Final ID: Sa1030
Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Lone Elevated Coronary Artery Calcium and No Traditional Risk Factors: A 5- and 10-Year Propensity-Matched Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring improves cardiovascular risk prediction, especially in patients with intermediate risk. However, the long-term implications of elevated CAC in otherwise low-risk individuals remain uncertain.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that CAC >100 and no traditional risk factors would be associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes compared with those with CAC = 0 and ≥1 risk factor.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective cohort study using a de-identified national database with over 113 million patients (TriNetX Research Network, Cambridge, MA; IRB exempt). We identified adults ≥18 years without established coronary artery disease who underwent CAC scoring. Group A included patients with CAC >100, no history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or nicotine dependence. Group B included patients with CAC = 0 and ≥1 traditional risk factor. Propensity score matching (1:1) was performed on age, sex, and race, yielding 11,746 patients per group. The primary outcome was 5- and 10-year rates of myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic stroke, coronary revascularization, and all-cause death. Outcomes were analyzed using odds ratios and Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
Results:
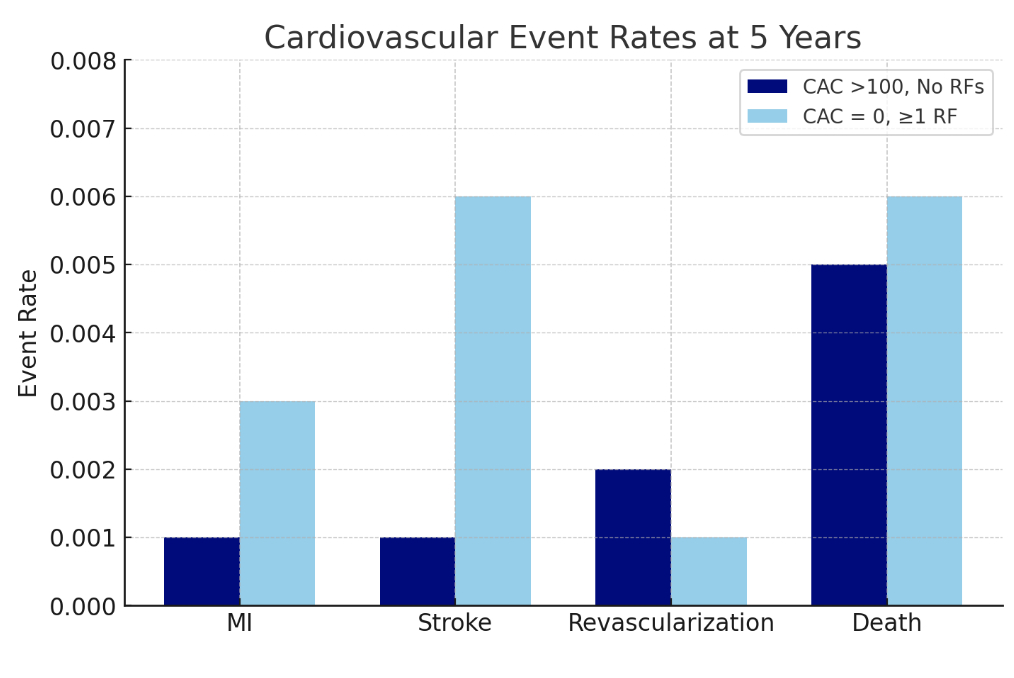
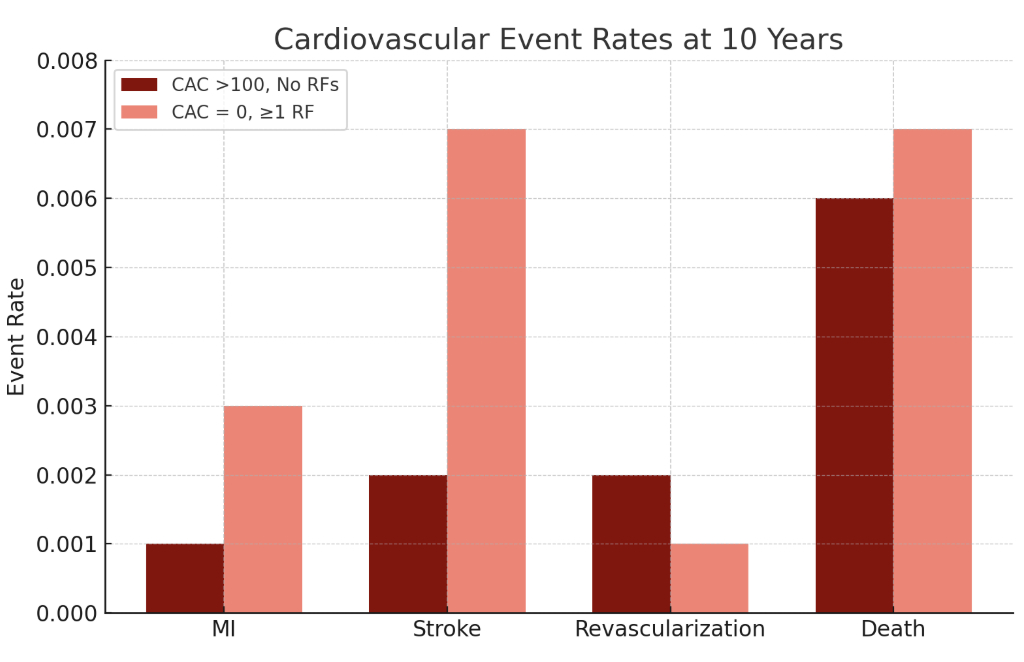
At 5 years, those with lone CAC were less likely to have an MI (0.1% vs. 0.3%, OR 0.34, 95%, p=0.029) or stroke (0.1% vs. 0.6%, OR 0.18, p<0.001), but were more likely to undergo revascularization (0.2% vs. 0.1%, OR 2.03, p=0.047). Similar findings were seen at 10 years: MI (0.1% vs. 0.3%, OR 0.52, p=0.024), stroke (0.2% vs. 0.7%, OR 0.22, p<0.001), revascularization (0.2% vs. 0.1%, OR 2.28, p=0.019). There were no significant differences in mortality at 5 and 10 years (0.5% vs. 0.6%, p=0.27; 0.6% vs. 0.7%, p=0.21, respectively).
Conclusion:
Patients with CAC >100 and no traditional risk factors were less likely to have an MI or stroke, and more likely to undergo coronary revascularization compared with CAC = 0 with traditional risk factors. These results support CAC scoring as durable, independent prognostic test and supports its use in refining preventive strategies.
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring improves cardiovascular risk prediction, especially in patients with intermediate risk. However, the long-term implications of elevated CAC in otherwise low-risk individuals remain uncertain.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that CAC >100 and no traditional risk factors would be associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes compared with those with CAC = 0 and ≥1 risk factor.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective cohort study using a de-identified national database with over 113 million patients (TriNetX Research Network, Cambridge, MA; IRB exempt). We identified adults ≥18 years without established coronary artery disease who underwent CAC scoring. Group A included patients with CAC >100, no history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or nicotine dependence. Group B included patients with CAC = 0 and ≥1 traditional risk factor. Propensity score matching (1:1) was performed on age, sex, and race, yielding 11,746 patients per group. The primary outcome was 5- and 10-year rates of myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic stroke, coronary revascularization, and all-cause death. Outcomes were analyzed using odds ratios and Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
Results:
At 5 years, those with lone CAC were less likely to have an MI (0.1% vs. 0.3%, OR 0.34, 95%, p=0.029) or stroke (0.1% vs. 0.6%, OR 0.18, p<0.001), but were more likely to undergo revascularization (0.2% vs. 0.1%, OR 2.03, p=0.047). Similar findings were seen at 10 years: MI (0.1% vs. 0.3%, OR 0.52, p=0.024), stroke (0.2% vs. 0.7%, OR 0.22, p<0.001), revascularization (0.2% vs. 0.1%, OR 2.28, p=0.019). There were no significant differences in mortality at 5 and 10 years (0.5% vs. 0.6%, p=0.27; 0.6% vs. 0.7%, p=0.21, respectively).
Conclusion:
Patients with CAC >100 and no traditional risk factors were less likely to have an MI or stroke, and more likely to undergo coronary revascularization compared with CAC = 0 with traditional risk factors. These results support CAC scoring as durable, independent prognostic test and supports its use in refining preventive strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Delayed Diagnosis of Anti-HMG-CoA Reductase Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy
Jadhav Reshma, Shekar Arush, Westenhaver Zack, Skandhan Amith
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic DiametersMarway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas