Final ID: Sa3073
Targeting Liver Epsins Ameliorates Dyslipidemia in Atherosclerosis through Inhibition of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9-Mediated Low-density Lipoprotein Receptor Degradation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
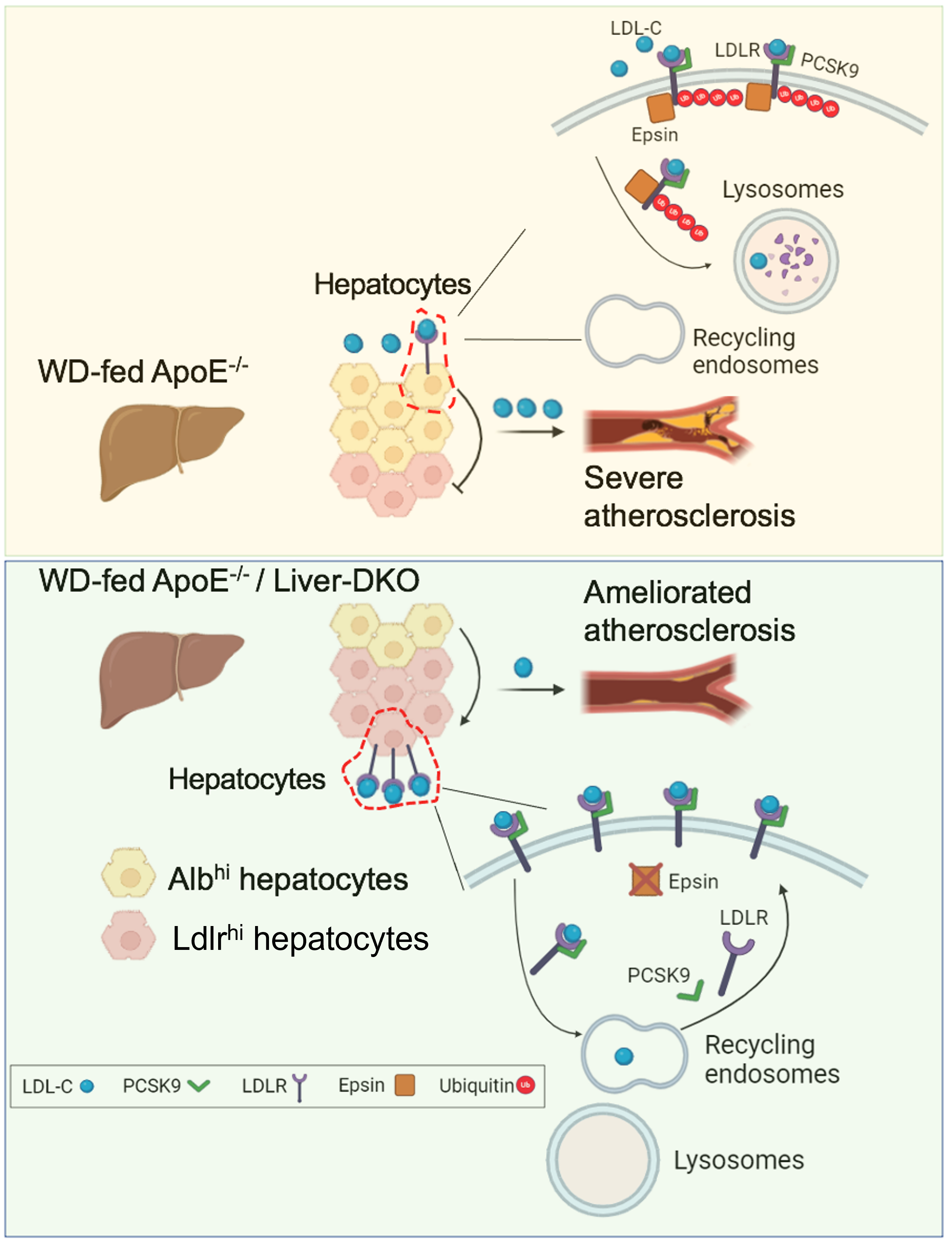
The low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) in the liver plays a crucial role in clearing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from the bloodstream. Under atherogenic conditions, Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9), secreted by the liver, binds to LDLR on hepatocytes, preventing its recycling and enhancing its lysosomal degradation. Epsins, a family of ubiquitin-binding endocytic adaptors, are key regulators of atherogenesis. We aimed to determine whether and how liver epsins contribute to PCSK9-mediated LDLR endocytosis and degradation, thereby impairing LDL-C clearance and accelerating atherosclerosis.
Methods:
We utilized single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), along with molecular, cellular, and biochemical analyses, to investigate the role of liver epsins in PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation. Liver-specific epsin knockout (Liver-DKO) atherosclerotic models were generated in ApoE-/- and PCSK9-AAV8-induced atheroprone mice fed on a Western diet. Additionally, we explored the therapeutic potential of nanoparticle-encapsulated siRNAs targeting epsins 1 and 2 in ApoE-/- mice with established atherosclerosis.
Results:
Western diet (WD)-induced atherosclerosis was significantly attenuated in ApoE-/- /Liver-DKO mice compared with ApoE-/- controls, as well as in PCSK9-AAV8-induced Liver-DKO mice compared with PCSK9-AAV8-induced wild-type (WT) mice accompanied by reductions in blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Mechanistically, hepatocyte-derived scRNA-seq data analysis revealed increased pathways of LDL particle clearance in WD-fed ApoE-/- /Liver-DKO mice compared with WD-fed ApoE-/- controls, correlating with decreased plasma LDL-C levels. The absence of liver epsins led to an upregulation of LDLR protein expression in hepatocytes. We further demonstrated that epsins bind LDLR via the ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM), enabling PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation. Depleting epsins abolished this degradation, thereby preventing atheroma progression. Lastly, targeting liver epsins with nanoparticle-encapsulated epsins siRNAs effectively ameliorates dyslipidemia and inhibits atherosclerosis progression.
Conclusions:
Liver epsins drive atherogenesis by promoting PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation, elevating circulating LDL-C levels and heightening lesional inflammation. Targeting epsins in the liver represents a promising therapeutic strategy to mitigate atherosclerosis by preserving LDLR and enhancing LDL-C clearance in the liver.
The low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) in the liver plays a crucial role in clearing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from the bloodstream. Under atherogenic conditions, Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9), secreted by the liver, binds to LDLR on hepatocytes, preventing its recycling and enhancing its lysosomal degradation. Epsins, a family of ubiquitin-binding endocytic adaptors, are key regulators of atherogenesis. We aimed to determine whether and how liver epsins contribute to PCSK9-mediated LDLR endocytosis and degradation, thereby impairing LDL-C clearance and accelerating atherosclerosis.
Methods:
We utilized single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), along with molecular, cellular, and biochemical analyses, to investigate the role of liver epsins in PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation. Liver-specific epsin knockout (Liver-DKO) atherosclerotic models were generated in ApoE-/- and PCSK9-AAV8-induced atheroprone mice fed on a Western diet. Additionally, we explored the therapeutic potential of nanoparticle-encapsulated siRNAs targeting epsins 1 and 2 in ApoE-/- mice with established atherosclerosis.
Results:
Western diet (WD)-induced atherosclerosis was significantly attenuated in ApoE-/- /Liver-DKO mice compared with ApoE-/- controls, as well as in PCSK9-AAV8-induced Liver-DKO mice compared with PCSK9-AAV8-induced wild-type (WT) mice accompanied by reductions in blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Mechanistically, hepatocyte-derived scRNA-seq data analysis revealed increased pathways of LDL particle clearance in WD-fed ApoE-/- /Liver-DKO mice compared with WD-fed ApoE-/- controls, correlating with decreased plasma LDL-C levels. The absence of liver epsins led to an upregulation of LDLR protein expression in hepatocytes. We further demonstrated that epsins bind LDLR via the ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM), enabling PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation. Depleting epsins abolished this degradation, thereby preventing atheroma progression. Lastly, targeting liver epsins with nanoparticle-encapsulated epsins siRNAs effectively ameliorates dyslipidemia and inhibits atherosclerosis progression.
Conclusions:
Liver epsins drive atherogenesis by promoting PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation, elevating circulating LDL-C levels and heightening lesional inflammation. Targeting epsins in the liver represents a promising therapeutic strategy to mitigate atherosclerosis by preserving LDLR and enhancing LDL-C clearance in the liver.
More abstracts on this topic:
2-Deoxyuridine Associates with Recurrent Coronary Events
Pistritu Dan, Castano David, Liehn Elisa, Koh Cho Yeow, Gerszten Robert, Singaraja Roshni, Chan Mark, Shah Svati
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney diseaseJha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia