Final ID: MP954
Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Rheumatic Heart Disease Presents a Major Unmet Disease Burden in Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: In rheumatic heart disease (RHD), post-streptococcal rheumatic fever causes valvular heart destruction leading to pulmonary hypertension (PH), a prognostic and potentially modifiable cause of adverse outcomes. Indeed, RHD is a major contributor to global disease burden with most patients living in low-middle income countries, such as sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). The prevalence of PH-RHD in SSA is unknown, but its determination is a key step toward population health initiatives to mitigate RHD burden and improve clinical care.
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search following PRISMA and GATHER guidelines searching PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and LILACS for studies published until 09/2023 on patients in SSA with RHD, diagnosed based on WHO criteria, who underwent echocardiography or right heart catheterization. We excluded studies without a clear PH definition and performed a meta-analysis using a random-effects model of proportions. Risk of bias was assessed for all studies. We then extrapolated results to the total RHD population in SSA, while accounting for RHD severity.
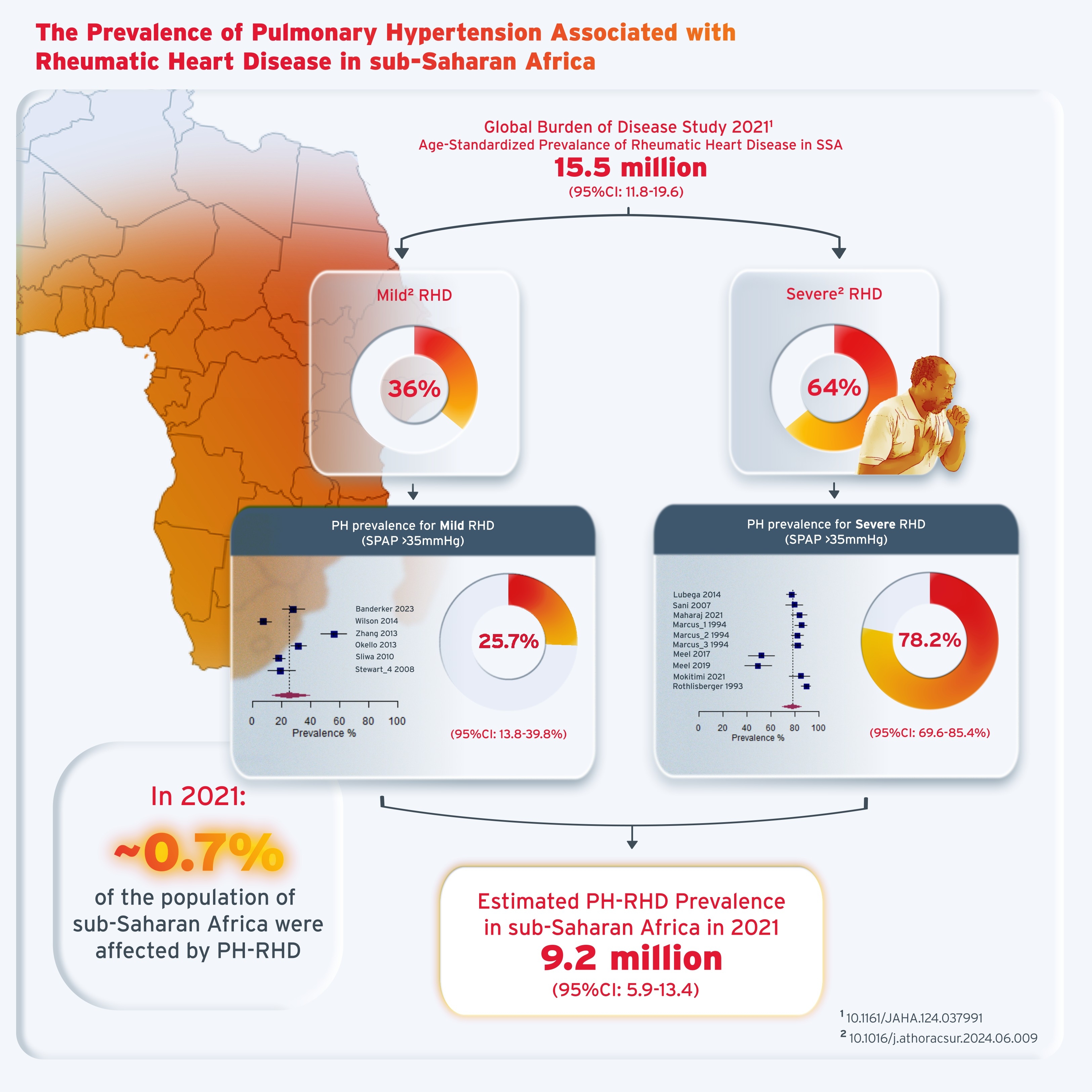
Results: In total, we included N=18 studies compromising N=3,181 patients (mean age, 32±14 years; male, 17±12%) of which 72%, 11%, and 17% originated from high-middle, lower-middle and low-income countries, respectively. The majority of studies had a retrospective (61%) and single-centre design (83%). In n=16 studies (89%), echocardiography was used to diagnose PH. The estimated PH prevalence based on estimated systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (sPAP) >35mmHg was 58.9% (95%CI: 43.3–73.7% from n=16 studies), which was three-fold greater in severe vs. mild RHD (78.2% [95%CI: 69.6–85.4%], n=10 studies vs. 25.7% [95%CI: 13.8–39.8%], n=6 studies; p<0.001). Based on data from the Global Burden of Disease Study, RHD affected 15.5 (95%CI: 11.8–19.6) million people in SSA in 2021. Using this is a referent and weighting our calculations by the proportion of those who have severe vs. mild RHD, we extrapolated that 9.2 (95%CI: 6.5–11.9) million people are affected by PH-RHD, corresponding to ~0.7% of the SSA population in 2021 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: PH is common in RHD, and PH-RHD prevalence exceeds disorders of seemingly greater notoriety, such as ischemic or congenital heart disease. Public health measures aimed at reducing PH-RHD risk through primary prevention of RHD are expected to improve longevity in this large and highly vulnerable at-risk population.
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search following PRISMA and GATHER guidelines searching PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and LILACS for studies published until 09/2023 on patients in SSA with RHD, diagnosed based on WHO criteria, who underwent echocardiography or right heart catheterization. We excluded studies without a clear PH definition and performed a meta-analysis using a random-effects model of proportions. Risk of bias was assessed for all studies. We then extrapolated results to the total RHD population in SSA, while accounting for RHD severity.
Results: In total, we included N=18 studies compromising N=3,181 patients (mean age, 32±14 years; male, 17±12%) of which 72%, 11%, and 17% originated from high-middle, lower-middle and low-income countries, respectively. The majority of studies had a retrospective (61%) and single-centre design (83%). In n=16 studies (89%), echocardiography was used to diagnose PH. The estimated PH prevalence based on estimated systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (sPAP) >35mmHg was 58.9% (95%CI: 43.3–73.7% from n=16 studies), which was three-fold greater in severe vs. mild RHD (78.2% [95%CI: 69.6–85.4%], n=10 studies vs. 25.7% [95%CI: 13.8–39.8%], n=6 studies; p<0.001). Based on data from the Global Burden of Disease Study, RHD affected 15.5 (95%CI: 11.8–19.6) million people in SSA in 2021. Using this is a referent and weighting our calculations by the proportion of those who have severe vs. mild RHD, we extrapolated that 9.2 (95%CI: 6.5–11.9) million people are affected by PH-RHD, corresponding to ~0.7% of the SSA population in 2021 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: PH is common in RHD, and PH-RHD prevalence exceeds disorders of seemingly greater notoriety, such as ischemic or congenital heart disease. Public health measures aimed at reducing PH-RHD risk through primary prevention of RHD are expected to improve longevity in this large and highly vulnerable at-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aladyn Individual: Dynamic Individual Comorbidity Modeling for Genomic Discovery and Clinical Prediction
Urbut Sarah, Natarajan Pradeep, Ding Yi, Taraszka Kodi, Yeung Ming Wai, Patel Aniruddh, Hornsby Whitney, Duan Rui, Gusev Alexander, Parmigiani Giovanni
CASE MANAGERS AND PEER SUPPORT GROUPS (CAMPS) FOR PROPHYLAXIS ADHERENCE IN RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASEDe Loizaga Sarah, Rwebembera Joselyn, Beaton Andrea, Pulle Jafesi, Okumu Atanas, Alepere Juliet, Nambogo Jane-liz, Ndagire Emma, Kaudha Gloria, Ollberding Nicholas, Okello Emmy