Final ID: MP2801
Digital Twin Matching for Real-World Cardiometabolic Medication Effect Estimation using Genomically informed Longitudinal Bayesian Disease Trajectories
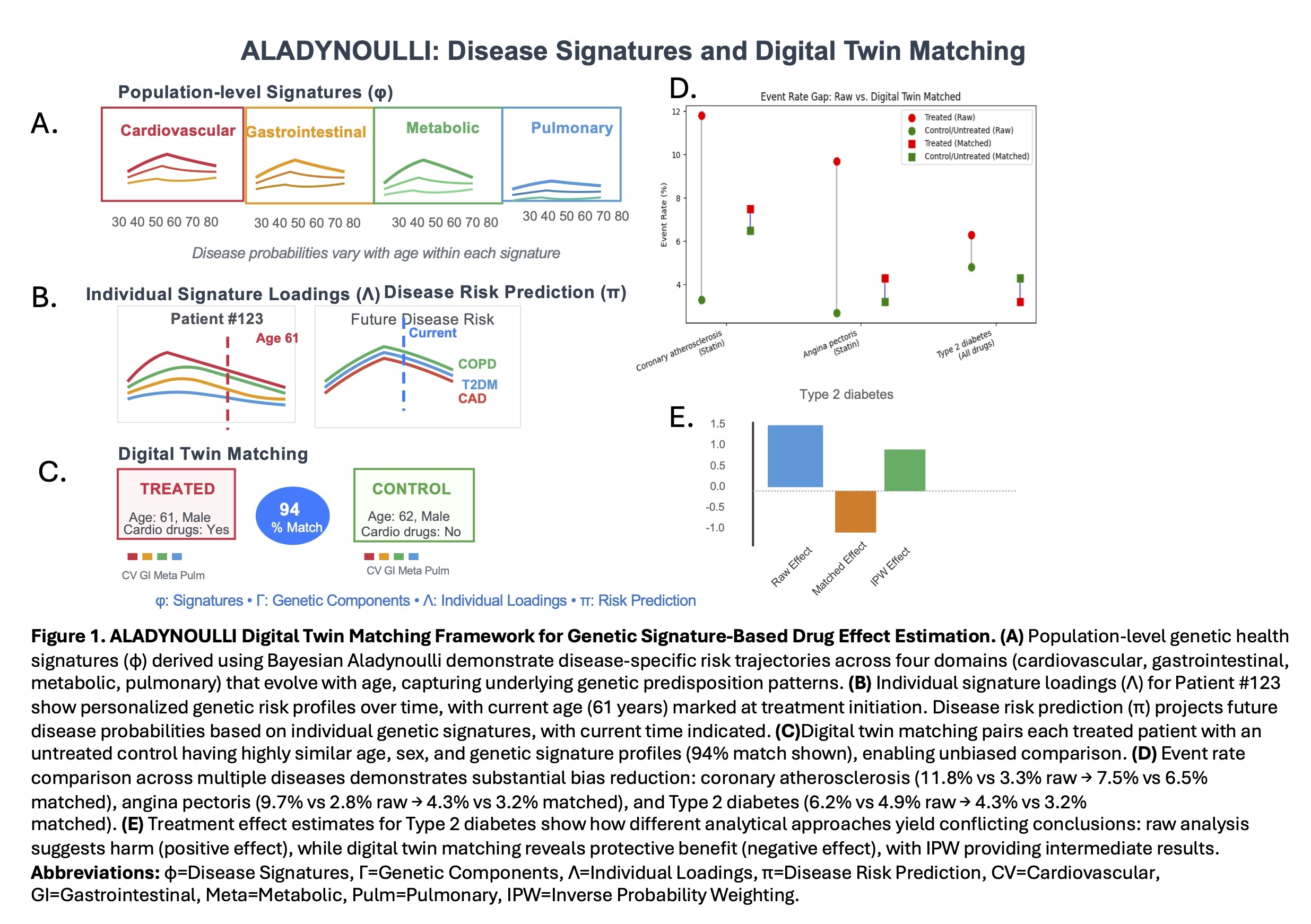
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Confounding differences between treated and untreated patients in observational studies of medication effects lead to biased estimates of drug effectiveness and safety. We present a digital twin matching framework that pairs treated individuals with highly similar untreated controls, enabling robust, disease-specific estimation of drug effects across 358 phenotypes.
We analyzed prescription and disease event data from over 400,000 participants in a large UK Biobank GP data set, covering 348 disease phenotypes and 5 major drug classes. We identified treated individuals and matched them to untreated controls using our novel approach considering enrollment, sex, and Bayesian time-varying latent health signatures derived from longitudinal genetic and clinical data. Each signature represents an underlying disease process with genetic predisposition and co-occurring disease patterns. We compared post-treatment event rates between matched treated and control groups, contrasting with unmatched and inverse probability weighting.
Results: Our novel approach of matching substantially reduced baseline differences between treated and control groups across major drug classes. Unmatched analyses showed inflated event rates in treated patients due to confounding by indication. After matching, event rates in controls closely mirrored those in treated patients, and post-treatment differences more plausibly reflected drug effects. For cardiometabolic drugs and Type 2 diabetes, the raw event rate was higher in the treated group (6.3%) compared to the untreated group (4.9%), persisting with inverse probability weighting (IPW: 6.2% vs 5.0%). After digital twin matching, the treated group correctly demonstrated lower event rate (3.2%) than their matched controls (4.3%). Our matching also substantially reduced the apparent risk difference between treated and control individuals for several statin outcomes. In coronary atherosclerosis, the raw event rate was 11.8% in treated vs 3.3% in untreated, but after matching, rates were 7.5% vs 6.5% (Fig 1).
Conclusions: Digital twin matching offers a scalable, generalizable solution for emulating randomized comparisons in real-world data. By aligning treated and control groups on genetic and clinical latent health features over time, this approach mitigates confounding and enables robust estimation of drug effects by capturing inherited disease susceptibility and clinical propensity to receive treatment and exposure.
We analyzed prescription and disease event data from over 400,000 participants in a large UK Biobank GP data set, covering 348 disease phenotypes and 5 major drug classes. We identified treated individuals and matched them to untreated controls using our novel approach considering enrollment, sex, and Bayesian time-varying latent health signatures derived from longitudinal genetic and clinical data. Each signature represents an underlying disease process with genetic predisposition and co-occurring disease patterns. We compared post-treatment event rates between matched treated and control groups, contrasting with unmatched and inverse probability weighting.
Results: Our novel approach of matching substantially reduced baseline differences between treated and control groups across major drug classes. Unmatched analyses showed inflated event rates in treated patients due to confounding by indication. After matching, event rates in controls closely mirrored those in treated patients, and post-treatment differences more plausibly reflected drug effects. For cardiometabolic drugs and Type 2 diabetes, the raw event rate was higher in the treated group (6.3%) compared to the untreated group (4.9%), persisting with inverse probability weighting (IPW: 6.2% vs 5.0%). After digital twin matching, the treated group correctly demonstrated lower event rate (3.2%) than their matched controls (4.3%). Our matching also substantially reduced the apparent risk difference between treated and control individuals for several statin outcomes. In coronary atherosclerosis, the raw event rate was 11.8% in treated vs 3.3% in untreated, but after matching, rates were 7.5% vs 6.5% (Fig 1).
Conclusions: Digital twin matching offers a scalable, generalizable solution for emulating randomized comparisons in real-world data. By aligning treated and control groups on genetic and clinical latent health features over time, this approach mitigates confounding and enables robust estimation of drug effects by capturing inherited disease susceptibility and clinical propensity to receive treatment and exposure.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian Community
Deo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan
EMAGINE 2.0: Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of App-Controlled Electromagnetic Network Targeting Field Treatment to Reduce Disability in Subacute Ischemic StrokeSaver Jeffrey, Sheth Kevin, Cramer Steven, Stein Joel, Bornstein Natan