Final ID: Su4021
Mitochondrial dynamics modulators promoted favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming in doxorubicin-induced heart failure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Doxorubicin is an effective chemotherapeutic agent for various types of cancer. Unfortunately, the clinical utilization of doxorubicin is limited due to doxorubicin-induced heart failure. The pathophysiology of heart failure is strongly correlated with cardiac mitochondrial dysfunctions and cardiac metabolic reprogramming. In fact, these two parameters reciprocally link to the development of heart failure. A previous study showed that mitochondrial dynamics modulators could improve cardiac mitochondrial functions and attenuate doxorubicin-induced heart failure. However, the effect of mitochondrial dynamics modulators on cardiac metabolic reprogramming has never been determined.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that improving mitochondrial functions by mitochondrial dynamics modulators could promote favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming, leading to the alleviation of doxorubicin-induced heart failure.
Aims: We investigated the effects of a mitochondrial fission inhibitor (MDiVi1) and a mitochondrial fusion promoter (M1) on cardiac metabolic reprogramming in rats treated with doxorubicin.
Methods: Male Wistar rats received either 1) vehicle, 2) 6 doses of 3 mg/kg of doxorubicin and vehicle, 3) 6 doses of 3 mg/kg of doxorubicin and 1.2 mg/kg/day of MDiVi1, or 4) 6 doses of 3 mg/kg of doxorubicin and 2 mg/kg/day of M1 for 30 days. Then, the rats were euthanized to collect cardiac tissues for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics studies.
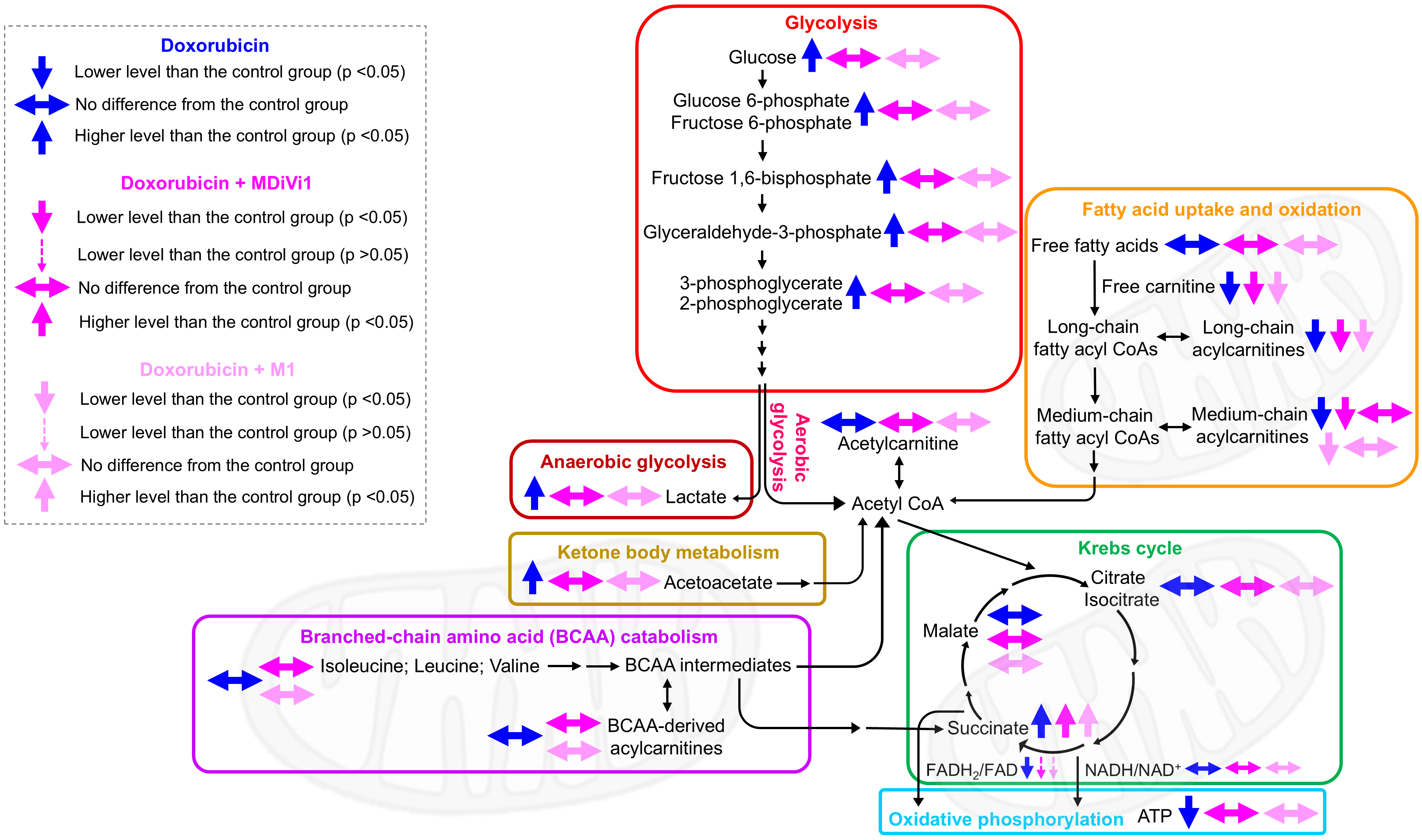
Results: Doxorubicin increased glycolysis, increased ketone body metabolism, decreased fatty acid utilization, decreased succinate oxidation, and decreased ATP production. Either co-treatment with MDiVi1 or M1 promoted favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming, as detailed in the figure.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the potential of mitochondrial dynamics modulation in the promotion of favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming. Also, metabolomics may be used as tools for diagnosis and treatment monitoring in doxorubicin-induced heart failure.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that improving mitochondrial functions by mitochondrial dynamics modulators could promote favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming, leading to the alleviation of doxorubicin-induced heart failure.
Aims: We investigated the effects of a mitochondrial fission inhibitor (MDiVi1) and a mitochondrial fusion promoter (M1) on cardiac metabolic reprogramming in rats treated with doxorubicin.
Methods: Male Wistar rats received either 1) vehicle, 2) 6 doses of 3 mg/kg of doxorubicin and vehicle, 3) 6 doses of 3 mg/kg of doxorubicin and 1.2 mg/kg/day of MDiVi1, or 4) 6 doses of 3 mg/kg of doxorubicin and 2 mg/kg/day of M1 for 30 days. Then, the rats were euthanized to collect cardiac tissues for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics studies.
Results: Doxorubicin increased glycolysis, increased ketone body metabolism, decreased fatty acid utilization, decreased succinate oxidation, and decreased ATP production. Either co-treatment with MDiVi1 or M1 promoted favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming, as detailed in the figure.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the potential of mitochondrial dynamics modulation in the promotion of favorable patterns of cardiac metabolic reprogramming. Also, metabolomics may be used as tools for diagnosis and treatment monitoring in doxorubicin-induced heart failure.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acetylation of mitochondrial LCAD and SOD2 promotes metabolic dysfunction, oxidative stress, multi-organ damage and hypertension
Dikalov Sergey, Nogueira Marina, Polosukhin Vasiliy, Gius David, Milne Ginger, Dikalova Anna
Age-Related Impairment of Mitochondrial Protein Turnover Exacerbates Pathogenesis of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in Old MiceKobak Kamil, Zarzycka Weronika, King Catherine, Borowik Agnieszka, Peelor Frederick, Kinter Michael, Miller Benjamin, Chiao Ying Ann