Final ID: MP2137
Three-Dimensional Echocardiographic Evaluation of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction is a significant contributor to morbidity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), yet often remains underdiagnosed. Advanced echocardiographic techniques, including 3D imaging and strain analysis, offer enhanced sensitivity for early detection of RV impairment.
Research Questions:
What is the prevalence and extent of RV dysfunction in COPD patients using advanced echocardiography?
How does RV function correlate with COPD severity and functional capacity?
Methods: Eighty-five COPD patients (as per 2023 GOLD guidelines) and 40 matched healthy controls were enrolled. All subjects underwent transthoracic echocardiography, including 2D imaging, tissue Doppler, speckle tracking, and 3D echocardiography. RV parameters assessed included TAPSE, RV FAC, 3D RV ejection fraction (RVEF), RV longitudinal strain (RVLS), and RV free wall strain (RVFWS). Pulmonary function testing and six-minute walk test (6MWT) were also performed.
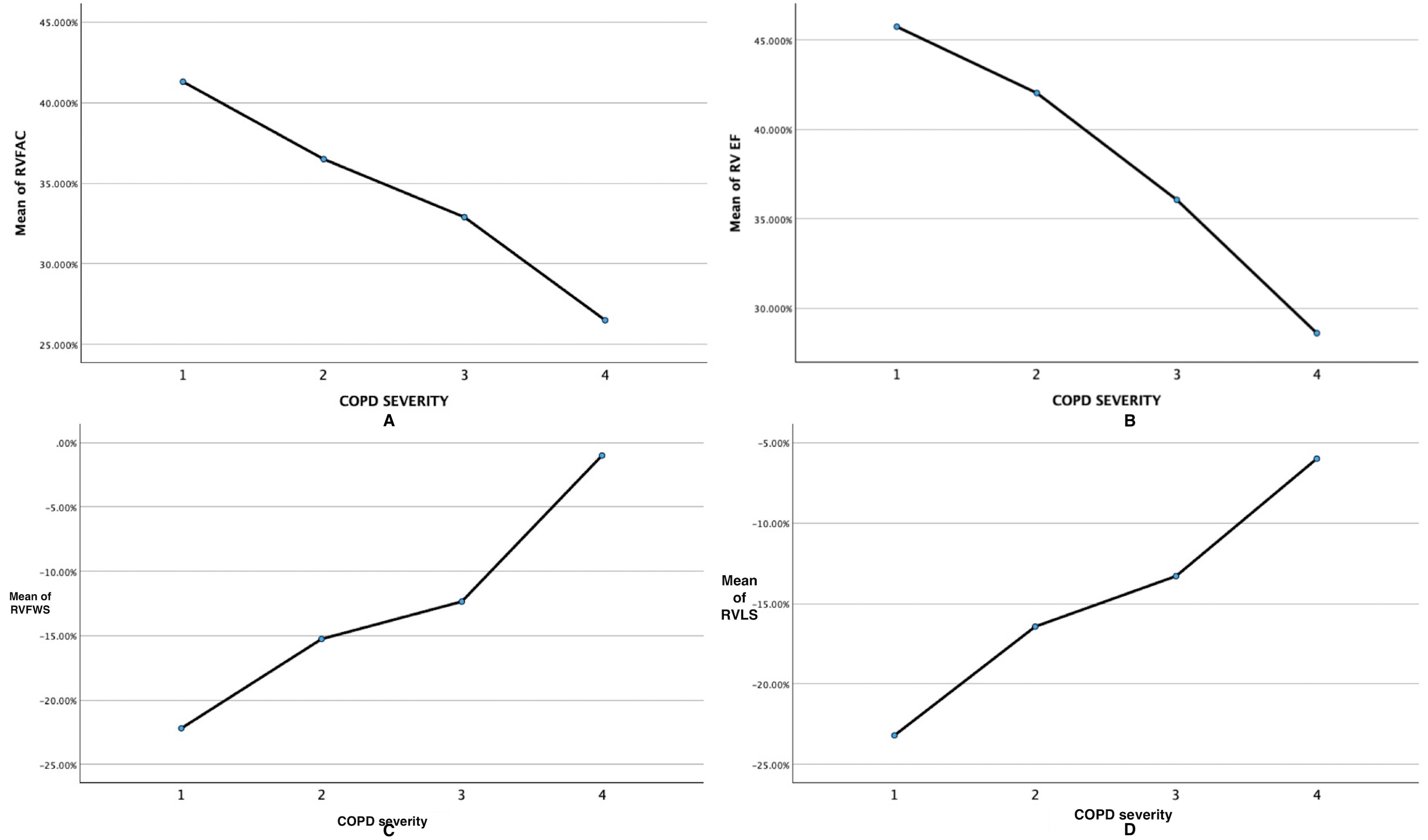
Results: Mean age of the study population was 62.1+ 9.2 years with majority (69; 81.2%) of them being males. A significant proportion (68; 80%) were smokers while 15 (17.6%) had biomass fuel smoke exposure. Most patients had either moderate (39; 45.9%) or severe COPD (35; 41.2%). COPD patients showed significantly lower RVLS (−15.4 ± 5.9% vs −22.7 ± 4.9%), RVFWS (−14.2 ± 9.1% vs −23.2 ± 5.2%), and RVEF (39.5±8.5% vs 54.1±5.6%; all P< 0.0001) as compared to controls. RV dysfunction was present in 52 [61.2%] (by FAC) and 67 [78.8%] (by RVEF). Subjects with severe COPD had significantly lower mean RV longitudinal strain (RVLS) [-13.3 + 5.6% vs -23.2 + 2.1% ; P<0.0001], mean RV free wall strain [-12.3+7.9% vs -22.2+2.2%; P<0.0001] and mean RVEF [ 36.1+7.6% vs 45.7+ 5.5%; P=0.014] as compared to mild cases. Severe COPD patients had markedly worse RV parameters, RVLS and RVFWS correlated negatively with FEV1 (r = −0.551 and −0.448, respectively; both P = 0.001)
Conclusion:
3D echocardiography and strain imaging are effective in detecting subclinical RV dysfunction in COPD. Their incorporation into routine evaluation may enhance risk stratification and guide timely therapeutic interventions.
Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction is a significant contributor to morbidity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), yet often remains underdiagnosed. Advanced echocardiographic techniques, including 3D imaging and strain analysis, offer enhanced sensitivity for early detection of RV impairment.
Research Questions:
What is the prevalence and extent of RV dysfunction in COPD patients using advanced echocardiography?
How does RV function correlate with COPD severity and functional capacity?
Methods: Eighty-five COPD patients (as per 2023 GOLD guidelines) and 40 matched healthy controls were enrolled. All subjects underwent transthoracic echocardiography, including 2D imaging, tissue Doppler, speckle tracking, and 3D echocardiography. RV parameters assessed included TAPSE, RV FAC, 3D RV ejection fraction (RVEF), RV longitudinal strain (RVLS), and RV free wall strain (RVFWS). Pulmonary function testing and six-minute walk test (6MWT) were also performed.
Results: Mean age of the study population was 62.1+ 9.2 years with majority (69; 81.2%) of them being males. A significant proportion (68; 80%) were smokers while 15 (17.6%) had biomass fuel smoke exposure. Most patients had either moderate (39; 45.9%) or severe COPD (35; 41.2%). COPD patients showed significantly lower RVLS (−15.4 ± 5.9% vs −22.7 ± 4.9%), RVFWS (−14.2 ± 9.1% vs −23.2 ± 5.2%), and RVEF (39.5±8.5% vs 54.1±5.6%; all P< 0.0001) as compared to controls. RV dysfunction was present in 52 [61.2%] (by FAC) and 67 [78.8%] (by RVEF). Subjects with severe COPD had significantly lower mean RV longitudinal strain (RVLS) [-13.3 + 5.6% vs -23.2 + 2.1% ; P<0.0001], mean RV free wall strain [-12.3+7.9% vs -22.2+2.2%; P<0.0001] and mean RVEF [ 36.1+7.6% vs 45.7+ 5.5%; P=0.014] as compared to mild cases. Severe COPD patients had markedly worse RV parameters, RVLS and RVFWS correlated negatively with FEV1 (r = −0.551 and −0.448, respectively; both P = 0.001)
Conclusion:
3D echocardiography and strain imaging are effective in detecting subclinical RV dysfunction in COPD. Their incorporation into routine evaluation may enhance risk stratification and guide timely therapeutic interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Cardiac Mass
Mallipeddi Tarun, Rantanen Petra, Debakey Michael, Cheng Lily, Waheed Nida
A diagnostic challenge overcome with persistent clinical suspicion in a case of cardiac AL amyloidosisZimmerman Allison, Kuriakose Philip, Godfrey Amanda, Ananthasubramaniam Karthikeyan, Cowger Jennifer, Al-darzi Waleed