Final ID: MP1608
Preoperative Blood Biomarkers Outperform Clinical Variables in Predicting Poor Outcome After Neonatal Cardiopulmonary Bypass Surgery
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Neonates undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease (CHD) are at risk of death, longer intensive care unit (ICU) stays, and readmissions. Current prognostic models rely predominantly on unmodifiable clinical factors.
Aims: We aimed to compare machine learning methods for predicting ICU-30, a validated composite outcome after neonatal surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), using pre-operative blood biomarkers versus clinical features.
Hypothesis: Inflammatory and organ injury biomarkers will predict ICU-30 better than clinical factors alone.
Methods: Plasma and clinical data were collected from consecutively enrolled neonates (<30 days of age) immediately before CPB. Twenty-eight biomarkers were measured via individual or multiplexed ELISA and tested for association with ICU-30, defined as (1) mortality within 30 days of CPB, (2) ICU stay >30 days after CPB, or (3) ICU readmission within 30 days after CPB. Predictive performance of the machine learning techniques XGBoost, LASSO, and random forest (RF) were compared based on area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve. For XGBoost, we identified the top 20 features based on importance (gain) to the model.
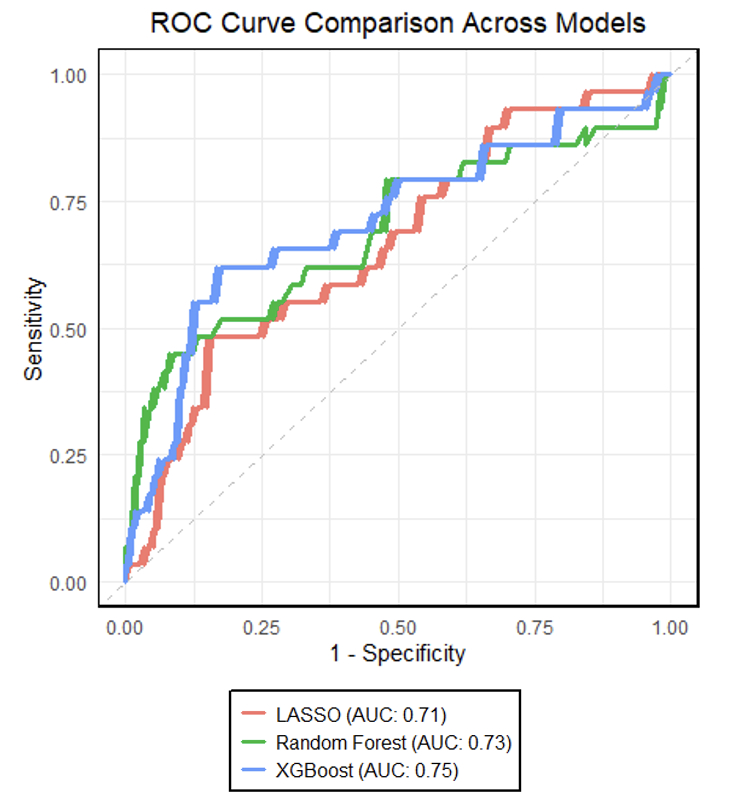
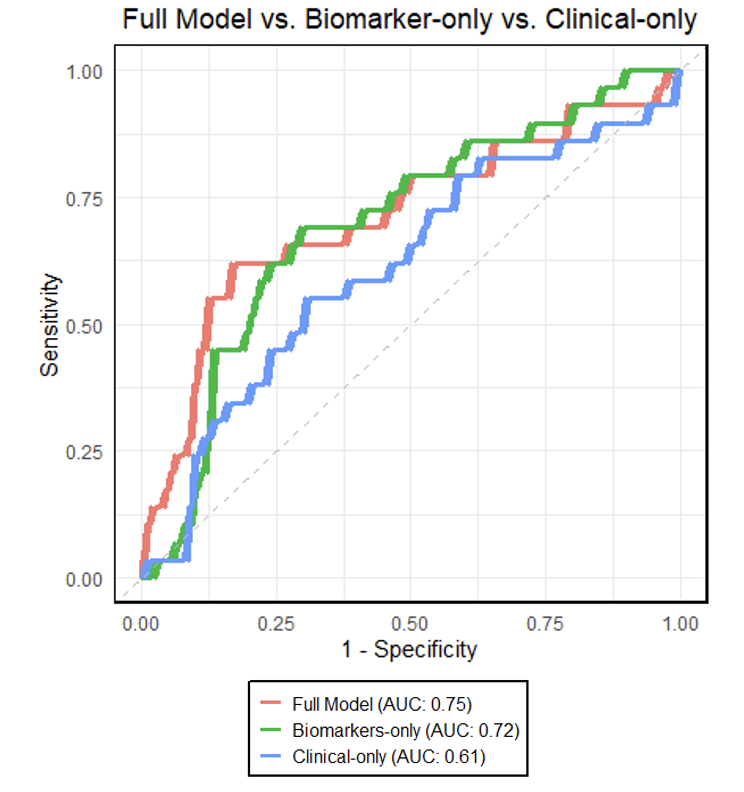
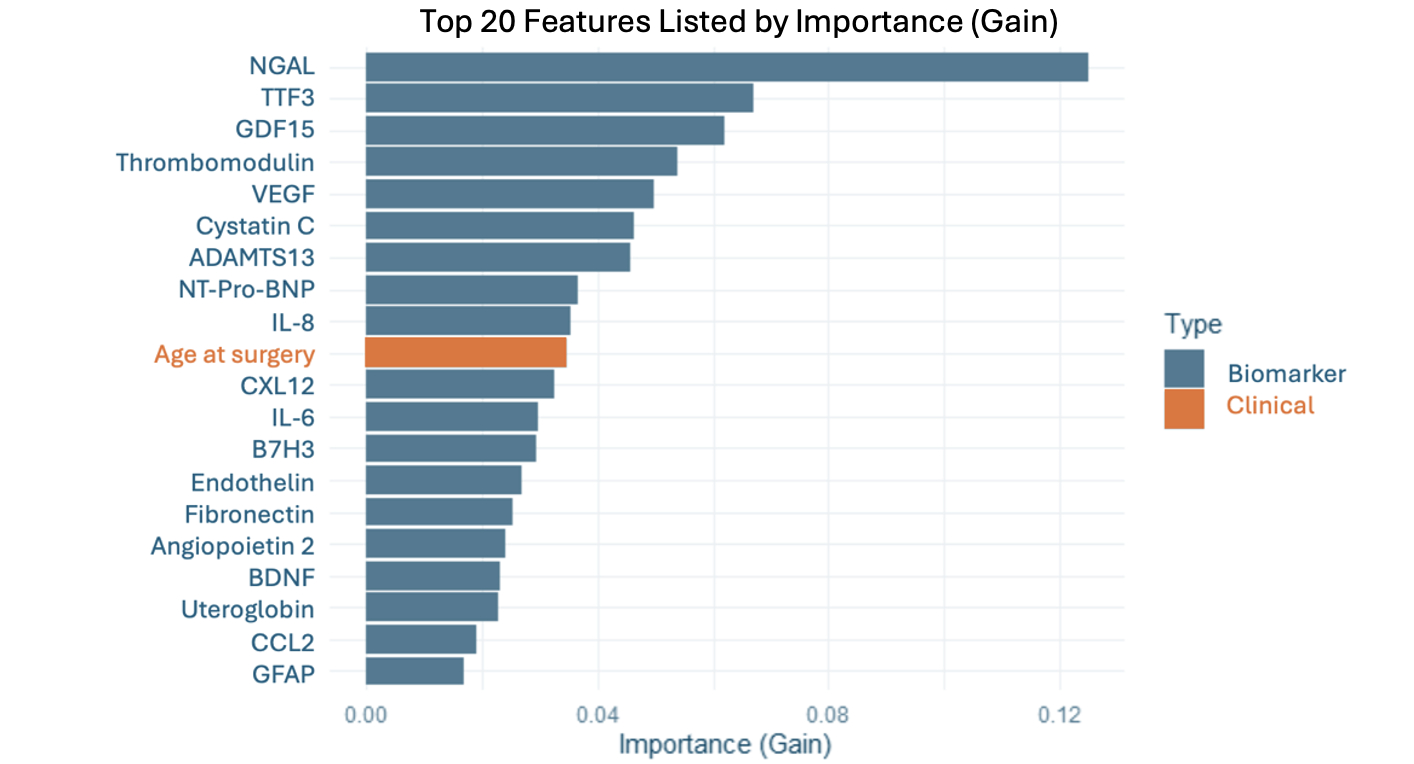
Results: Biomarkers were available for 144 patients. Most were male (51%), White (64%), and non-Hispanic (75%). Median age at surgery was 3.6 days (IQR 2.6-5.2). Most operations were STAT 3 (32%) or STAT 5 (28%). ICU-30 occurred in 29 (20%) subjects. Using clinical and biomarker data, XGBoost performed moderately well (AUROC 0.75) to predict ICU-30, and was superior to RF (AUROC 0.73) and LASSO (AUROC 0.71) (Figure 1). Biomarkers alone performed better (AUROC 0.72) than clinical data alone (AUROC 0.61) (Figure 2). For XGBoost, 19 of the top 20 features were biomarkers, with the top 3 being neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), trefoil factor 3 (TTF3) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) (Figure 3).
Conclusions: This preliminary data demonstrates moderate performance of a multi-biomarker model for predicting poor outcome post-CPB for neonatal CHD. A biomarker-only model outperformed a clinical-only model. Two of the top three most important features were biomarkers for renal and gut inflammation, suggesting preoperative splanchnic inflammation may be relevant for postoperative outcomes. Further investigation may identify mechanistic pathways for improved prognostication and could offer insights for targeted therapeutic interventions.
Aims: We aimed to compare machine learning methods for predicting ICU-30, a validated composite outcome after neonatal surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), using pre-operative blood biomarkers versus clinical features.
Hypothesis: Inflammatory and organ injury biomarkers will predict ICU-30 better than clinical factors alone.
Methods: Plasma and clinical data were collected from consecutively enrolled neonates (<30 days of age) immediately before CPB. Twenty-eight biomarkers were measured via individual or multiplexed ELISA and tested for association with ICU-30, defined as (1) mortality within 30 days of CPB, (2) ICU stay >30 days after CPB, or (3) ICU readmission within 30 days after CPB. Predictive performance of the machine learning techniques XGBoost, LASSO, and random forest (RF) were compared based on area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve. For XGBoost, we identified the top 20 features based on importance (gain) to the model.
Results: Biomarkers were available for 144 patients. Most were male (51%), White (64%), and non-Hispanic (75%). Median age at surgery was 3.6 days (IQR 2.6-5.2). Most operations were STAT 3 (32%) or STAT 5 (28%). ICU-30 occurred in 29 (20%) subjects. Using clinical and biomarker data, XGBoost performed moderately well (AUROC 0.75) to predict ICU-30, and was superior to RF (AUROC 0.73) and LASSO (AUROC 0.71) (Figure 1). Biomarkers alone performed better (AUROC 0.72) than clinical data alone (AUROC 0.61) (Figure 2). For XGBoost, 19 of the top 20 features were biomarkers, with the top 3 being neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), trefoil factor 3 (TTF3) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) (Figure 3).
Conclusions: This preliminary data demonstrates moderate performance of a multi-biomarker model for predicting poor outcome post-CPB for neonatal CHD. A biomarker-only model outperformed a clinical-only model. Two of the top three most important features were biomarkers for renal and gut inflammation, suggesting preoperative splanchnic inflammation may be relevant for postoperative outcomes. Further investigation may identify mechanistic pathways for improved prognostication and could offer insights for targeted therapeutic interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Hard Start: Early, Intensive Healthcare Utilization for Children with Critical Congenital Heart Disease
Ellis Danielle, Hall Matthew, Blume Elizabeth, Wolfe Joanne, Snaman Jennifer, Berry Jay
Efficacy of Restrictive versus Liberal Oxygenation in Patients undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting or Aortic Valve Replacement – a randomized clinical trialWiberg Sebastian, Boesgaard Soeren, Hassager Christian, Kober Lars, Nilsson Jens Christian, Moeller Christian Holdflod, Kjaergaard Jesper, Mikkelsen Astrid, Møller-sørensen Peter Hasse, Olsen Peter Skov, Høfsten Dan, Ravn Jesper, Ravn Hanne Berg