDL particle concentration mediated 41.13% and 25.46% of the MACE risk, respectively, in the discordantly high ApoB group (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: ApoB is a more comprehensive marker of cardiovascular risk, with increased ApoB in discordant group mainly driven by VLDL particles, highlighting the importance of VLDL management in individuals with discordant LDL-C and ApoB levels.
More abstracts on this topic:
Apolipoprotein A-I Proteoforms, Cardiometabolic Status, and Coronary Heart Disease: Insights from the Dallas Heart Study
Gangwar Anamika, Des Soye Benjamin, Saldanha Suzanne, Jaiswal Shailesh, Patel Parthvi Bharatkumar, Shah Amil, Pandey Ambarish, Wilkins John, Rohatgi Anand
Assessing Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with New Onset Diabetes After Statin InitiationSchaaf Lucas, Nadar Priyanka, Gebrehiwot Ledya, Jean-marie Elizabeth, Simon Steven, Rosenberg Michael