Final ID: MP406
Trends in Hypertension-Related Mortality Among U.S. Adults Aged 15–44: A Pre-, Peak-, and Post-COVID-19 Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Hypertension (HTN) is a key modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Though often linked to older adults, HTN-related deaths are rising among younger individuals. Healthcare disruptions from COVID-19 likely impacted medication adherence and chronic disease management, potentially worsening hypertension outcomes. This study evaluates HTN-related mortality in U.S. adults aged 15–44 before, during, and after the pandemic.
Methods: Mortality data were extracted from the CDC Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (CDC WONDER) database to assess age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 population for HTN-related deaths in the US from 2018-2023. AAMRs were standardized to the 2000 US standard population. Trends were examined across three periods: pre-pandemic (2018–2019), peak pandemic (2020–2021), and post-pandemic (2022–2023), stratified by sex and race. Absolute mean differences (AMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated, and an independent z-test was used to determine statistical significance (p<0.05).
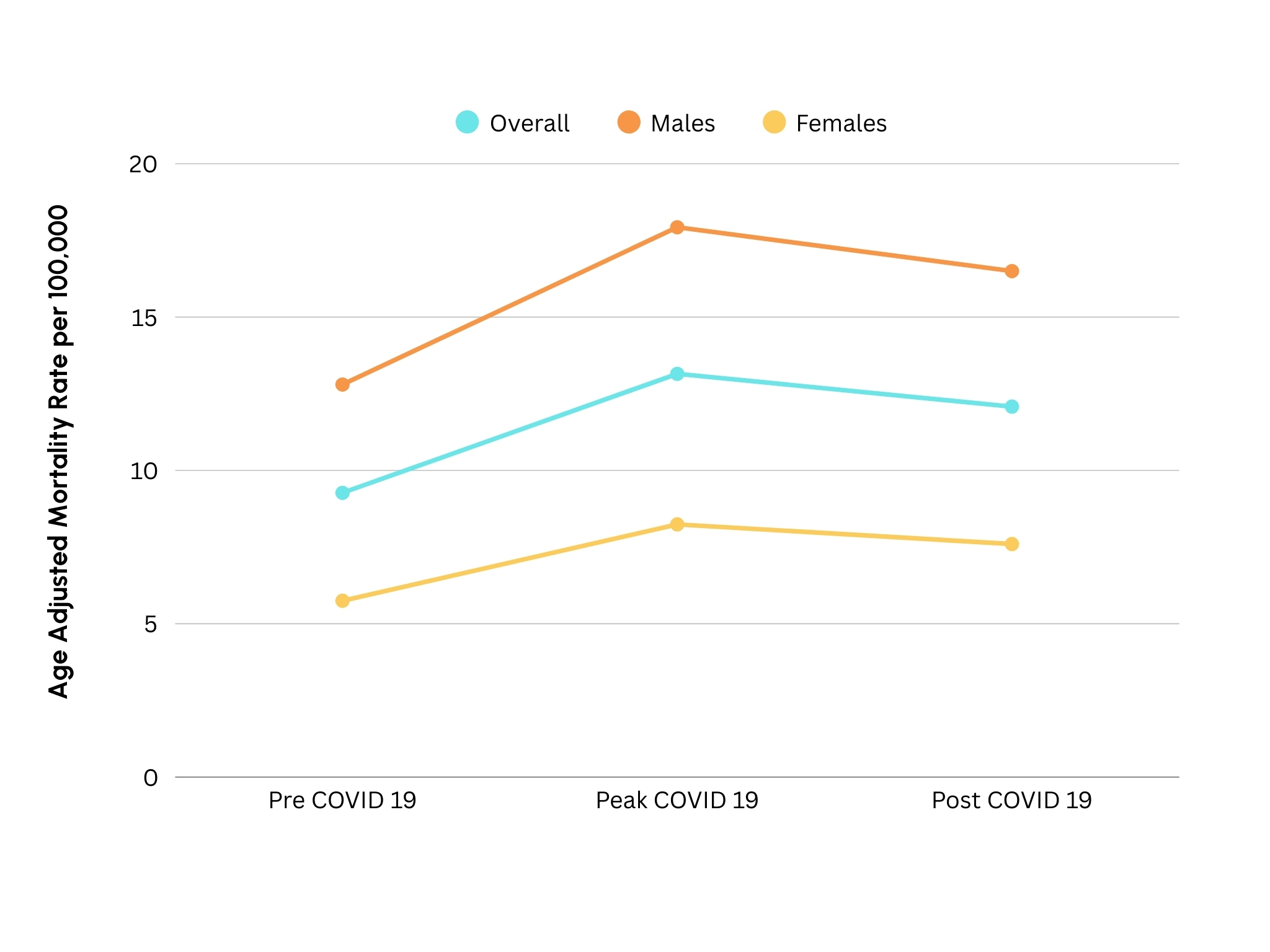
Results: Between 2018 and 2023, 83,329 HTN-related deaths occurred. AAMR rose significantly from 9.27 in the pre-pandemic to 13.15 during the peak-pandemic (AMD: 3.88; 95% CI, 3.69 to 4.07; p<0.001), followed by a decline to 12.08 post-pandemic (AMD: -1.07; 95% CI, -1.27 to -0.87; p<0.001). Males experienced a greater increase than females during the peak-pandemic (AMD: 5.13 vs. 2.49; both p<0.001), compared to the pre-pandemic. Post-pandemic, females had a significant decline (AMD: -0.64, p<0.001), whereas males’ decline was not significant (AMD: -0.24, p=0.15). All racial groups reported an increase in AAMR during the pandemic, with the highest in NH Native Hawaiians (AMD: 15.57; p<0.001) and NH American Indians (AMD: 10.34; p<0.001), compared to the pre-pandemic period. During the post-pandemic period, most racial groups showed a decline, notably NH Blacks (AMD: -3.41; p<0.001). However, AAMR continued to rise non-significantly in NH Native Hawaiians (AMD: 1.11; p=0.76) and NH multiracial individuals (AMD: 0.24; p=0.52), but these effects were not significant.
Conclusion: HTN-related mortality among younger adults increased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in males and specific racial minorities. Despite declines post-pandemic, rates remain above pre-pandemic levels, underscoring the need for targeted preventive interventions to reduce cardiovascular risk.
Methods: Mortality data were extracted from the CDC Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (CDC WONDER) database to assess age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 population for HTN-related deaths in the US from 2018-2023. AAMRs were standardized to the 2000 US standard population. Trends were examined across three periods: pre-pandemic (2018–2019), peak pandemic (2020–2021), and post-pandemic (2022–2023), stratified by sex and race. Absolute mean differences (AMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated, and an independent z-test was used to determine statistical significance (p<0.05).
Results: Between 2018 and 2023, 83,329 HTN-related deaths occurred. AAMR rose significantly from 9.27 in the pre-pandemic to 13.15 during the peak-pandemic (AMD: 3.88; 95% CI, 3.69 to 4.07; p<0.001), followed by a decline to 12.08 post-pandemic (AMD: -1.07; 95% CI, -1.27 to -0.87; p<0.001). Males experienced a greater increase than females during the peak-pandemic (AMD: 5.13 vs. 2.49; both p<0.001), compared to the pre-pandemic. Post-pandemic, females had a significant decline (AMD: -0.64, p<0.001), whereas males’ decline was not significant (AMD: -0.24, p=0.15). All racial groups reported an increase in AAMR during the pandemic, with the highest in NH Native Hawaiians (AMD: 15.57; p<0.001) and NH American Indians (AMD: 10.34; p<0.001), compared to the pre-pandemic period. During the post-pandemic period, most racial groups showed a decline, notably NH Blacks (AMD: -3.41; p<0.001). However, AAMR continued to rise non-significantly in NH Native Hawaiians (AMD: 1.11; p=0.76) and NH multiracial individuals (AMD: 0.24; p=0.52), but these effects were not significant.
Conclusion: HTN-related mortality among younger adults increased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in males and specific racial minorities. Despite declines post-pandemic, rates remain above pre-pandemic levels, underscoring the need for targeted preventive interventions to reduce cardiovascular risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
A community-engaged approach to culturally tailoring a dietary intervention to improve cardiometabolic health among Black adults with obesity in Los Angeles County
Adeyemo Mopelola, Thorpe Roland
Active Screening in Black, Hispanic/LatinX, Asian/Pacific Islander, and Native American Individuals Reduces Racial Disparities in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm DiagnosisMiner Grace, Govindarajulu Usha, Smolock Christopher, Faries Peter, Marin Michael