Final ID: Mo2062
Cardiovascular Outcomes Following Autoimmune Myocarditis: A Propensity Matched Analysis of SLE, SSc, and Overlap Syndromes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and systemic sclerosis (SSc) are auto-immunological disorders with recognized cardiovascular involvement, such as myocarditis. Although myocarditis is an uncommon event, its impact can be considerable. The present study compares the cardiovascular outcomes following acute myocarditis in SLE, SSc, and SLE-SSc overlap patients with those with no autoimmune disorder.
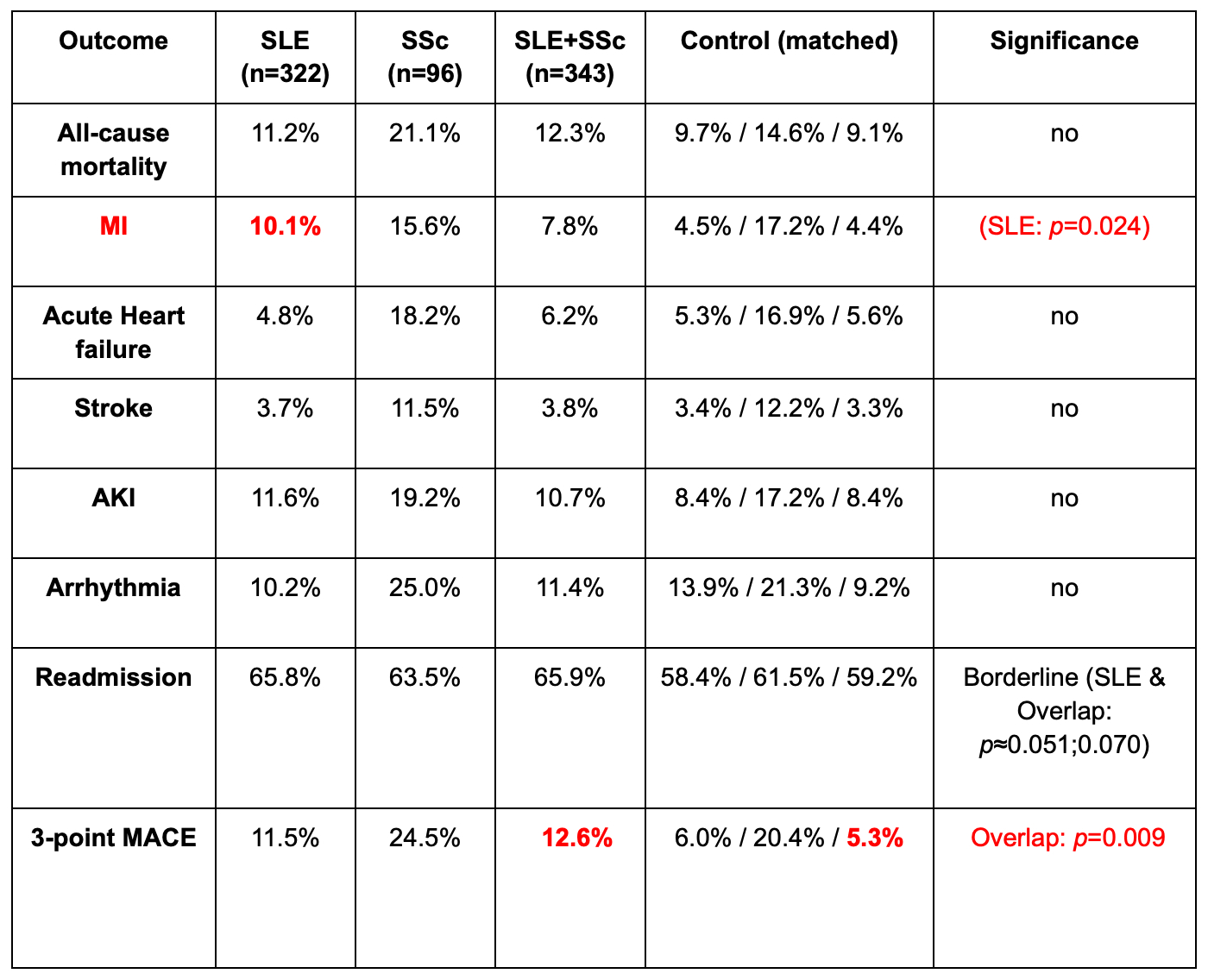
Three retrospective, propensity-matched cohort studies using the TriNetX Research Network compared adults with acute myocarditis and comorbid SLE (n=322), SSc (n=96), or SLE-SSc overlap (n=343) with matched non-autoimmune myocarditis controls. Matching variables included sex, race, insurance, and Charlson Comorbidity Index. Outcomes measured included 1-year all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), acute heart failure, stroke, acute kidney injury (AKI), arrhythmia, readmission, and 3-point major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: heart failure, stroke, or cardiac arrest). Odds ratios (OR) and 95% CIs were determined.
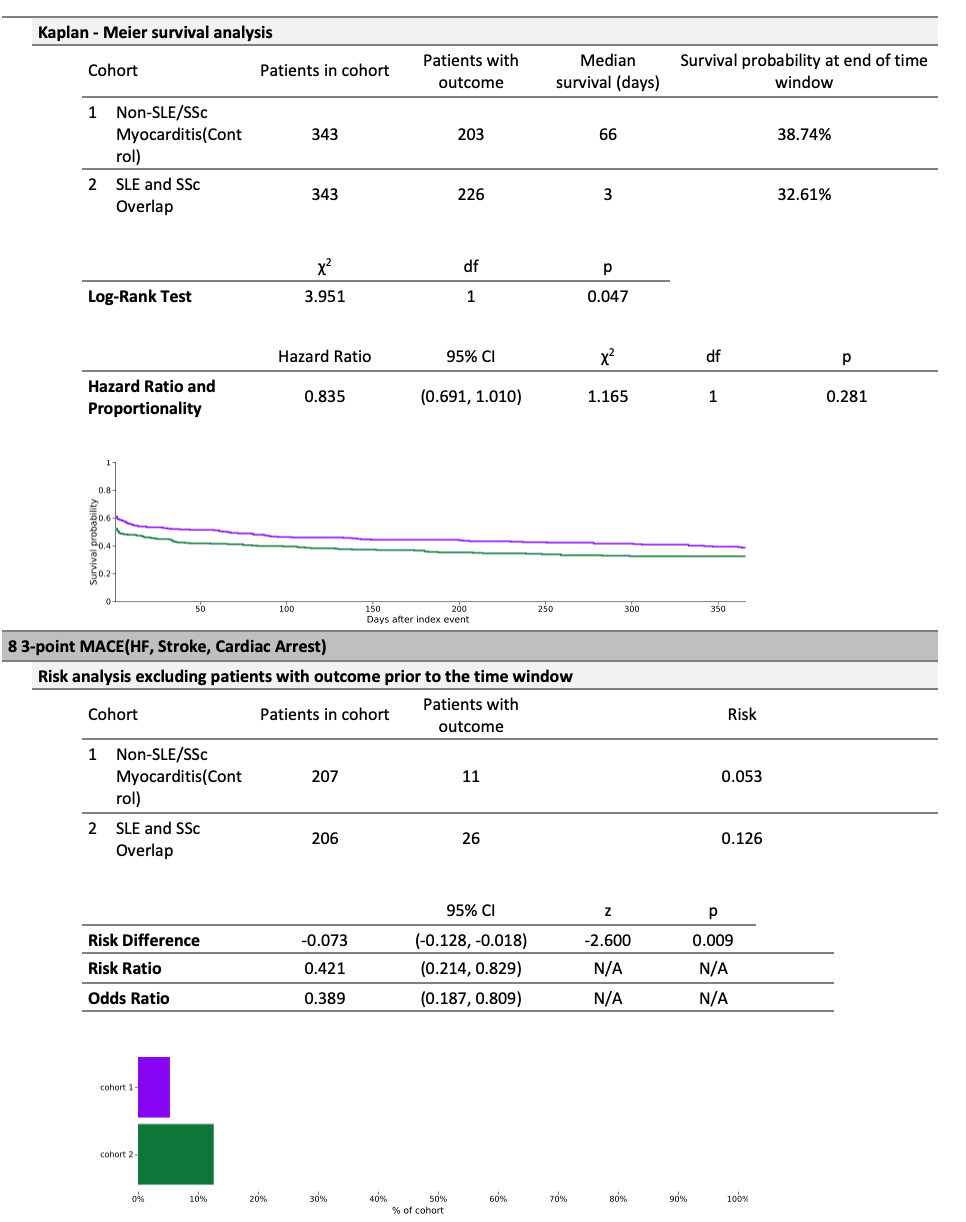
No differences were noted in 1-year mortality, heart failure, stroke, AKI, or arrhythmia between the autoimmune cohorts and controls. However, SLE patients had a higher risk for MI (10.1% vs 4.5%, OR 0.42 [0.19–0.91], p=0.024), and SLE-SSc overlapping patients had a higher 3-point MACE (12.6% vs 5.3%, OR 0.39 [0.19–0.81], p=0.009). Readmission was more frequent in both SLE and overlapping cohorts and did not achieve statistical significance. No such differences were noted in the SSc cohort.
Whereas most cardiovascular complications in patients with autoimmune versus non-autoimmune myocarditis were similar, SLE and SLE-SSc overlapped patients had an increased risk for adverse outcomes. The propensity for increased MI in SLE can be ascribed to underlying vasculopathic autoimmunity superimposed by myocarditis. Patients with SLE-SSc overlap would be a group with increased systemic immune dysregulation, as indicated by their increased MACE. Although with lower numbers, the SSc patients did not have an increased risk, perhaps because of pathophysiologic dissimilarities or limitations of the sample size. The observations underscore the importance of intensified cardiovascular monitoring in patients with autoimmune myocarditis, particularly in patients with SLE or overlapping syndromes. Prospective studies are indicated to confirm the above observations and for the development of management strategies.
Three retrospective, propensity-matched cohort studies using the TriNetX Research Network compared adults with acute myocarditis and comorbid SLE (n=322), SSc (n=96), or SLE-SSc overlap (n=343) with matched non-autoimmune myocarditis controls. Matching variables included sex, race, insurance, and Charlson Comorbidity Index. Outcomes measured included 1-year all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), acute heart failure, stroke, acute kidney injury (AKI), arrhythmia, readmission, and 3-point major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: heart failure, stroke, or cardiac arrest). Odds ratios (OR) and 95% CIs were determined.
No differences were noted in 1-year mortality, heart failure, stroke, AKI, or arrhythmia between the autoimmune cohorts and controls. However, SLE patients had a higher risk for MI (10.1% vs 4.5%, OR 0.42 [0.19–0.91], p=0.024), and SLE-SSc overlapping patients had a higher 3-point MACE (12.6% vs 5.3%, OR 0.39 [0.19–0.81], p=0.009). Readmission was more frequent in both SLE and overlapping cohorts and did not achieve statistical significance. No such differences were noted in the SSc cohort.
Whereas most cardiovascular complications in patients with autoimmune versus non-autoimmune myocarditis were similar, SLE and SLE-SSc overlapped patients had an increased risk for adverse outcomes. The propensity for increased MI in SLE can be ascribed to underlying vasculopathic autoimmunity superimposed by myocarditis. Patients with SLE-SSc overlap would be a group with increased systemic immune dysregulation, as indicated by their increased MACE. Although with lower numbers, the SSc patients did not have an increased risk, perhaps because of pathophysiologic dissimilarities or limitations of the sample size. The observations underscore the importance of intensified cardiovascular monitoring in patients with autoimmune myocarditis, particularly in patients with SLE or overlapping syndromes. Prospective studies are indicated to confirm the above observations and for the development of management strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Dabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey
A Novel Multivariate Scoring System for Diagnosing Post-Myocardial Infarction Pericarditis Following Percutaneous Coronary InterventionBolaji Olayiwola, Omoru Okiemute, Upreti Prakash, Echari Blanche, Shoar Saeed, Basit Jawad, Alraies M Chadi