Final ID: MP1194
Integrating Polygenic and Clinical Risk Factors Enhances Stability of Coronary Artery Disease Risk Prediction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction
The interest in using Polygenic Risk Scores (PRSs) for CAD risk assessment is growing, but variability in individual risk estimates between different PRS models is a significant concern for their use in primary prevention treatment guidance. This study examines the impact of integrating PRSs with an established clinical model in reducing variability and stabilizing the classification of high-risk individuals.
Methods
Using a cohort of 195,688 participants (6,751 incident cases) from the UK Biobank, who were CAD-free at baseline, we compared the stability of PRS-only models with those integrated with the Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) for 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk assessment. We analyzed 14 CAD PRSs from the PGS catalog, developed independently of UK Biobank, and ensemble PRS models combining multiple scores. We used the coefficient of variation (CV) as a scale-independent metric to compare individual-level prediction variability between PRS percentiles and absolute risk estimates from integrated PRS models. To evaluate agreement in classifying high-risk participants, we used the Jaccard index.
Results
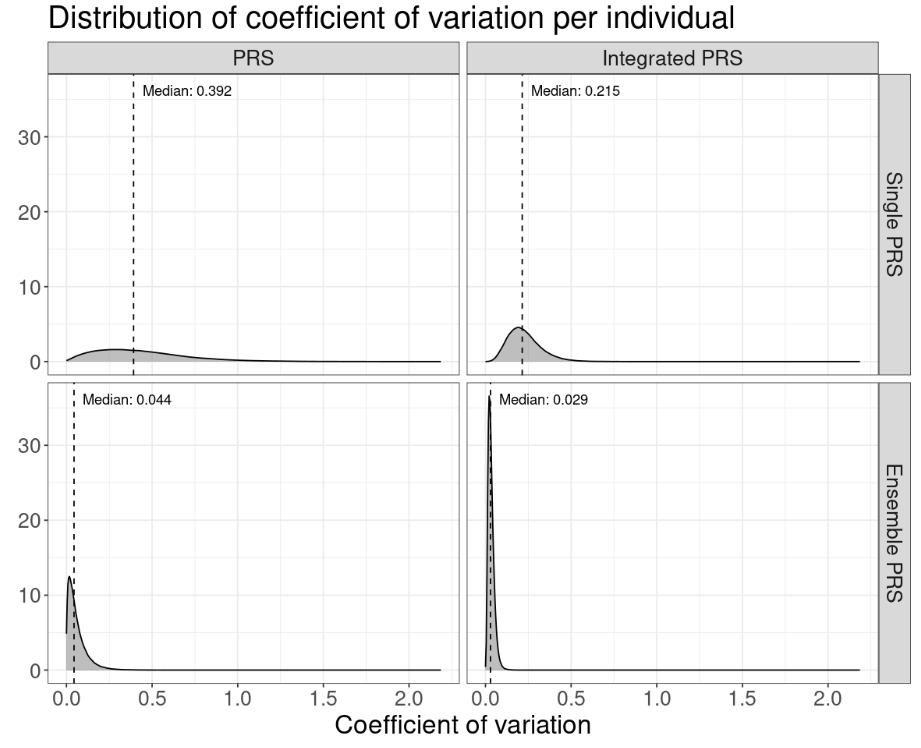
The variability in individual-level risk estimates from models integrating PRS with ASCVD-PCE was lower than predictions based solely on PRS. The CV of individual-level predictions across the top 5 PRSs was 0.392, compared to 0.215 for the corresponding integrated models. Combining PRSs into ensembles further stabilised predictions, with a median CV of 0.044 and 0.029 across the top 5 PRS ensembles and their integrated models, respectively.
Consistency in classifying high-risk individuals also improved upon integrating PRS with ASCVD-PCE. The median Jaccard index for single PRS-based classifications (top 5%) was 0.113, compared to 0.497 for the integrated PRS (≥7.5% absolute risk). Similarly, the median Jaccard index was 0.262 for ensemble PRSs and 0.59 for their integrated PRS. Notably, classification concordance improved with successive PRS ensemble iterations (incorporating newly released PRSs), with the Jaccard index ranging from 0.86 to 0.97 between the 5 latest integrated PRS ensembles.
Conclusions
Integrating PRSs with clinical risk factors enhances the accuracy and stability of CAD risk predictions, making it superior in comparison to classification based solely on PRS percentiles. Ensemble PRS models present a promising method for incorporating newly developed PRSs, further boosting performance and stability.
Introduction
The interest in using Polygenic Risk Scores (PRSs) for CAD risk assessment is growing, but variability in individual risk estimates between different PRS models is a significant concern for their use in primary prevention treatment guidance. This study examines the impact of integrating PRSs with an established clinical model in reducing variability and stabilizing the classification of high-risk individuals.
Methods
Using a cohort of 195,688 participants (6,751 incident cases) from the UK Biobank, who were CAD-free at baseline, we compared the stability of PRS-only models with those integrated with the Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) for 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk assessment. We analyzed 14 CAD PRSs from the PGS catalog, developed independently of UK Biobank, and ensemble PRS models combining multiple scores. We used the coefficient of variation (CV) as a scale-independent metric to compare individual-level prediction variability between PRS percentiles and absolute risk estimates from integrated PRS models. To evaluate agreement in classifying high-risk participants, we used the Jaccard index.
Results
The variability in individual-level risk estimates from models integrating PRS with ASCVD-PCE was lower than predictions based solely on PRS. The CV of individual-level predictions across the top 5 PRSs was 0.392, compared to 0.215 for the corresponding integrated models. Combining PRSs into ensembles further stabilised predictions, with a median CV of 0.044 and 0.029 across the top 5 PRS ensembles and their integrated models, respectively.
Consistency in classifying high-risk individuals also improved upon integrating PRS with ASCVD-PCE. The median Jaccard index for single PRS-based classifications (top 5%) was 0.113, compared to 0.497 for the integrated PRS (≥7.5% absolute risk). Similarly, the median Jaccard index was 0.262 for ensemble PRSs and 0.59 for their integrated PRS. Notably, classification concordance improved with successive PRS ensemble iterations (incorporating newly released PRSs), with the Jaccard index ranging from 0.86 to 0.97 between the 5 latest integrated PRS ensembles.
Conclusions
Integrating PRSs with clinical risk factors enhances the accuracy and stability of CAD risk predictions, making it superior in comparison to classification based solely on PRS percentiles. Ensemble PRS models present a promising method for incorporating newly developed PRSs, further boosting performance and stability.
More abstracts on this topic:
A New Comprehensive Parameter Residual C-Reactive Protein And Neutrophil Risk Predict Adverse Events In Chinese Patients After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: a National Multi-Center Prospective Cohort Study
Yang Fen, Yu Miao, Cheng Xiang
A novel method for measuring HDL-bound unconjugated bilirubin using an eel fluorescent protein reveals its association with reduced coronary artery diseaseFujioka Tomoo, Iino Takuya, Toh Ryuji, Harada Amane, Nagao Manabu, Shinohara Masakazu, Ishida Tatsuro, Otake Hiromasa