Final ID: MP237
Metabolic pathways differ in Black adults with heart failure with and without diabetes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Black adults experience disproportionately high rates of heart failure (HF) and type 2 diabetes (DM). Comorbid HF and DM pose unique clinical challenges and are accompanied by significant health disparities. The metabolic mechanisms underlying these comorbidities are not well understood.
Objective: To identify differential metabolic pathways in Black adults with HF with and without comorbid DM.
Methods: In this pilot study, untargeted metabolomics data were collected using C18 negative and HILIC positive ion modes from plasma samples of Black adults with HF (N=41; 15 with DM, 26 without). After filtering and transformation, feature selection was performed via linear models with covariates (age, sex, BMI, and LVEF). Pathway enrichment analysis was conducted using Mummichog v1.0.10.
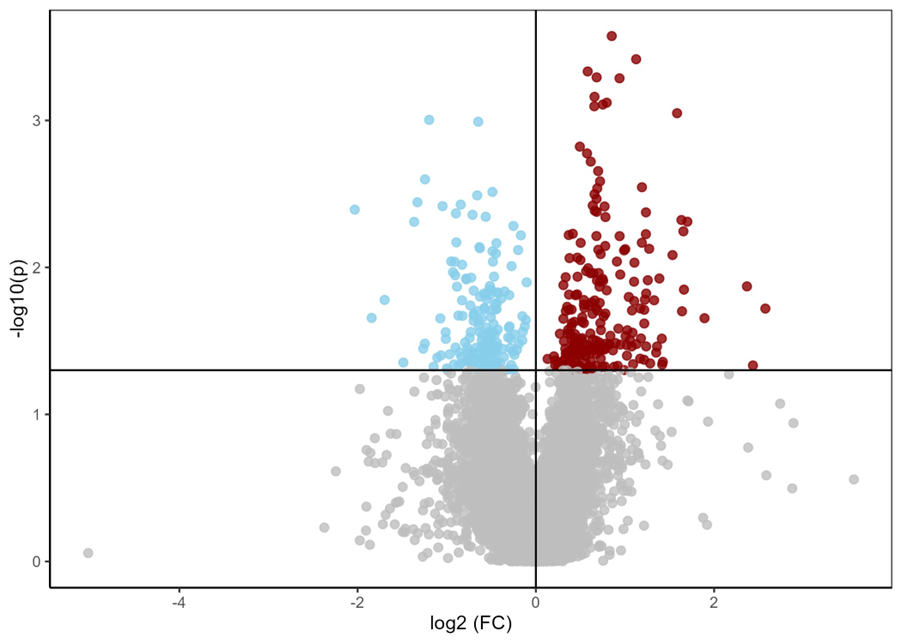
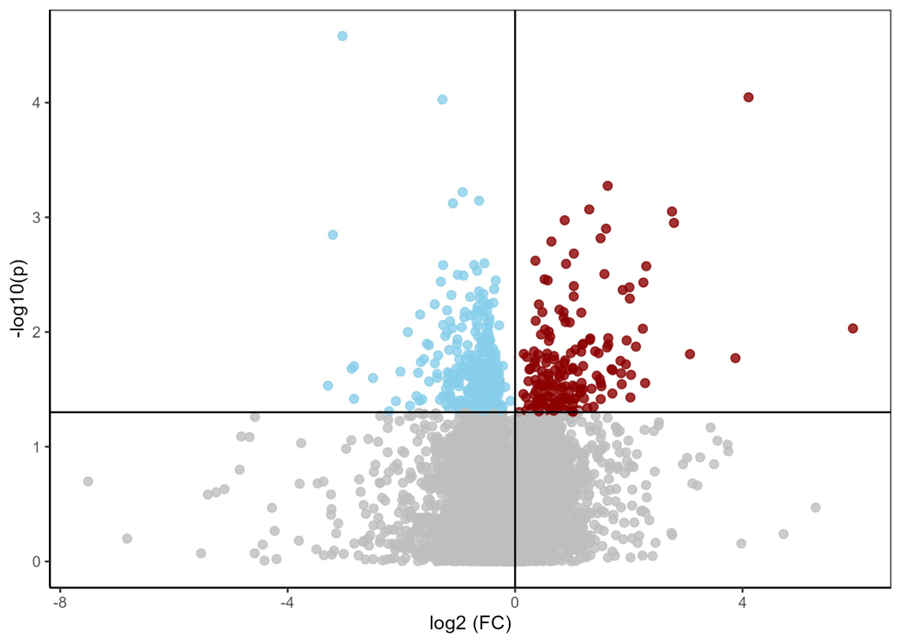
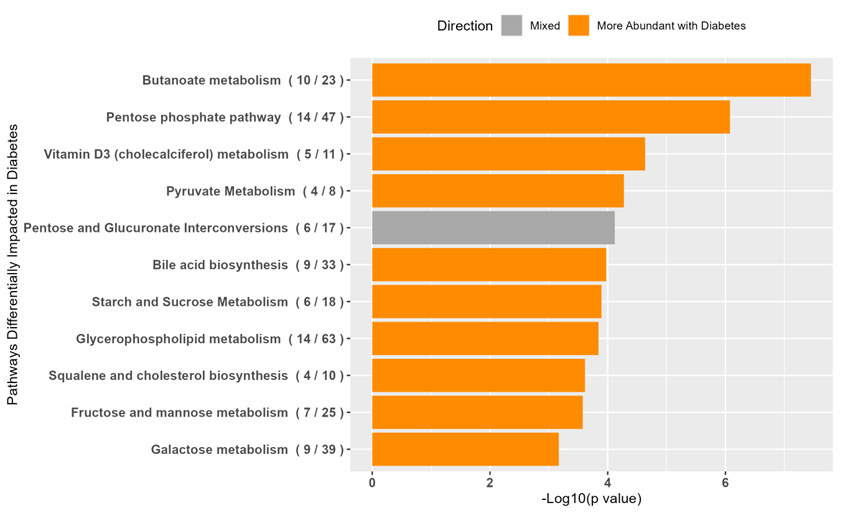
Results: Participants’ mean age was 57±11 years, 66% were female, and mean LVEF was 33±14%. After covariate adjustment, 410 and 526 features remained significantly different between groups in C18neg and HILICpos modes, respectively. The top pathway identified was butanoate metabolism, which regulates short-chain fatty acid energy supply and insulin sensitivity. Other consistently observed pathways included pyruvate metabolism and the pentose phosphate pathway, both related to cellular energy homeostasis. Pathways related to bile acid signaling, squalene and cholesterol biosynthesis, and vitamin D3 metabolism were also identified. Directional trends suggested upregulation of metabolites involved in energy regulation and lipid metabolism in participants with DM. Findings were robust across covariate-adjusted models.
Conclusions: We identified differentially abundant metabolites related to multiple energy and metabolic homeostasis, cholesterol, and biosynthesis pathways in Black adults with HF and DM, suggesting a complex network of metabolic regulatory mechanisms. Findings suggest shifts in metabolic regulation in Black adults with HF and comorbid DM, underscoring the intricate interplay between these conditions. The prominence of butanoate and bile acid pathways highlights potential mechanisms linking metabolic dysfunction to HF outcomes. Further investigation into these pathways in larger samples could offer critical insights into novel therapeutic interventions tailored to address the intricate metabolic disruptions observed in comorbid HF and DM for this population.
Objective: To identify differential metabolic pathways in Black adults with HF with and without comorbid DM.
Methods: In this pilot study, untargeted metabolomics data were collected using C18 negative and HILIC positive ion modes from plasma samples of Black adults with HF (N=41; 15 with DM, 26 without). After filtering and transformation, feature selection was performed via linear models with covariates (age, sex, BMI, and LVEF). Pathway enrichment analysis was conducted using Mummichog v1.0.10.
Results: Participants’ mean age was 57±11 years, 66% were female, and mean LVEF was 33±14%. After covariate adjustment, 410 and 526 features remained significantly different between groups in C18neg and HILICpos modes, respectively. The top pathway identified was butanoate metabolism, which regulates short-chain fatty acid energy supply and insulin sensitivity. Other consistently observed pathways included pyruvate metabolism and the pentose phosphate pathway, both related to cellular energy homeostasis. Pathways related to bile acid signaling, squalene and cholesterol biosynthesis, and vitamin D3 metabolism were also identified. Directional trends suggested upregulation of metabolites involved in energy regulation and lipid metabolism in participants with DM. Findings were robust across covariate-adjusted models.
Conclusions: We identified differentially abundant metabolites related to multiple energy and metabolic homeostasis, cholesterol, and biosynthesis pathways in Black adults with HF and DM, suggesting a complex network of metabolic regulatory mechanisms. Findings suggest shifts in metabolic regulation in Black adults with HF and comorbid DM, underscoring the intricate interplay between these conditions. The prominence of butanoate and bile acid pathways highlights potential mechanisms linking metabolic dysfunction to HF outcomes. Further investigation into these pathways in larger samples could offer critical insights into novel therapeutic interventions tailored to address the intricate metabolic disruptions observed in comorbid HF and DM for this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Metabolomic Study of Cardiac Dysfunction in Hyperglycemia
Yoshida Yilin, Qi Qibin, Cheng Susan, Kaplan Robert, Rodriguez Carlos, Shah Amil, Yu Bing, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh, Moon Eun Hye, Casey Rebholz, Skali Hicham, Arthur Victoria, Echouffo Justin, Ballantyne Christie, Selvin Elizabeth
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting FerroptosisJiang Meng, Guo Xinning