Final ID: Mo4034
Comprehensive Ranking of Maintenance Immunosuppressive Therapies for Heart Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Prior studies report mixed efficacy of maintenance immunosuppressive regimens in heart transplantation (HT). We conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare and rank these regimens.
Methods:
Six databases were searched for studies comparing HT immunosuppressive regimens. A Bayesian NMA (R v4.5.1, "geMTC") ranked treatments via SUCRA values, evaluating regimens including antimetabolite (AM), mTOR inhibitor (mTA), and calcineurin inhibitor (CNI).
Results:
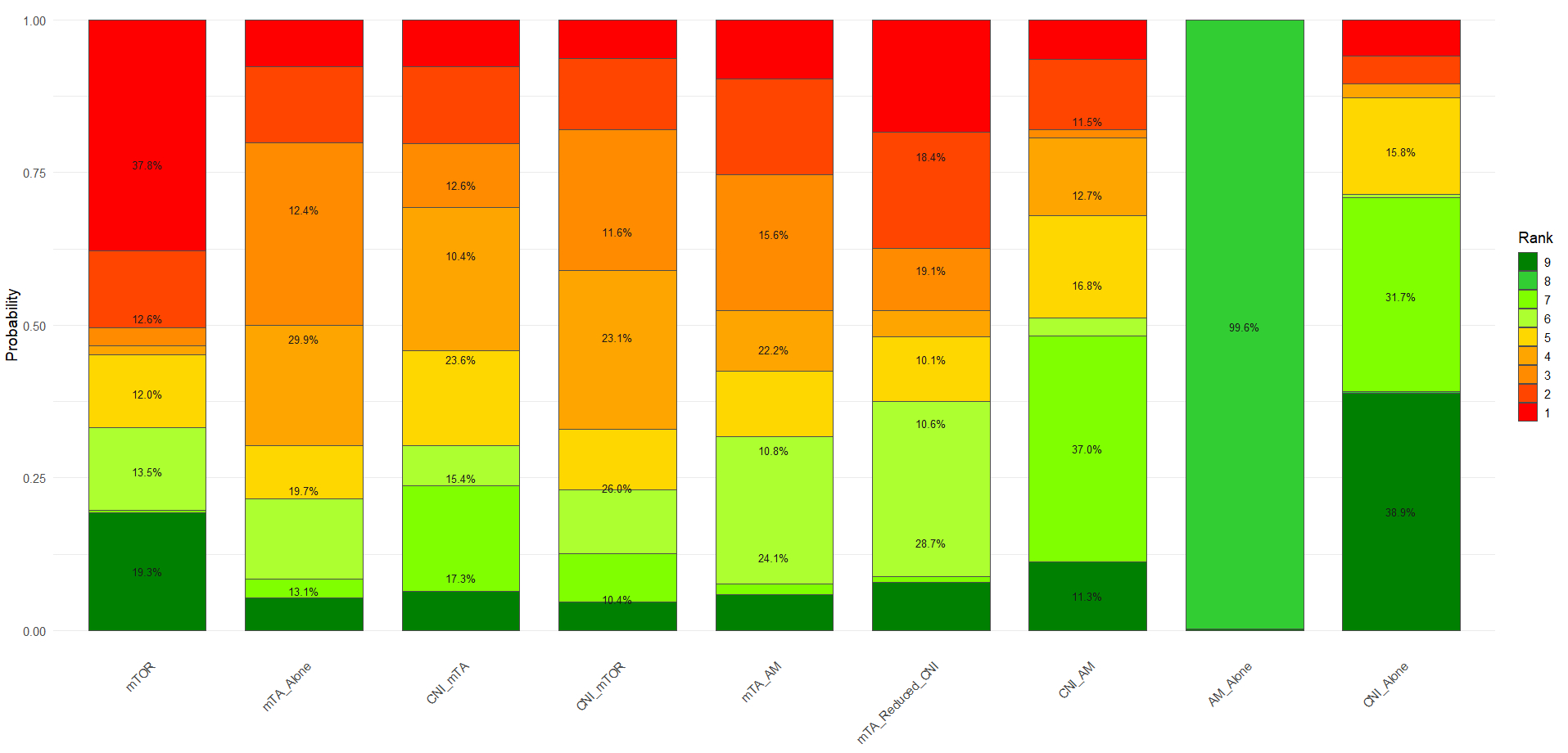
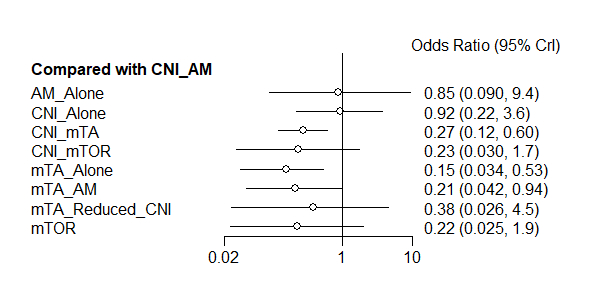
A total of 38 studies involving 5,451 patients were included, evaluating five key outcomes. For all-cause mortality, AM_Alone ranked highest (SUCRA: 0.744), followed closely by mTA_Alone (SUCRA: 0.734), both demonstrating modest but consistent benefits (OR range: 0.73–0.87 vs. other regimens). mTA+Reduced+CNI ranked lowest (SUCRA: 0.001) with an implausibly extreme OR (1.1e-16, 95% CI: 3.5e-28–0.017), likely due to data limitations. In terms of acute rejection, AM_Alone again ranked highest (SUCRA: 0.841), with CNI+mTOR (SUCRA: 0.719) and CNI_AM (SUCRA: 0.587) as favorable alternatives. Although mTA+Reduced+CNI ranked lowest (SUCRA: 0.097), its odds ratio (OR) of 0.084 (95% CI: 0.0072–0.99) suggests possible efficacy, albeit with low confidence. For CMV prevention, CNI_AM performed best (SUCRA: 0.843), with all other regimens associated with increased CMV risk (ORs <1 vs. CNI_AM). CNI_Alone (SUCRA: 0.808; OR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.22–3.6) and AM_Alone (SUCRA: 0.762; OR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.09–9.4) performed similarly, while mTA_Alone was least effective (SUCRA: 0.185; OR: 0.15, 95% CI: 0.034–0.53). For cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV), AM_Alone was the most protective (SUCRA: 0.922), followed by CNI_Alone (SUCRA: 0.812). CNI_AM and mTOR also showed benefits (ORs: 0.28 and 0.35, respectively). mTA+AM (SUCRA: 0.205) and CNI+mTA (SUCRA: 0.208) ranked lower, although both showed promising point estimates (OR: 0.18), albeit with wide confidence intervals (e.g., 0.024–1.1). For renal function (eGFR), mTA+AM ranked highest (SUCRA: 0.750). Compared to this, CNI_AM showed a modest decline (MD: –21 mL/min, 95% CI: –70 to 27 mL/min). In contrast, CNI_Alone and mTA+Reduced+CNI had the poorest outcomes (MD: –46 and –55 mL/min, respectively), although with broad confidence intervals.
Conclusions:
AM_Alone showed consistent benefits, while reduced-CNI regimens underperformed. These findings may guide post-HT care, though some estimates require cautious interpretation.
Prior studies report mixed efficacy of maintenance immunosuppressive regimens in heart transplantation (HT). We conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare and rank these regimens.
Methods:
Six databases were searched for studies comparing HT immunosuppressive regimens. A Bayesian NMA (R v4.5.1, "geMTC") ranked treatments via SUCRA values, evaluating regimens including antimetabolite (AM), mTOR inhibitor (mTA), and calcineurin inhibitor (CNI).
Results:
A total of 38 studies involving 5,451 patients were included, evaluating five key outcomes. For all-cause mortality, AM_Alone ranked highest (SUCRA: 0.744), followed closely by mTA_Alone (SUCRA: 0.734), both demonstrating modest but consistent benefits (OR range: 0.73–0.87 vs. other regimens). mTA+Reduced+CNI ranked lowest (SUCRA: 0.001) with an implausibly extreme OR (1.1e-16, 95% CI: 3.5e-28–0.017), likely due to data limitations. In terms of acute rejection, AM_Alone again ranked highest (SUCRA: 0.841), with CNI+mTOR (SUCRA: 0.719) and CNI_AM (SUCRA: 0.587) as favorable alternatives. Although mTA+Reduced+CNI ranked lowest (SUCRA: 0.097), its odds ratio (OR) of 0.084 (95% CI: 0.0072–0.99) suggests possible efficacy, albeit with low confidence. For CMV prevention, CNI_AM performed best (SUCRA: 0.843), with all other regimens associated with increased CMV risk (ORs <1 vs. CNI_AM). CNI_Alone (SUCRA: 0.808; OR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.22–3.6) and AM_Alone (SUCRA: 0.762; OR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.09–9.4) performed similarly, while mTA_Alone was least effective (SUCRA: 0.185; OR: 0.15, 95% CI: 0.034–0.53). For cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV), AM_Alone was the most protective (SUCRA: 0.922), followed by CNI_Alone (SUCRA: 0.812). CNI_AM and mTOR also showed benefits (ORs: 0.28 and 0.35, respectively). mTA+AM (SUCRA: 0.205) and CNI+mTA (SUCRA: 0.208) ranked lower, although both showed promising point estimates (OR: 0.18), albeit with wide confidence intervals (e.g., 0.024–1.1). For renal function (eGFR), mTA+AM ranked highest (SUCRA: 0.750). Compared to this, CNI_AM showed a modest decline (MD: –21 mL/min, 95% CI: –70 to 27 mL/min). In contrast, CNI_Alone and mTA+Reduced+CNI had the poorest outcomes (MD: –46 and –55 mL/min, respectively), although with broad confidence intervals.
Conclusions:
AM_Alone showed consistent benefits, while reduced-CNI regimens underperformed. These findings may guide post-HT care, though some estimates require cautious interpretation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Mimicking Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Diagnostic Challenge with Critical Clinical Implications
Vemula Shree Laya, Dey Dipon, Efa Jessica, Foster Allison, Toreli Aleksandre
Analysis of 30-Day Readmission Rates and Costs Post-Heart Transplant: A 12-Year Retrospective Study Using Nationwide Readmission Database(NRD) : 2010-2021Pinninty Dheeraj, Mogga Phanidhar, Raol Karanrajsinh, Pillai Ashwin, Mudduluru Prathyusha, Singh Kerry, Jedeon Zeina, Jaiswal Abhishek