Final ID: MP2364
Temporal Trends in Cardiometabolic Risk Among U.S. Women Veterans: Widening Racial and Age-Based Disparities over a 20-year period
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Cardiometabolic risk factors remain the leading cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and death in the US. US women veterans (WV) are a growing, high-risk population with higher rates of chronic conditions and increasing engagement with veteran affair (VA) healthcare yet remain understudied.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the potential ethnic/racial and age group differences in the life-long prevalence of traditional cardiometabolic risk factors among US WV from 2000-2019.
Methods: The national VA electronic health records (her) were used to assess the prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and neuroendocrine disorders among US WV who visited a VA facility from 1/1/2000 to 12/31/2019. Diagnoses were based on international classification of disease (ICD)-9 and -10 codes. Participants were stratified by races/ethnicities (non-Hispanic White, Black, Asian, American Indian/Pacific Islander, and Hispanic/Latino) and age group (18-39, 40-59, 60+). Age-standardized lifelong prevalence of CVD risk factors was assessed overall, by races/ethnicities, and by age groups. Age-standardized lifelong prevalence represents the sum of raw age-specific risk factor rates multiplying the standard age-specific proportion in the 2000 U.S. census reference population
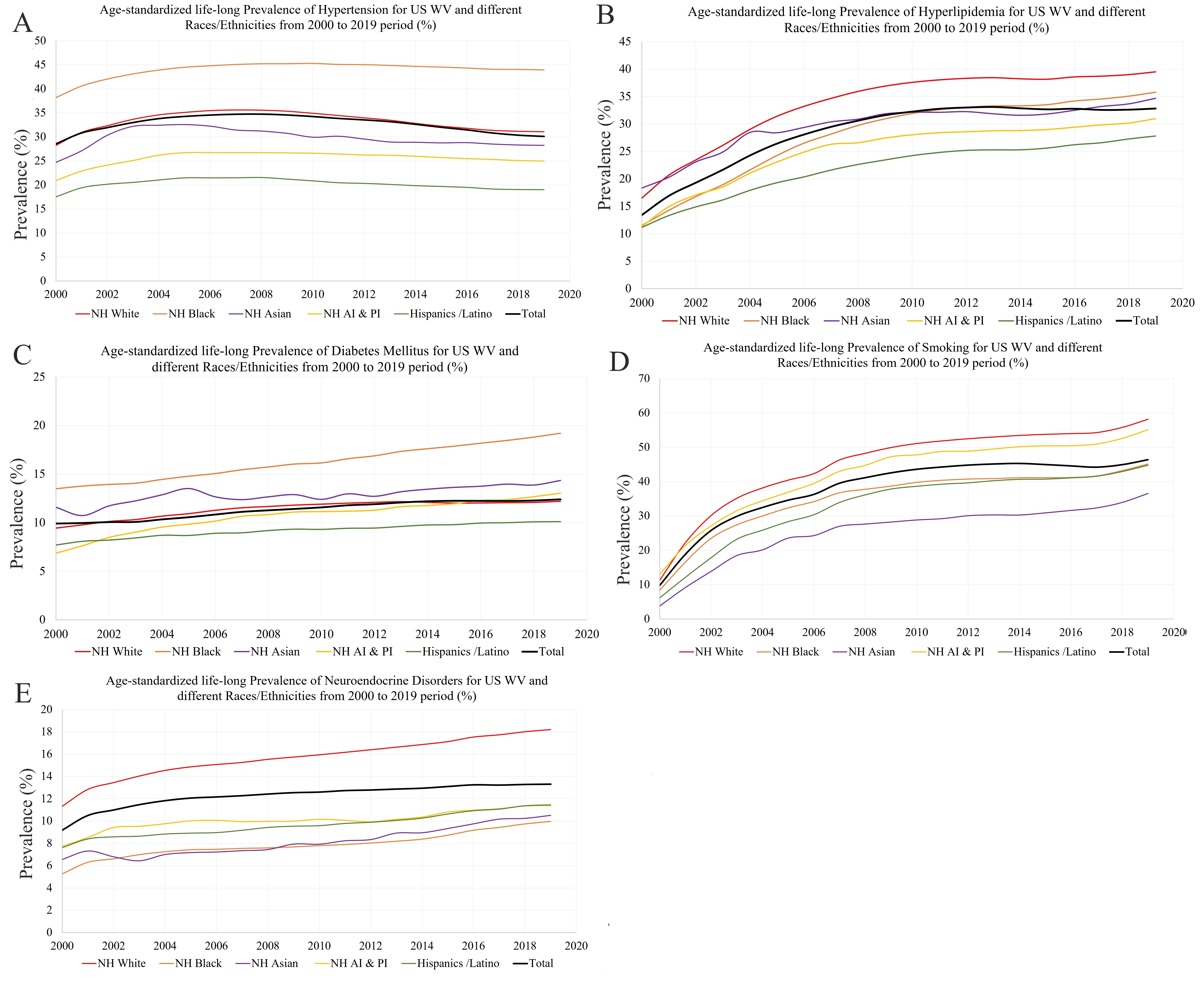
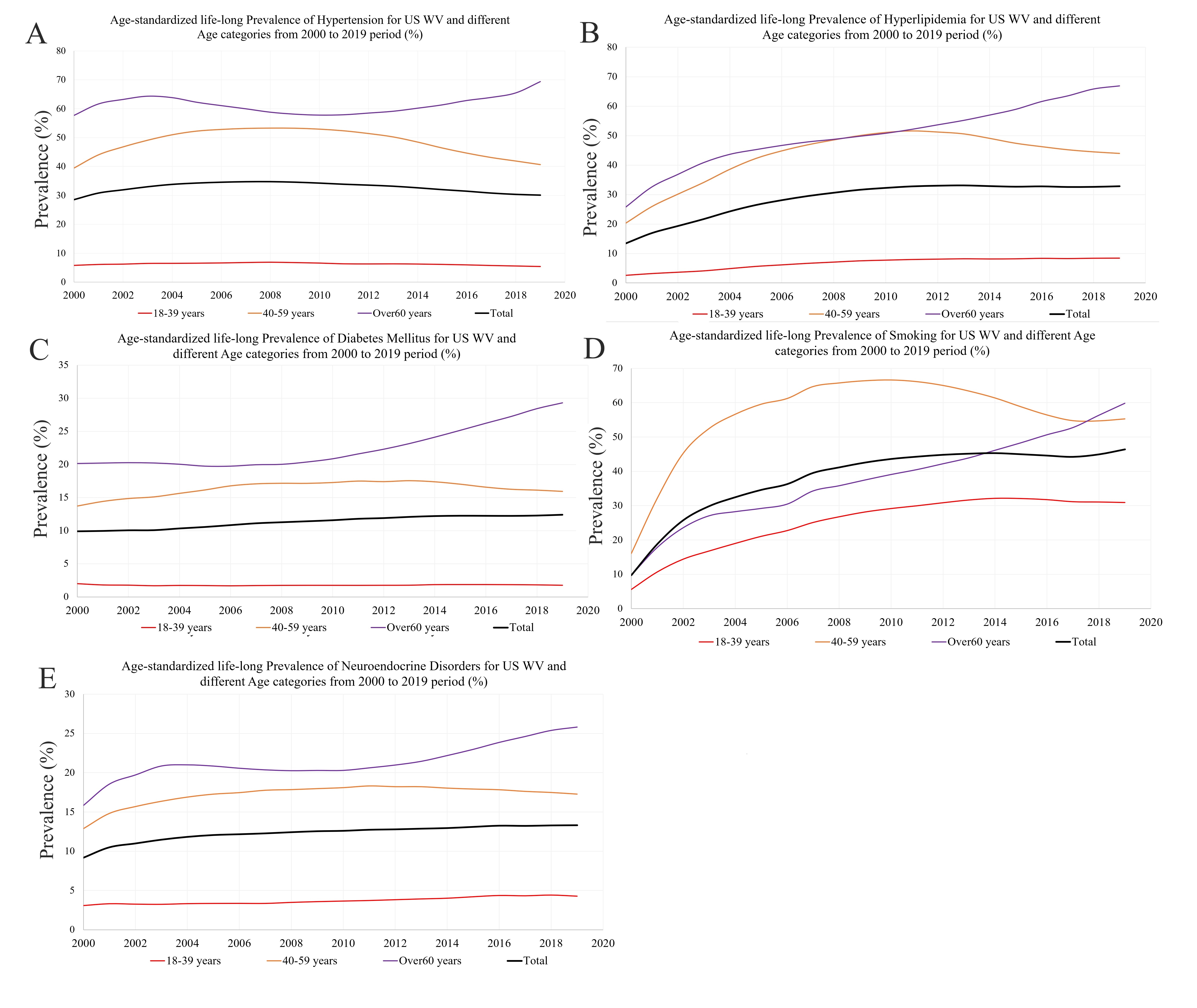
Results: The WV cohort expanded from 80,707 in 2000 to 739,309 in 2019. Significant racial/ethnic disparities emerged. Blacks demonstrated the highest prevalence of diabetes (from 13.5% to 19.2%) and hypertension (38.2% to 43.9%). Notably, American Islanders showed the most rapid escalation in diabetes (1.9-fold increase). Whites maintained the highest prevalence of smoking, hyperlipidemia, and neuroendocrine disorders. Asians experienced a 9.6-fold surge in smoking (3.8% to 36.5%), while Black saw a 3.1-fold rise in hyperlipidemia (11.5% to 35.8%) and a 3.1-fold rise in neuroendocrine disorders. The remaining subgroups exhibited absolute prevalence increases of approximately 40% for smoking and 20% for hyperlipidemia. Marked age-related patterns also emerged. The 60+ age group had the highest prevalence of risk factors from 2000-2019, except smoking. This group also exhibited the greatest fold increases in every category except hypertension.
Conclusion: The cardiometabolic risk burden among U.S. women veterans has reached critical levels, with pronounced racial/ethnic and age group disparities, necessitating immediate targeted public health interventions.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the potential ethnic/racial and age group differences in the life-long prevalence of traditional cardiometabolic risk factors among US WV from 2000-2019.
Methods: The national VA electronic health records (her) were used to assess the prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and neuroendocrine disorders among US WV who visited a VA facility from 1/1/2000 to 12/31/2019. Diagnoses were based on international classification of disease (ICD)-9 and -10 codes. Participants were stratified by races/ethnicities (non-Hispanic White, Black, Asian, American Indian/Pacific Islander, and Hispanic/Latino) and age group (18-39, 40-59, 60+). Age-standardized lifelong prevalence of CVD risk factors was assessed overall, by races/ethnicities, and by age groups. Age-standardized lifelong prevalence represents the sum of raw age-specific risk factor rates multiplying the standard age-specific proportion in the 2000 U.S. census reference population
Results: The WV cohort expanded from 80,707 in 2000 to 739,309 in 2019. Significant racial/ethnic disparities emerged. Blacks demonstrated the highest prevalence of diabetes (from 13.5% to 19.2%) and hypertension (38.2% to 43.9%). Notably, American Islanders showed the most rapid escalation in diabetes (1.9-fold increase). Whites maintained the highest prevalence of smoking, hyperlipidemia, and neuroendocrine disorders. Asians experienced a 9.6-fold surge in smoking (3.8% to 36.5%), while Black saw a 3.1-fold rise in hyperlipidemia (11.5% to 35.8%) and a 3.1-fold rise in neuroendocrine disorders. The remaining subgroups exhibited absolute prevalence increases of approximately 40% for smoking and 20% for hyperlipidemia. Marked age-related patterns also emerged. The 60+ age group had the highest prevalence of risk factors from 2000-2019, except smoking. This group also exhibited the greatest fold increases in every category except hypertension.
Conclusion: The cardiometabolic risk burden among U.S. women veterans has reached critical levels, with pronounced racial/ethnic and age group disparities, necessitating immediate targeted public health interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Insights from the All of Us Research Program
Renedo Daniela, Schwamm Lee, Kamel Hooman, Matouk Charles, Tal Reshef, Sheth Kevin, Falcone Guido, Chaves-rivera Maria Natalia, Rivier Cyprien, Koo Andrew, Clocchiatti-tuozzo Santiago, Huo Shufan, Sujijantarat Nanthiya, Torres Lopez Victor, Hebert Ryan
Active Screening in Black, Hispanic/LatinX, Asian/Pacific Islander, and Native American Individuals Reduces Racial Disparities in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm DiagnosisMiner Grace, Govindarajulu Usha, Smolock Christopher, Faries Peter, Marin Michael