Final ID: Mo2044
Impact of Push Notifications on Physical Activity and Sodium Intake Amongst Patients with Hypertension: A Micro-Randomized Trial of a Just-In-Time Adaptive Intervention
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Achieving adequate blood pressure (BP) control is challenging for patients and clinicians given the episodic nature of clinical encounters, high patient volumes, and silent nature of the disease. Digital hypertension (HTN) management solutions aim to improve BP control though the effectiveness of each digital component within a multicomponent intervention is unknown.
Question: What are the independent and short-term effects of tailored push notifications on physical activity (PA) levels and sodium intake amongst patients with HTN?
Methods: The myBPmyLife study was a 6-month randomized clinical trial of patients with HTN recruited from an academic medical center and federally qualified health centers. Both the intervention and enhanced usual care arms received a Fitbit Versa 2 and Bluetooth-connected BP monitor. At 6 months, the mobile health intervention increased step count and reduced sodium intake though it did not reduce systolic BP compared to enhanced usual care. A core of the intervention included micro-randomized push notifications which were randomly delivered at four daily time points and focused on increasing PA and reducing dietary sodium intake. Our primary outcome was step count 60 minutes after a PA notification and lower sodium food choices 24 hours after a dietary notification. Analyses used centered and weighted least squares method to estimate treatment effects.
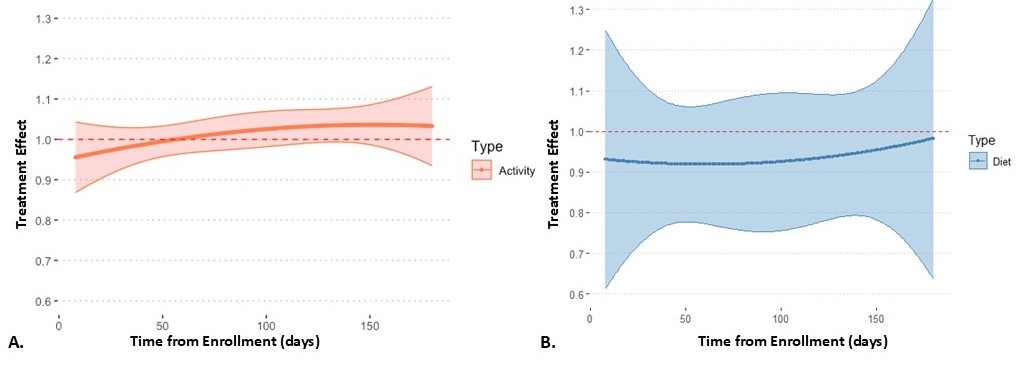
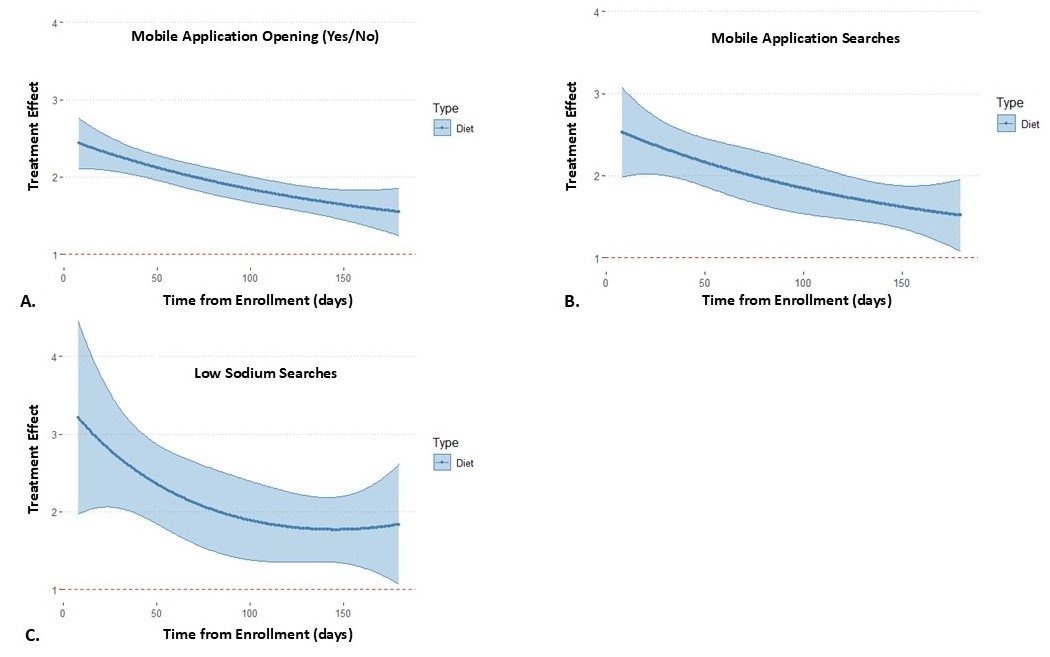
Results: 298 participants were randomized to the intervention arm, of whom 287 were available for the micro-randomized analysis. Participants were randomized at 187,517 time points, which led to 0.96 (SD 0.86) push notifications/day (50.4% [SD 0.4]) PA and 49.8% [SD 0.4] dietary). Participants’ mean age was 59.5 (SD 13.5) years, 137 (47.7%) were women, and 210 (73.2%) White. PA notifications did not increase step count in the subsequent 60 minutes (Estimate 1.01, 95% CI 0.98 – 1.04; p=0.40; Figure 1) though may be more effective in less active participants (Estimate 1.04, 95% CI 1.00 – 1.08; p=0.03). Similarly, dietary notifications did not impact the number of lower sodium food choices in the subsequent 24 hours (Estimate 0.93, 95% CI 0.83 – 1.04; p=0.23), though did increase mobile application engagement (Figure 2).
Conclusions: A mobile health intervention improved step counts and sodium intake over 6 months in patients with HTN. Tailored push notifications did not impact short-term PA or dietary sodium intake, though they did improve intervention engagement.
Question: What are the independent and short-term effects of tailored push notifications on physical activity (PA) levels and sodium intake amongst patients with HTN?
Methods: The myBPmyLife study was a 6-month randomized clinical trial of patients with HTN recruited from an academic medical center and federally qualified health centers. Both the intervention and enhanced usual care arms received a Fitbit Versa 2 and Bluetooth-connected BP monitor. At 6 months, the mobile health intervention increased step count and reduced sodium intake though it did not reduce systolic BP compared to enhanced usual care. A core of the intervention included micro-randomized push notifications which were randomly delivered at four daily time points and focused on increasing PA and reducing dietary sodium intake. Our primary outcome was step count 60 minutes after a PA notification and lower sodium food choices 24 hours after a dietary notification. Analyses used centered and weighted least squares method to estimate treatment effects.
Results: 298 participants were randomized to the intervention arm, of whom 287 were available for the micro-randomized analysis. Participants were randomized at 187,517 time points, which led to 0.96 (SD 0.86) push notifications/day (50.4% [SD 0.4]) PA and 49.8% [SD 0.4] dietary). Participants’ mean age was 59.5 (SD 13.5) years, 137 (47.7%) were women, and 210 (73.2%) White. PA notifications did not increase step count in the subsequent 60 minutes (Estimate 1.01, 95% CI 0.98 – 1.04; p=0.40; Figure 1) though may be more effective in less active participants (Estimate 1.04, 95% CI 1.00 – 1.08; p=0.03). Similarly, dietary notifications did not impact the number of lower sodium food choices in the subsequent 24 hours (Estimate 0.93, 95% CI 0.83 – 1.04; p=0.23), though did increase mobile application engagement (Figure 2).
Conclusions: A mobile health intervention improved step counts and sodium intake over 6 months in patients with HTN. Tailored push notifications did not impact short-term PA or dietary sodium intake, though they did improve intervention engagement.
More abstracts on this topic:
A machine learning model for individualized risk prediction of ischemic heart disease in people with hypertension in Thailand
Sakboonyarat Boonsub, Poovieng Jaturon, Rangsin Ram
Assessment of Dietary Recall Plausibility Using an Updated Formula that Considers Energy Intake Measured by Doubly-Labeled WaterSantos Baez Leinys, Ravelli Michele N., Diaz-rizzolo Diana A., Popp Collin, Cheng Bin, Gallagher Dympna, Schoeller Dale, Laferrere Blandine