Final ID: MP953
Influence of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging Phenotype and Variant Type on Ventricular Arrhythmia Risk in RBM20-Related Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants in the RBM20-encoded RNA-binding protein motif 20 splicing factor result in a penetrant form of arrhythmogenic/dilated cardiomyopathy (ACM/DCM) characterized by ventricular arrhythmias (VA) and early-onset heart failure. The role of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging in characterizing RBM20 cardiomyopathy and guiding risk stratification remains inadequately defined. Objectives: To characterize CMR phenotypes in patients with RBM20 cardiomyopathy and explore associations between variant type, CMR phenotype, and VA risk.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of 1,061 genotype-positive ACM/DCM patients was used to identify individuals with P/LP arginine/serine-rich domain-localizing missense (RBM20msv) or truncating (RBM20tv) variants in RBM20. Clinical outcomes, including major VA (MVA; sudden cardiac arrest, sustained ventricular arrhythmia, or appropriate ICD therapy) events, were compared between RBM20msv and RBM20tv-positive patients. When available, CMR findings were also analyzed by variant type and correlated with MVA events.
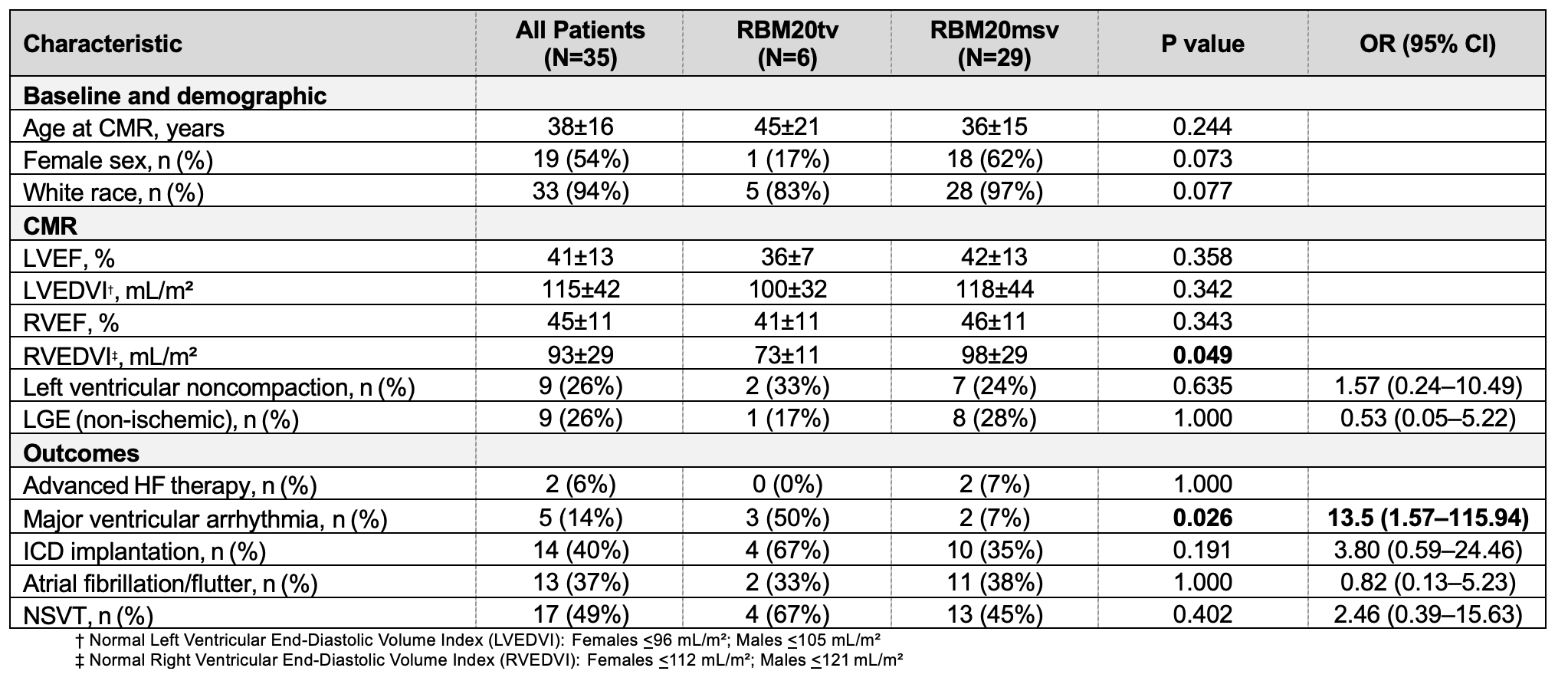
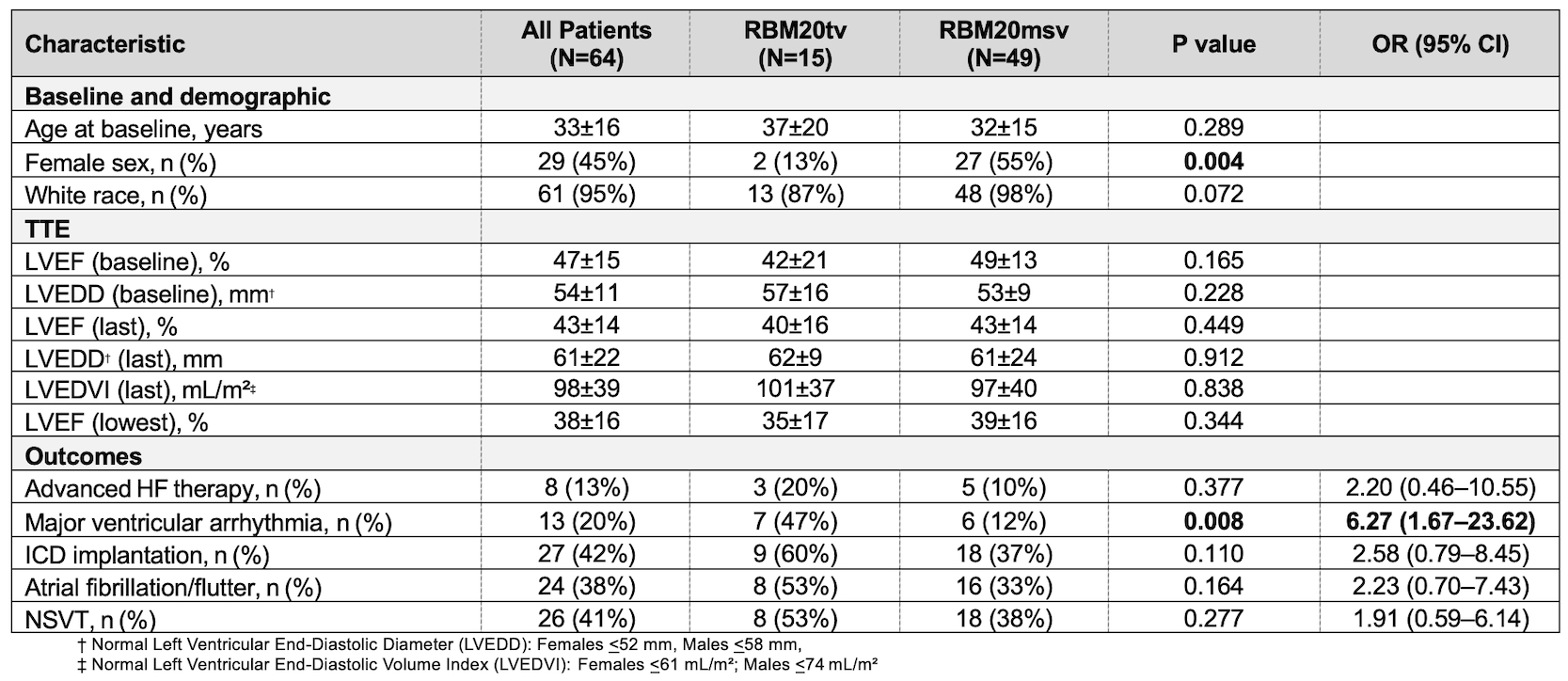
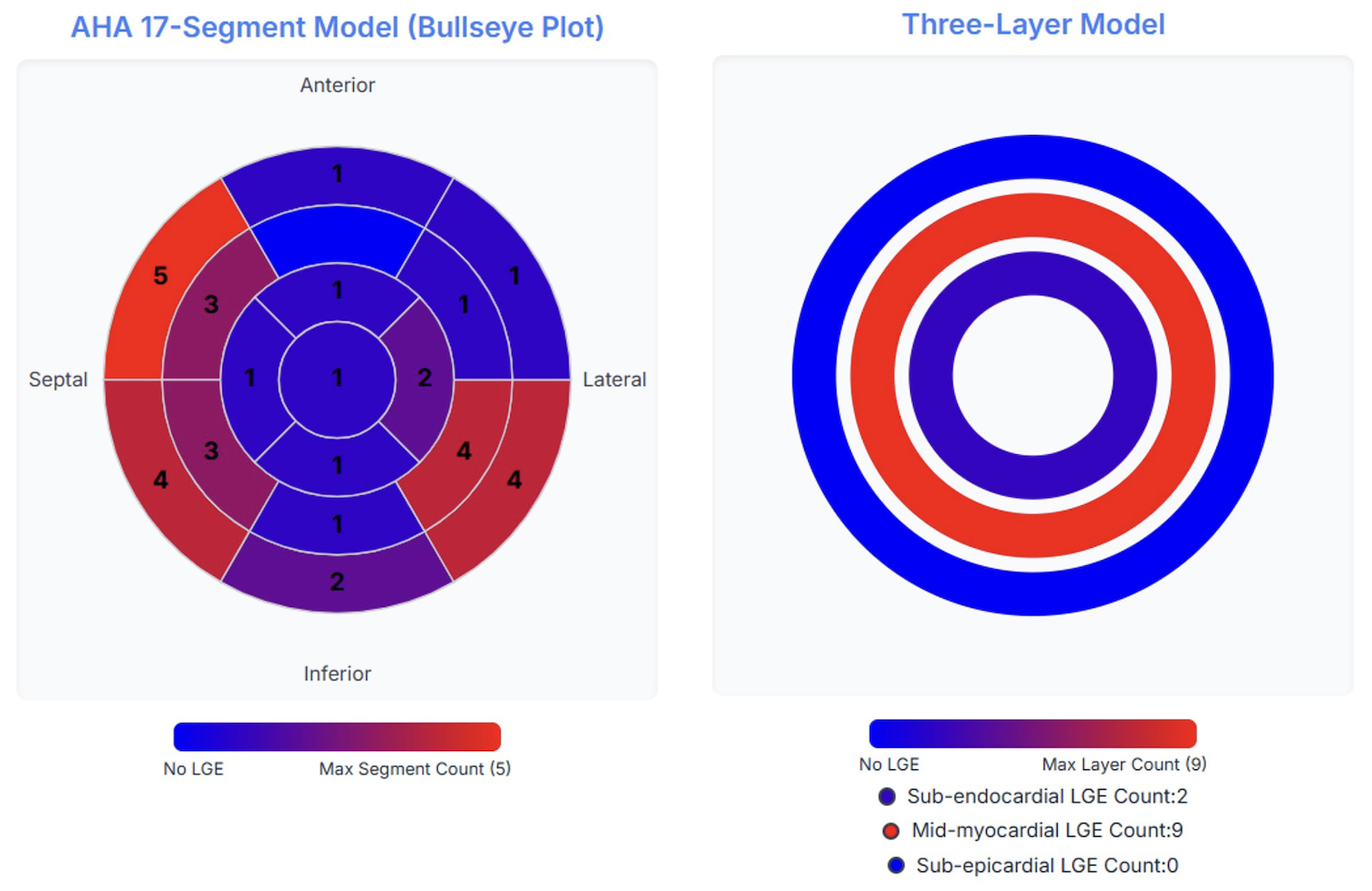
Results: Overall, 64 of 1,061 (6%) ACM/DCM patients possessed an RBM20msv or RBM20tv. Of those, 35 (mean age 38±16 years, 54% female, 94% Caucasian) underwent CMR. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was present in 9/35 (26%), typically in a mid-myocardial septal or inferolateral pattern. Left ventricular (LV) noncompaction was noted in 9/35 (26%). Within the CMR subgroup, RBM20msv accounted for 29/35 (83%) of cases, while RBM20tv was observed in 6/35 (17%). No significant difference in LV ejection fraction (36±7% vs. 42±13%, p=0.358), LV end-diastolic volume index (100±32 mL/m2 vs. 118±44 mL/m2, p=0.342), or LGE prevalence (1/6 [17%] vs. 8/29 [28%], p=1.000) was observed between RBM20tv- and RBM20msv-positive patients. However, MVA events were more frequent among RBM20tv-positive patients in the CMR subset (3/6 [50%] vs. 2/29 [7%], p=0.026) and the overall cohort (7/15 [47%] vs. 6/49 [12%], p=0.008).
Conclusions: RBM20tv-positive patients experienced a higher rate of MVA events despite similar rates of LGE and structural remodeling compared to those with RBM20msv. Future studies are needed to determine whether mechanisms independent of fibrosis/re-entry drive arrhythmogenesis in RBM20tv-positive patients and to establish if RBM20tv represents an independent risk factor for MVA events that merits incorporation into genotype-specific risk stratification strategies.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of 1,061 genotype-positive ACM/DCM patients was used to identify individuals with P/LP arginine/serine-rich domain-localizing missense (RBM20msv) or truncating (RBM20tv) variants in RBM20. Clinical outcomes, including major VA (MVA; sudden cardiac arrest, sustained ventricular arrhythmia, or appropriate ICD therapy) events, were compared between RBM20msv and RBM20tv-positive patients. When available, CMR findings were also analyzed by variant type and correlated with MVA events.
Results: Overall, 64 of 1,061 (6%) ACM/DCM patients possessed an RBM20msv or RBM20tv. Of those, 35 (mean age 38±16 years, 54% female, 94% Caucasian) underwent CMR. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was present in 9/35 (26%), typically in a mid-myocardial septal or inferolateral pattern. Left ventricular (LV) noncompaction was noted in 9/35 (26%). Within the CMR subgroup, RBM20msv accounted for 29/35 (83%) of cases, while RBM20tv was observed in 6/35 (17%). No significant difference in LV ejection fraction (36±7% vs. 42±13%, p=0.358), LV end-diastolic volume index (100±32 mL/m2 vs. 118±44 mL/m2, p=0.342), or LGE prevalence (1/6 [17%] vs. 8/29 [28%], p=1.000) was observed between RBM20tv- and RBM20msv-positive patients. However, MVA events were more frequent among RBM20tv-positive patients in the CMR subset (3/6 [50%] vs. 2/29 [7%], p=0.026) and the overall cohort (7/15 [47%] vs. 6/49 [12%], p=0.008).
Conclusions: RBM20tv-positive patients experienced a higher rate of MVA events despite similar rates of LGE and structural remodeling compared to those with RBM20msv. Future studies are needed to determine whether mechanisms independent of fibrosis/re-entry drive arrhythmogenesis in RBM20tv-positive patients and to establish if RBM20tv represents an independent risk factor for MVA events that merits incorporation into genotype-specific risk stratification strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Nationwide Italian Network for the Clinical and Genetic Diagnosis of Familial Dyslipidemias: The LIPIGEN registry
Casula Manuela, Galimberti Federica, Olmastroni Elena, Arca Marcello, Averna Maurizio, Catapano Alberico
A Pressure-Volume Loops Approach Predicts Outcomes After Double Switch Operation For Congenitally Corrected Transposition Of The Great Arteries with Intact Ventricular SeptumThatte Nikhil, Del Nido Pedro, Ghelani Sunil, Hammer Peter, Marx Gerald, Beroukhim Rebecca, Gauvreau Kimberlee, Callahan Ryan, Prakash Ashwin, Emani Sitaram, Hoganson David